Specific Heat Capacity (OCR A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: H556
Specific Heat Capacity
The specific heat capacity of a substance is defined as:
The amount of thermal energy required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of a substance by 1 °C
This quantity determines the amount of energy needed to change the temperature of a substance
The specific heat capacity is measured in units of Joules per kilogram per Kelvin (J kg-1 K-1) or Joules per kilogram per degree Celsius (J kg-1 °C-1) and has the symbol c
Different substances have different specific heat capacities
Specific heat capacity is mainly used when considering liquids and solids
From the definition of specific heat capacity, it follows that:
The greater the mass of the material, the more thermal energy that will be required to raise its temperature
The greater the change in temperature, the higher the thermal energy required to achieve this change
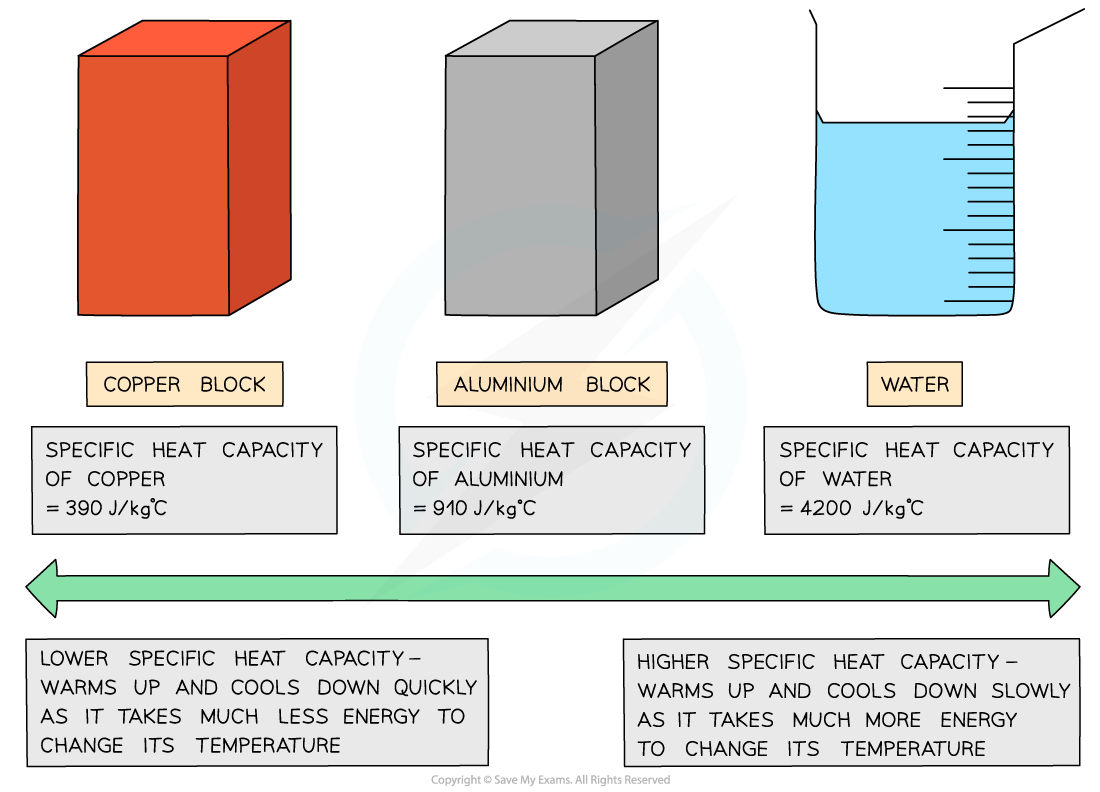
Low v high specific heat capacity
If a substance has a low specific heat capacity, it heats up and cools down quickly
If a substance has a high specific heat capacity, it heats up and cools down slowly
The specific heat capacity of different substances determines how useful they would be for a specific purpose eg. choosing the best material for kitchen appliances
Table of values of specific heat capacity for various substances

Good electrical conductors, such as copper and lead, have low specific heat capacities
This makes them excellent conductors of heat
It is due to their free electrons
Determining Specific Heat Capacity
The amount of thermal energy Q needed to raise the temperature by Δθ for a mass m with specific heat capacity c is equal to:
E = mcΔθ
Where:
E = change in thermal energy (J)
m = mass of the substance (kg)
c = specific heat capacity of the substance (J kg−1K−1 or J kg−1 °C−1)
Δθ = change in temperature (K or °C)
Worked Example
A kettle has a power rating of 1.7 kW. A mass of 650 g of liquid at 25 °C is poured into the kettle.
When the kettle is switched on, it takes 3.5 minutes to start boiling.
Calculate the specific heat capacity of the liquid.
Answer:
Step 1: State the known quantities
Power = 1.7 kW = 1.7 × 103 W
Time = 3.5 minutes = 3.5 × 60 s = 210 s
Mass, m = 650 g = 0.65 kg
Temperature change, Δθ = 100 − 25 = 75 °C
Step 2: State the equation linking energy, power and time
Energy = Power × Time
Step 3: Calculate the energy supplied
Energy = 1.7 × 103 × 210 = 3.57 × 105 J
Step 4: State the thermal energy equation
E = mcΔθ
Step 5: Rearrange to make specific heat capacity the subject
Step 6: Substitute in values and state the final answer
J kg−1 °C−1
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The difference in temperature Δθ will be exactly the same whether the temperature is given in Celsius or Kelvin. Therefore, there is no need to convert between the two since the difference in temperature will be the same for both units.
Procedures to Determine Specific Heat Capacity
In these experiments the following equation is used to determine the specific heat capacity of the substance:

Methods to Determine the Specific Heat Capacity of a Solid and a Liquid
Equipment List for a Solid:
A block of the substance (preferably 1kg in mass)
A thermometer
An appropriate heater (e.g., an immersion heater)
A power source
A joule meter or a voltmeter, ammeter and stop-clock
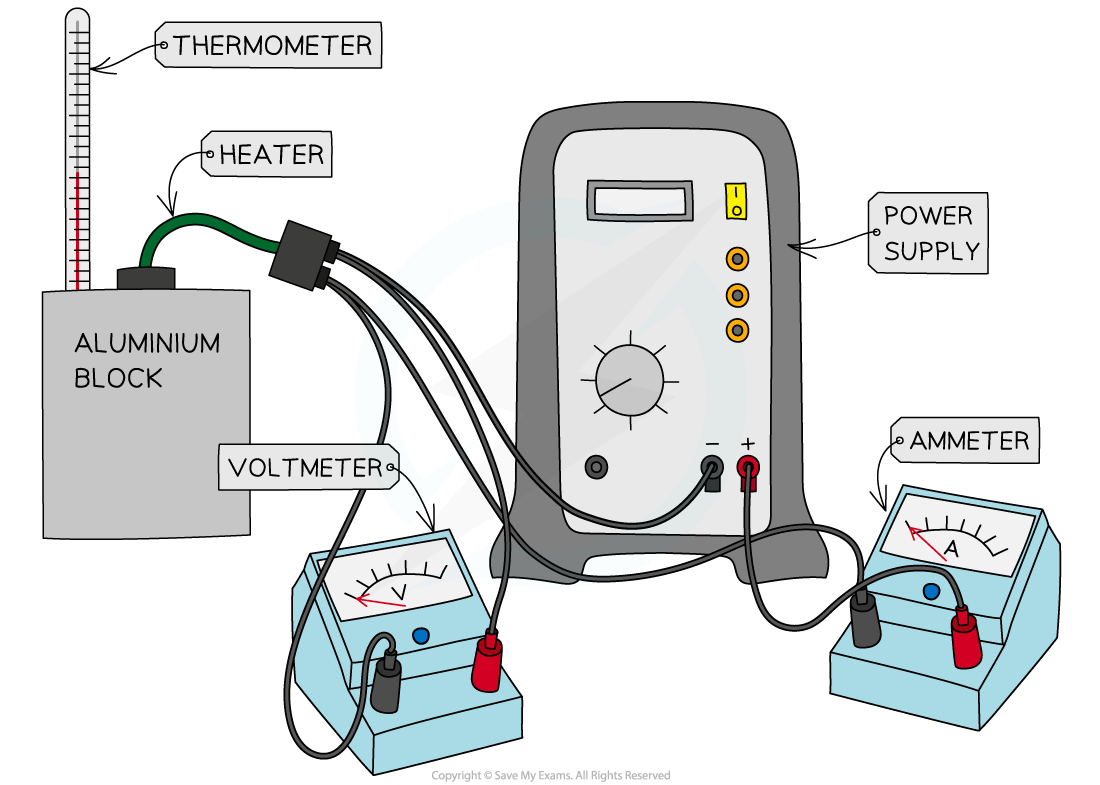
Apparatus to determine the specific heat capacity of a 1 kg Aluminium block
Method for a Solid
Assemble the apparatus as shown in the diagram above
Measure the initial temperature of the substance
Record the value
Turn on the power supply and start the stop-clock
Take readings of the voltage and current
Record these values
After 5 minutes (300 seconds) switch off the power supply, stop the stop-clock
Monitor the thermometer
Record the highest temperature reached
This may be a few minutes after the power supply is switched off
Equipment List for a Liquid:
A beaker of liquid (ideally containing 400 ml liquid)
A thermometer
An appropriate heater (e.g., an immersion heater)
A power source
A joule meter or a voltmeter, ammeter and stop-clock
A digital balance

Apparatus to determine the specific heat capacity of 400 ml of water
Method for a Liquid
Assemble the apparatus as shown in the diagram above
Measure the mass of the liquid
Record the value
Measure the initial temperature of the substance
Record the value
Turn on the power supply and start the stop-clock
Take readings of the voltage and current
Record these values
After 10 minutes (600 seconds) switch off the power supply, stop the stop-clock
Monitor the thermometer
Record the highest temperature reached
This may be a few minutes after the power supply is switched off
Analysis of the Results
Calculate the change in temperature
This is the final temperature minus the initial temperature
The heat supplied to the substance can be calculated using the equation:
energy = current (A) × voltage (V) × time (s)
The equation for specific heat capacity can be used to calculate specific heat capacity
E = mcΔθ
Where:
E = change in thermal energy (J)
m = mass of the substance (kg)
c = specific heat capacity of the substance (J kg−1K−1 or J kg−1 °C−1)
Δθ = change in temperature (K or °C)
Evaluation
Not all of the heat supplied by the heater will go into the substance
Some heat will be lost to the surroundings
This means that the value for energy supplied will be too large
This results in too high a value for specific heat capacity
There may be fluctuations in the power supply
Take several periodic measurements of the voltage and current
Calculate an average of these values

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?