Kinetic Theory of Gases (OCR A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: H556
Model of the Kinetic Theory of Gases
Gases consist of atoms or molecules randomly moving around at high speeds
The kinetic theory of gases models the thermodynamic behaviour of gases by linking:
The microscopic properties of particles i.e. mass and speed
The macroscopic properties of particles i.e. pressure and volume
The theory is based on a set of the following assumptions:
Molecules of a gas behave as identical (or all have the same mass)
Molecules of gas are hard, perfectly elastic spheres
The volume of the molecules is negligible compared to the volume of the container
The time of a collision is negligible compared to the time between collisions
There are no intermolecular forces between the molecules (except during impact)
The molecules move in continuous random motion
Newton's laws apply
There are a very large number of molecules
The number of molecules of gas in a container is very large, therefore the average behaviour (eg. speed) is usually considered
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Make sure to memorise all the assumptions for your exams, as it is a common exam question to be asked to recall them.
Pressure in the Model of Kinetic Theory of Gases
A gas is made of a large number of particles
Gas particles have mass and move randomly at high speeds
Pressure in a gas is due to the collisions of the gas particles with the walls of the container that holds the gas
When a gas particle hits a wall of the container, it undergoes a change in momentum due to the force exerted by the wall on the particle (as stated by Newton's Second Law)
Final momentum = –mv
Initial momentum = mv
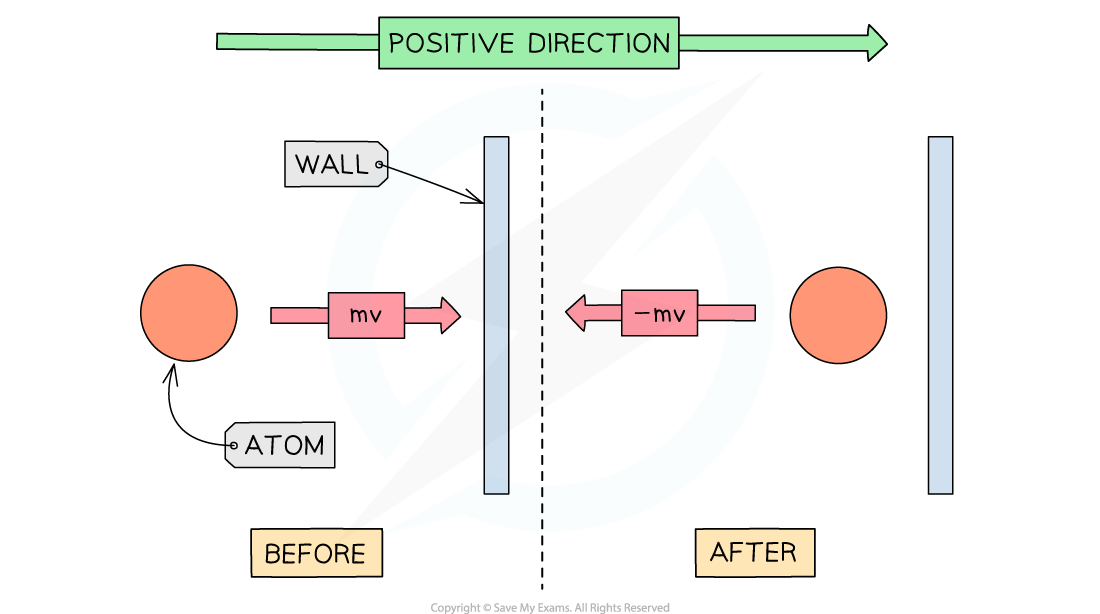
Therefore, the change in momentum Δp can be written as:
Δp = final momentum – initial momentum
Δp = –mv – mv = –2mv
According to Newton's Third Law, there is an equal and opposite force exerted by the particle on the wall (i.e. F =
)
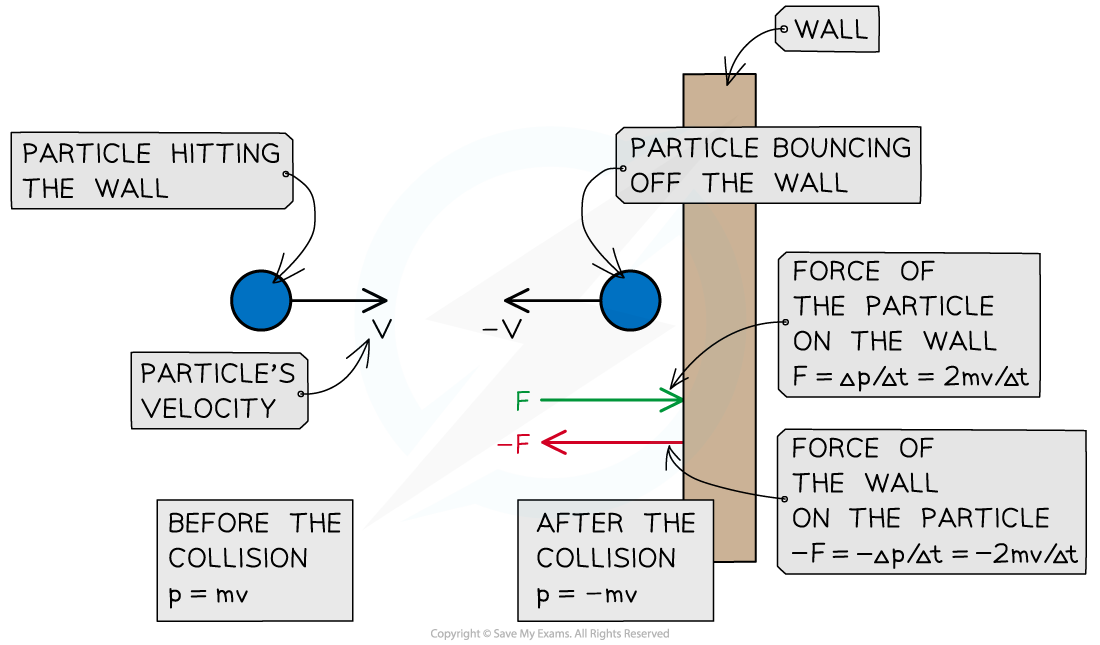
A particle hitting a wall of the container in which the gas is held experiences a force from the wall and a change in momentum. The particle exerts an equal and opposite force on the wall
Since there is a large number of particles, their collisions with the walls of the container give rise to gas pressure, which is calculated as follows:
Where:
p = pressure in pascals (Pa)
F = force in newtons (N)
A = area in metres squared (m2)
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Momentum is a Mechanics topic that should have been covered in a previous unit. The above derivation of change in momentum and resultant force should have already been studied - if you're not comfortable with it then make sure you go back to revise this!

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?