Force-Distance Graph (OCR A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: H556
Force Distance Graphs for Point or Spherical Masses
Recall that Newton's Law of Gravitation says the magnitude of the force F between a mass M and a mass m is given by the equation:
Therefore, a force-distance graph would be a curve, because F is inversely proportional to r2, or:
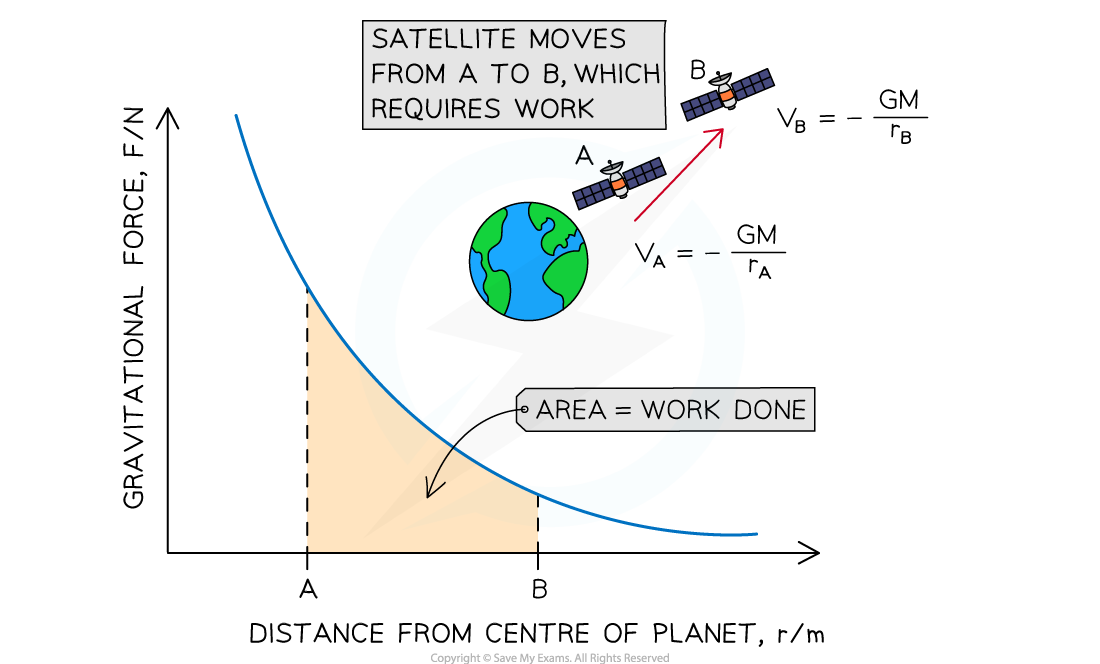
Work is done on the satellite of mass m to move it from A to B, because gravity is attractive. The area under the curve represents the magnitude of energy transferred
The product of force and distance is equal to work done (or energy transferred)
Therefore, the area under the force-distance graph for gravitational fields is equal to the work done
In the case of a mass m moving further away from a mass M, the potential increases
Since gravity is attractive, this requires work to be done on the mass m
The area between two points under the force-distance curve therefore gives the change in gravitational potential energy of mass m
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You should be able to interpret areas under curves by thinking about what the product of the quantities on the axes would represent. Since, in this case, force × distance = work done, then it follows that the area under the curve represents the change in energy between two points. Specifically, this would be a change in gravitational potential energy!

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?