Units for Astronomical Distances (OCR A Level Physics) : Revision Note
Units for Astronomical Distances
Astronomical distances are very large and as a result, are usually measured using:
Astronomical Units (AU)
Light–years (ly)
Parsecs (pc)
Astronomical Unit (AU)
The astronomical unit (AU) is defined as
The mean distance from the centre of the Earth to the centre of the Sun
As the Earth’s orbit around the Sun is elliptical it will be slightly closer to the Sun in January (1.471 × 1011 m) than it is in July (1.521 × 1011 m)
Calculating the mean of these two values gives:
= 1.496 × 1011 m
Therefore, 1 astronomical unit = 1.496 × 1011 m ≈ 1.5 × 1011 m
The astronomical unit is useful for studying distances on the scale of the solar system

Light–year (ly)
A light-year is defined as:
The distance travelled by light in one year
This can be calculated using:
Distance = speed × time
Where:
The speed of light is 3 × 108 m s–1
1 year = 60 × 60 × 24 × 365 = 3.15 × 107 s
Hence, the distance travelled by light in one year = (3 × 108) × (3.15 × 107) = 9.46 × 1015 m
Therefore, 1 light–year ≈ 9.5 × 1015 m
Parsec (pc)
Angles smaller than 1 degree can be measured in arcminutes or arcseconds
1 degree = 60 arcminutes
1 arcminute = 60 arcseconds
Therefore, 1 degree = 60 x 60 = 3600 arcseconds
1 arcsecond = 1/3600 degree
The parsec is defined as
A unit of distance that gives a parallax angle of 1 second of an arc (of a degree), using the radius of the Earth’s orbit (1 AU) as the baseline of a right–angled triangle
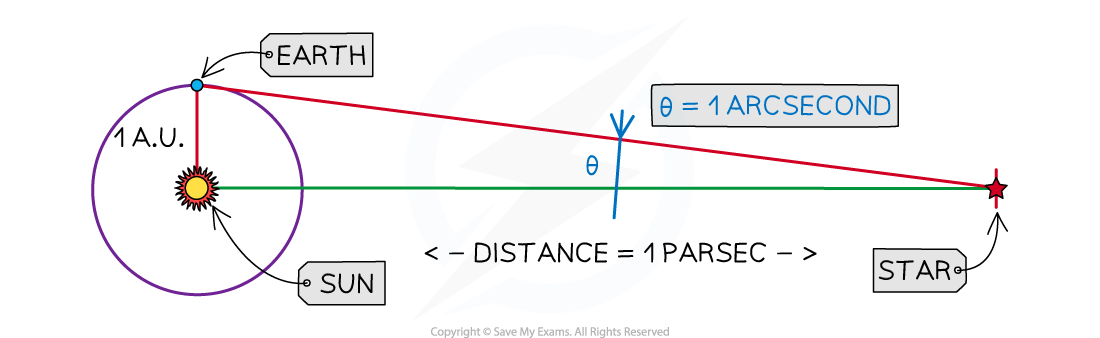
Given that 1 AU = 1.496 × 1011 m, trigonometry can be used to express 1 parsec in metres:
1 pc = = 3.09 × 1016 m
Therefore, 1 parsec ≈ 3.1 × 1016 m
The parsec (1 pc = 3.1 × 1016 m) and the light-year (1 ly = 9.5 × 1015 m) are much greater in size than the astronomical unit (1 AU = 1.496 × 1011 m)
This makes them useful when studying interstellar distances
For example, on the scale of distances between the Earth and stars, or neighbouring galaxies
Worked Example
The closest star to Earth is a triple–star system called Alpha Centauri, which is approximately 4.35 light-years from Earth.
Calculate the distance between the Earth and Alpha Centauri in:
a) Astronomical units
b) Parsecs
An astronomical unit is 1.496 × 1011 m
Answer:
Part (a)
Step 1: List the known quantities
1 light-year ≈ 9.5 × 1015 m (from data booklet)
1 AU = 1.496 × 1011 m
Distance to Alpha Centauri = 4.35 ly
Step 2: Convert 4.35 light–years into metres
4.35 ly = 4.35 × (9.5 × 1015) = 4.13 × 1016 m
Step 3: Convert from metres into AU
4.13 × 1016 m =
= 2.8 × 105 AU (to 2 s.f)
Part (b)
Step 1: List the known quantities
1 parsec ≈ 3.1 × 1016 m (from data booklet)
4.35 ly = 4.13 × 1016 m (from part a)
Step 2: Convert from metres into parsecs
4.13 × 1016 m =
= 1.3 pc (to 2 s.f)
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You do not need to learn all of the conversion factors for astronomical distances, you just need to know how to use them! The following are given in the data booklet:
1 light–year ≈ 9.5 × 1015 m
1 parsec ≈ 3.1 × 1016 m
However, the astronomical unit (AU) is not, so this could be useful to learn by heart!

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?

