Hubble's Law (OCR A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: H556
Hubble's Law
In 1929, the astronomer Edwin Hubble showed that the universe was expanding
He did this by observing that the absorption line spectra produced from the light of distant galaxies was shifted towards the red end of the spectrum
This doppler shift in the wavelength of the light is evidence that distant galaxies are moving away from the Earth
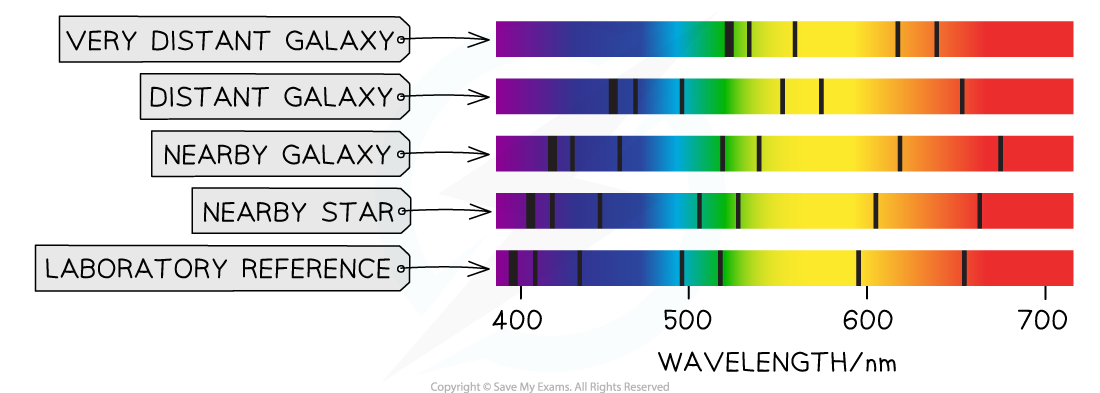
Hubble also observed that light from more distant galaxies was shifted further towards the red end of the spectrum compared to closer galaxies
From this observation he concluded that galaxies or stars which are further away from the Earth are moving faster than galaxies which are closer
Hubble’s law states:
The recessional velocity, v, of a galaxy is proportional to its distance from Earth
Hubble’s law can be expressed as an equation:
v ≈ H0d
Where:
v = recessional velocity of an object, the velocity of an object moving away from an observer (km s-1)
H0 = Hubble constant, this will be provided in your examination along with the correct units (km s-1 Mpc-1)
d = distance between the object and the Earth (Mpc)
Alternatively, if the velocity of the receding object was measured in km s–1 and the distance from the earth to the object was measured in km, then then unit for the Hubble constant would be s–1
This Hubble’s law shows:
The further away a star is from the Earth, the faster it is moving away from us
The closer a star is to the Earth, the slower it is moving away from us
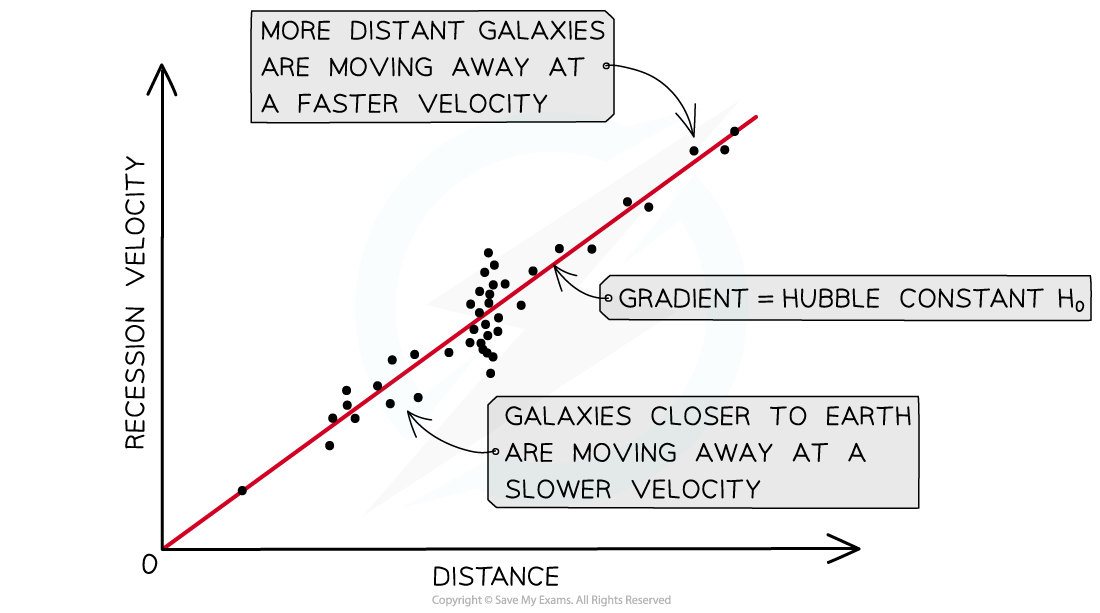
A key aspect of Hubble’s law is that the furthest galaxies appear to move away the fastest
Worked Example
A distant galaxy is 20 light-years away from Earth.
Use Hubble’s Law to determine the velocity of the galaxy as it moves away from Earth.
The Hubble constant is currently agreed to be 2.2 x 10-18 s-1.
Answer:
Step 1: List the known quantities
d = 20 light years
Ho = 2.2 x 10-18 s-1
Step 2: Convert 20 light-years to m
From the data booklet: 1 ly ≈ 9.5 x 1015 m
So, 20 ly = 20 x (9.5 x 1015) = 1.9 x 1017 m
Step 3: Substitute values into Hubble's Law
From the data booklet: v ≈ H0d
So, v ≈ (2.2 x 10-18 s-1) x (1.9 x 1017 m) = 0.418 m s-1
Step 4: Confirm your answer
The velocity of the galaxy as it moves away from Earth 0.42 m s-1
The Hubble Constant
By rearranging the equation for Hubble’s law, we can determine that the Hubble constant, H0, is:
H0 ≈
v = recessional velocity of an object (km s–1)
d = distance between the object and the Earth (Mpc)
Ho = Hubble constant (km s–1 Mpc–1)
The value for the Hubble constant has been estimated using data for thousands of galaxies
The latest estimate of the Hubble constant based on CMB observations by the Planck satellite is:
H0 = 67.4 ± 0.5 km s−1 Mpc−1 (Planck Collaboration VI 2020)
It is difficult to be certain about just how accurate the values for the Hubble constant are
This is due to the random and systematic errors involved when calculating the distance to a galaxy or star
Worked Example
The graph shows how the recessional velocity, v, of galaxies varies with their distance, d, measured from the Earth.
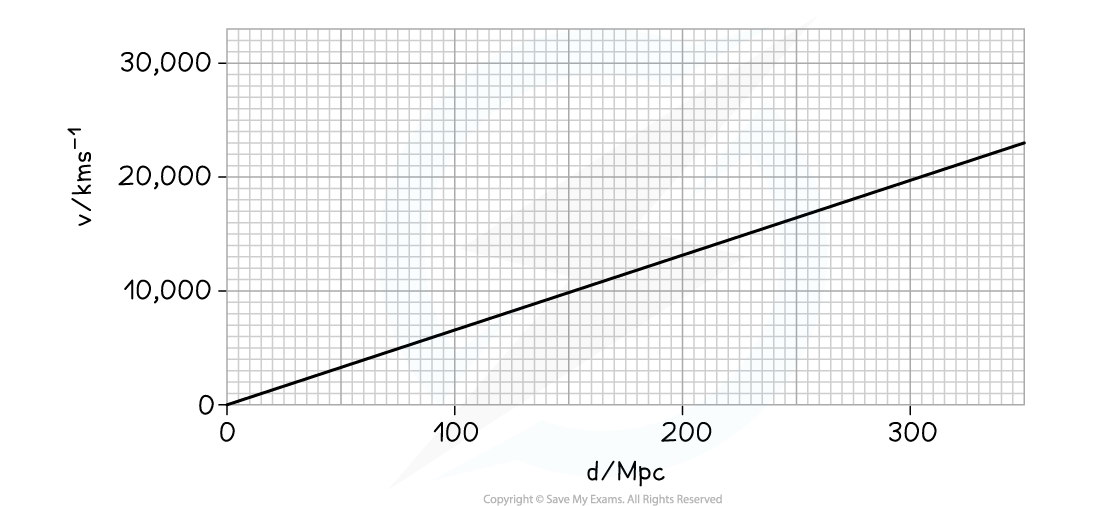
Use the graph to determine a value for the Hubble constant and state the unit for this constant.
Answer:
Step 1: From the data booklet
Hubble’s Law: v ≈ H0d
Step 2: Determine the Hubble constant, H0, from the graph
y–axis = v = 20, 000
x–axis = d = 305
gradient = H0
Step 3: Calculate the gradient of the graph
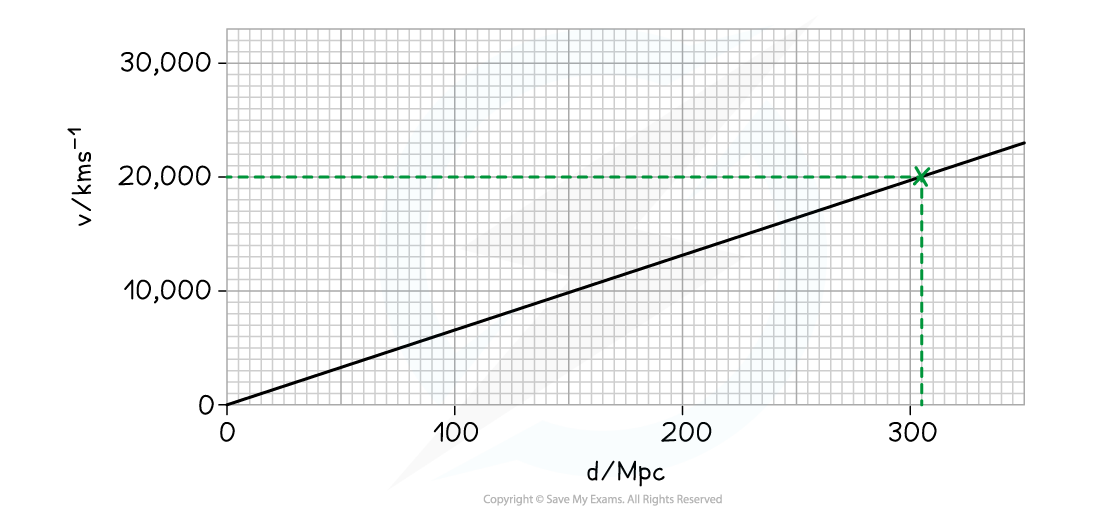
H0 =
= 66 km s–1 Mpc–1
Step 4: Confirm your answer
The Hubble Constant = 66 km s–1 Mpc–1
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The units for the quantities in Hubble's Law and for the Hubble Constant can change depending on the situation, Make sure you convert them to appropriate units and express your final answer correctly.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?