Neutron Stars & Black Holes (OCR A Level Physics) : Revision Note
Neutron Stars & Black Holes
In the final evolutionary stages of a massive star's life cycle, the remnant left after a supernova explosion will either be:
A neutron star
A black hole
Characteristics of a Neutron Star
Neutron stars are objects formed in stars with cores which have masses greater than the Chandrasekhar limit
Neutron stars are:
Extremely dense
Very small
To put into perspective how dense and small a neutron star is:
The density of a neutron star is 4 × 1017 kg m−3
The density of the Earth is 5 × 103 kg m−3
The density of a white dwarf is 1 × 109 kg m−3
A neutron star with the mass of the Sun would be only 30 km in diameter
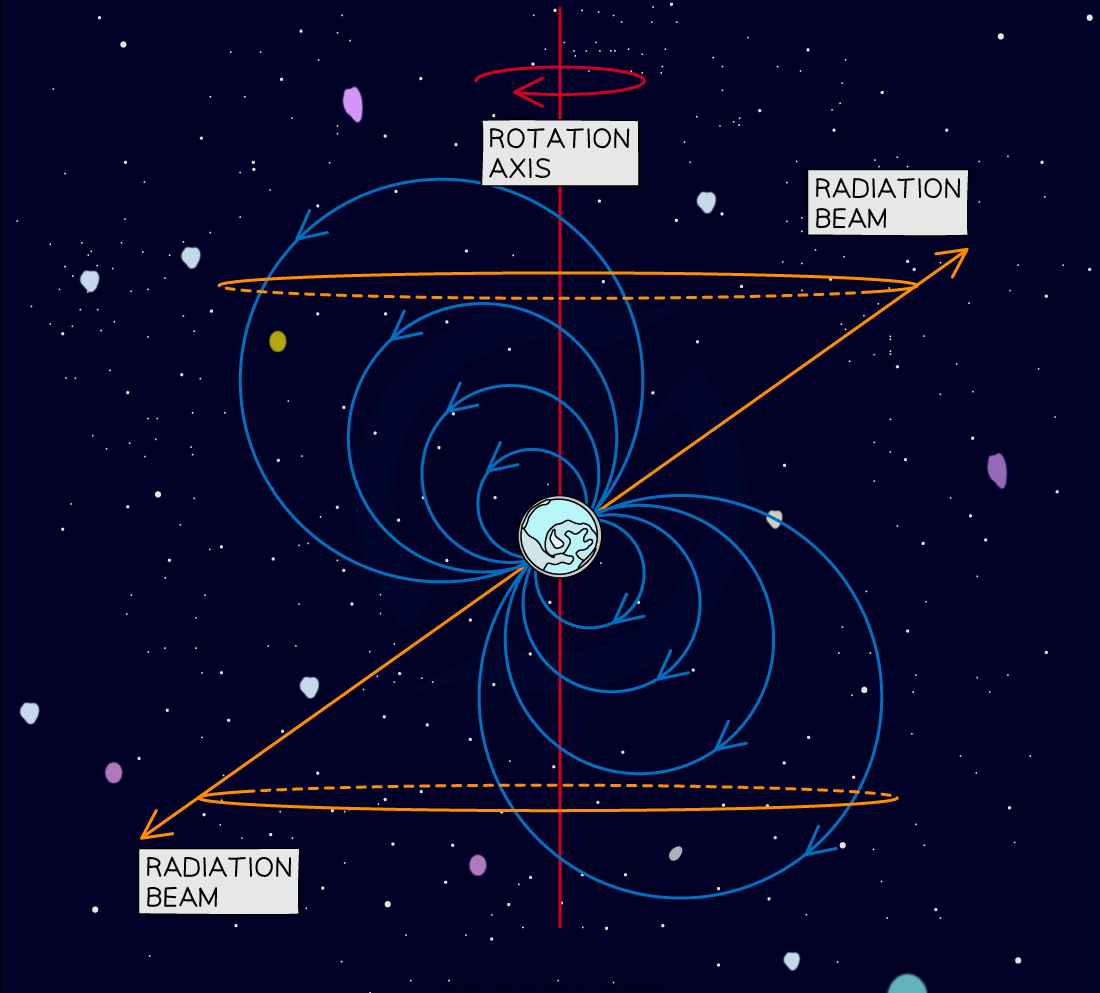
Some neutron stars rotate rapidly (up to 600 times per second) emitting bursts of highly directional electromagnetic radiation
These stars are called pulsars
Characteristics of Black Holes
The core collapses into an infinitely dense point called a singularity
A singularity is defined as:
A theoretical point at which matter is compressed to an infinitely small point and the laws of physics, as they are currently understood, break down
The gravitational field is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape it
This region is known as a black hole
The boundary at which light and matter cannot escape the gravitation pull of the black hole is called the event horizon
The escape velocity beyond the event horizon is greater than the speed of light, hence photons cannot escape from a black hole

Characteristics of a Black Hole

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
