Internal Energy of an Ideal Gas (OCR A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: H556
Internal Energy of an Ideal Gas
The internal energy of a gas is defined as:
The sum of the kinetic and potential energies of the particles inside the gas
One of the assumptions of an ideal gas states:
Electrostatic forces between particles in the gas are negligible except during collisions
So, there is no electrostatic potential energy in an ideal gas
All the internal energy is due to the kinetic energy of the particles
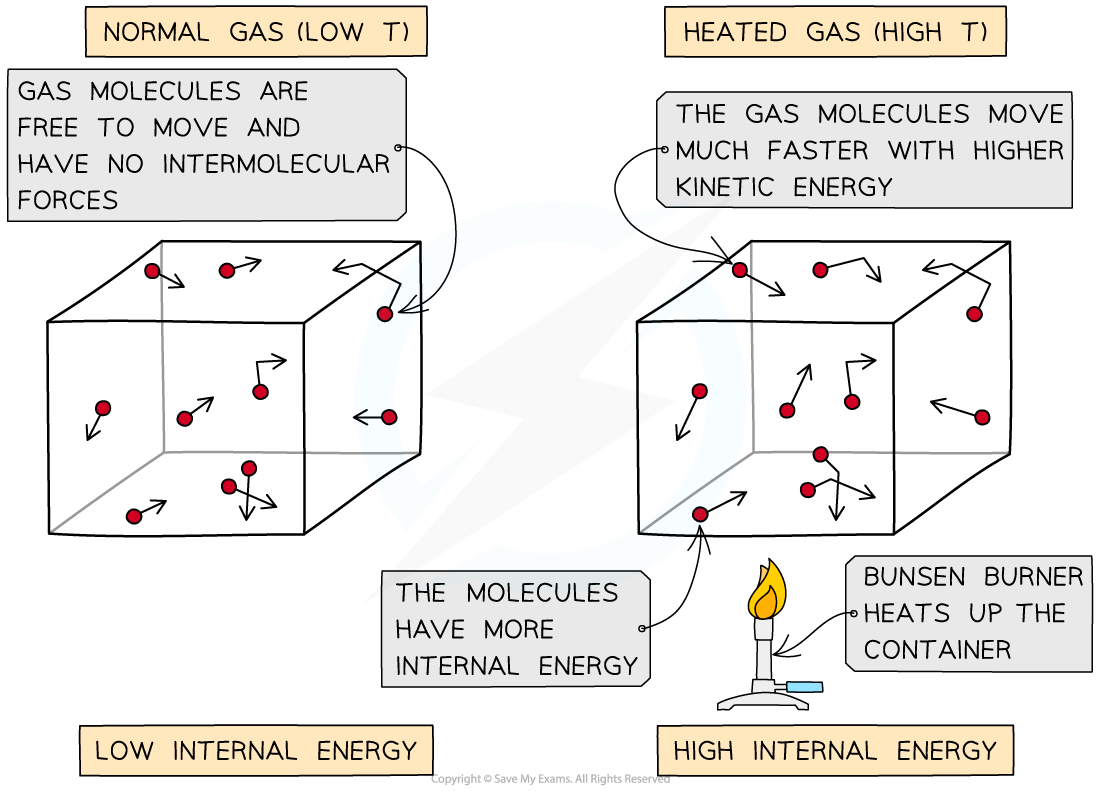
As the container is heated up, the gas molecules move faster with higher kinetic energy and therefore higher internal energy
Change in internal energy, ΔU is equal to the total kinetic energy, EK of all the particles
Where:
EK = total kinetic energy (J)
m = mass of one molecule (kg)
= mean square speed of a molecule (m2 s-2)
k = Boltzmann constant
T = temperature of the gas (K)
N = number of molecules
This equation shows that doubling the temperature will also double the internal energy of the particles

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?