Superposition (OCR A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: H556
The Principle of Superposition
The principle of superposition states:
When two or more waves with the same frequency arrived at a point, the resultant displacement is the sum of the displacements of each wave
The waves often travel in opposite directions because they're reflected at a boundary
This principle describes how waves that meet at a point in space interact
Superposition Experiments
Superposition experiments include using sound, light and microwaves
Sound
Superposition creates stationary, longitudinal sound waves in a resonance tube such as in an organ pipe or woodwind instruments such as a flute

Stationary waves in an organ pipe
Superposition experiments with sound often use air columns or speakers
If two loudspeakers are connected to the same signal generator, the superposition of the sound waves can be heard when walking along in front of the speakers
A loud sound is heard when the sound waves reinforce one another
A quiet or no sound is heard when the waves cancel each other out

The superposition of sound waves can be detected by the person walking past hearing a loud and soft sound in intervals
Light
The superposition of light waves is demonstrated through:
Young's double-slit experiment
Diffraction grating
The light waves are superposed when they reach a screen
This shows an interference pattern
Monochromatic laser light is commonly used for these experiment to produce the clearest interference pattern on the screen
The distance between the maxima and minima on the pattern varies with the frequency of the light (colour)
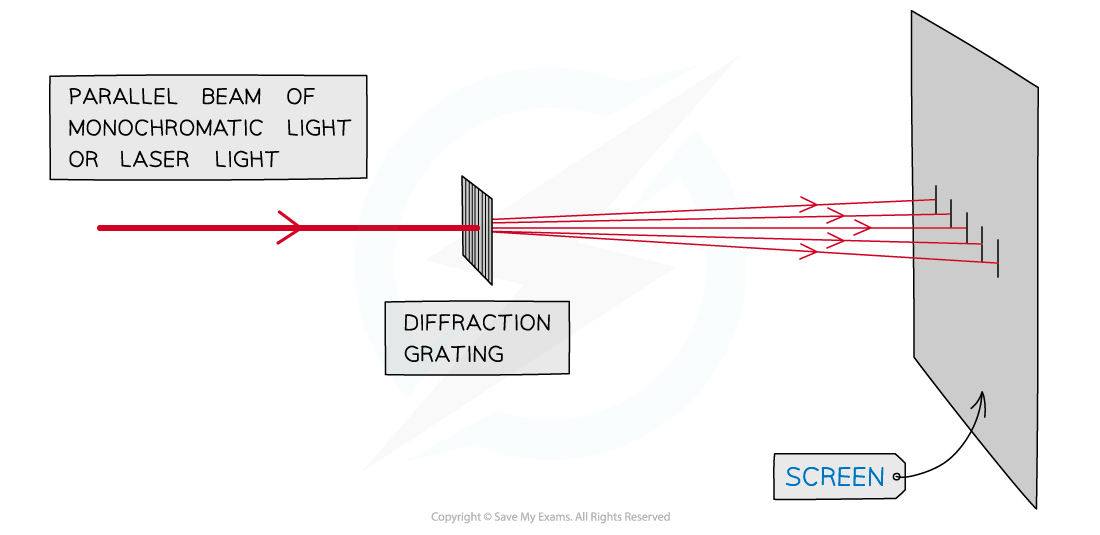
An example of an experiment that demonstrates superposition is light passing through a diffraction grating
Microwaves
Similar to light and sound, microwaves also superpose to create regions where the microwaves reinforce or cancel each other out
The interference of microwaves creates a standing wave inside a microwave oven, which is used to heat food
Microwave superposition experiments normally include:
Two microwave transmitters
A microwave detector
To produce a microwave stationary wave, a microwave reflector is often used too, with just one transmitter
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Always refer back to the experiment or scenario in an exam question e.g. the wave produced by a loudspeaker for sound or by the laser for light

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?