Polarisation (OCR A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: H556
Polarisation
Polarisation is when:
Particle oscillations occur in only one of direction perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation
Polarisation can only occur in transverse waves
This is because electromagnetic transverse waves are oscillating electric and magnetic fields in any plane perpendicular to the propagation direction
When transverse waves are polarised, this means:
Vibrations are restricted to one direction
These vibrations are still perpendicular to the direction of propagation / energy transfer
The difference between unpolarised and polarised waves is shown in the diagram below:
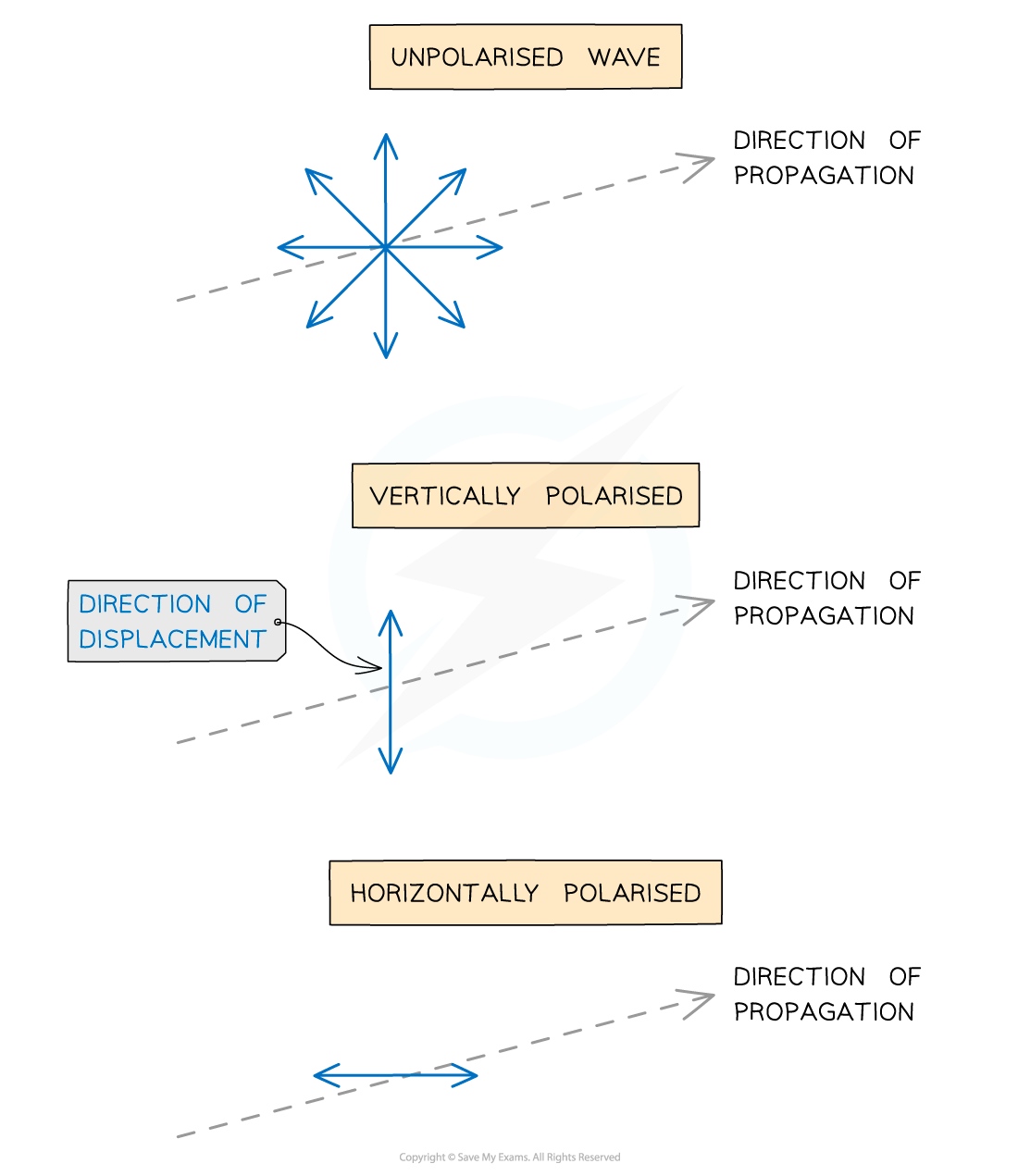
Diagram showing the displacement of unpolarised and polarised transverse waves
Light from the sun or a lightbulb, or any that hasn't gone through a polarising filter is unpolarised
Longitudinal waves (e.g. sound waves) cannot be polarised
This is because they oscillate parallel to the direction of travel
Waves can be polarised through a polariser such as a polarising filter (light) or metal grilles (microwaves)
This only allows oscillations in a certain plane to be transmitted
This is called a plane-polarised wave
Polarising Filters
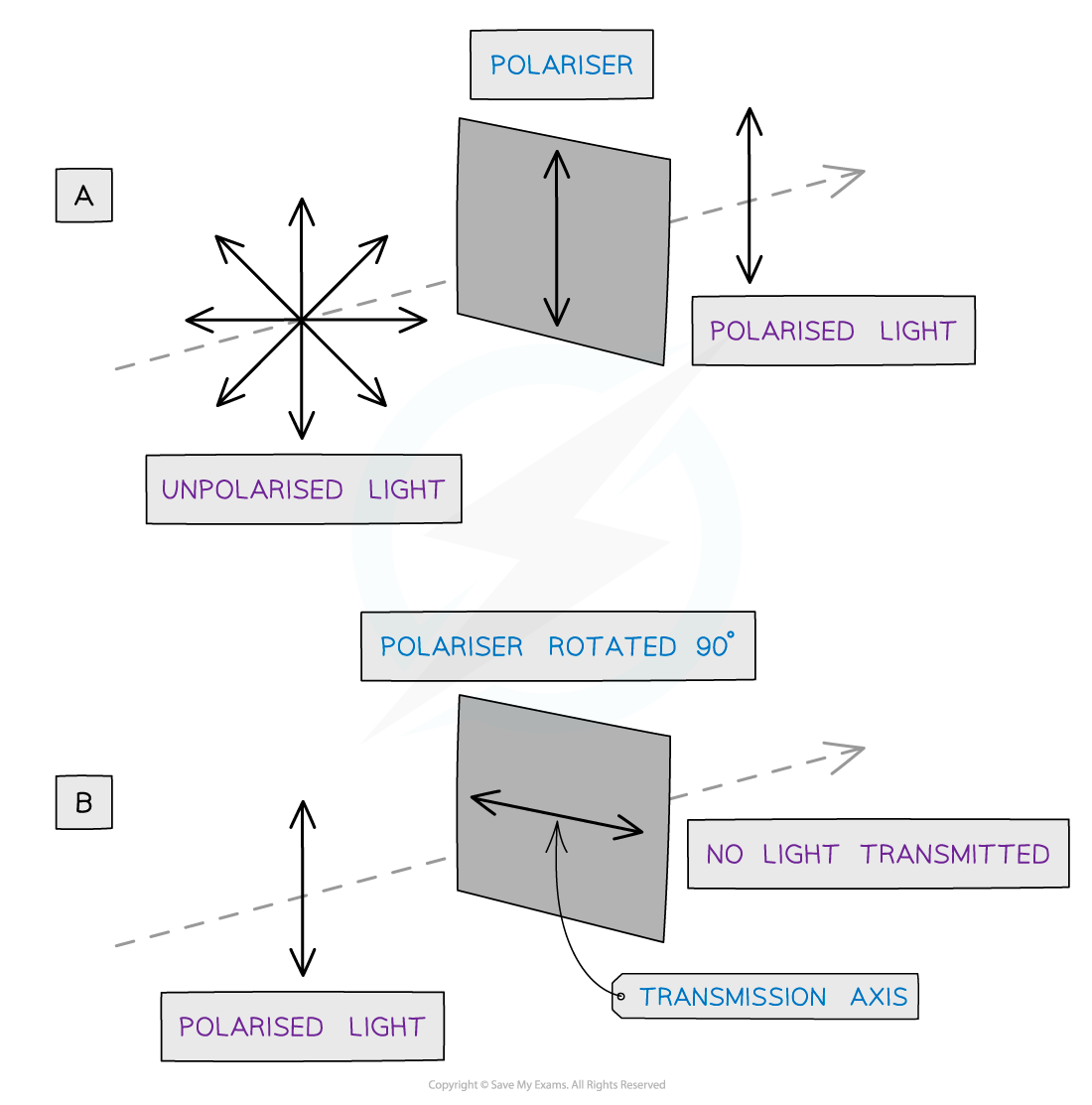
Diagram showing an unpolarised and polarised wave travelling through polarising filters
Diagram A shows:
Only unpolarised waves can be polarised
Diagram B shows:
When a polarised wave passes through a filter with a transmission axis perpendicular to the wave, none of the wave will pass through
Light can also be polarised through reflection, refraction and scattering
Metal Grilles
A metal grille is similar to a polarising filter, and commonly used for polarising microwaves
Microwaves are electromagnetic waves with a longer wavelength than visible light
By convention, the direction of polarisation is only the direction of the electric field propagation (rather than magnetic)
A metal grille is different from a polarising filter
The free electrons moving in the metal bar can cancel out the electric field in the same direction as the grille and completely absorb it
Thus the horizontal electric field passes if the grilles are positioned vertically and vice versa
This is the opposite of what happens in a polarising filter

A metal grille is used to polarise a microwave
Investigating Light Intensity with Two Polarisers
If an unpolarised light source is placed in front of two identical polarising filters, A and B, with their transmission axes parallel:
Filter A will polarise the light in a certain axis
All of the polarised light will pass through filter B unaffected
In this case, the maximum intensity of light is transmitted

When both polarisers have the same transmission axis, the intensity of the transmitted light is at its maximum
As the polarising filter B is rotated anticlockwise, the intensity of the light observed changes periodically depending on the angle B is rotated through
When A and B have their transmission axes perpendicular to each other:
Filter A will polarise the light in a certain axis
This time none of the polarised light will pass through filter B
In this case, the minimum intensity of light is transmitted

When one of the polarisers is rotated through 90°, the intensity of the transmitted light drops to zero
The resulting graph of the light intensity with angle, as the second polariser is rotated through 360°, looks as follows:

Graph showing how the intensity of the transmitted beam varies with the angle between the transmission axes of the two polarisers
Worked Example
Which statement below describes a situation in which polarisation should happen?
A. Radio waves pass through a metal grid
B. Surface water waves are diffracted
C. Sound waves are reflected
D. Ultrasound waves pass through a metal grid
Answer: A
Radio waves are transverse waves - they can be polarised by a metal grid so only the waves that fit through the grid will be transmitted, therefore, A is correct
B cannot be correct as waves are not polarised when diffracted, but are polarised only when reflected, refracted or scattered
C & D cannot be correct as polarisation only occurs for transverse waves, therefore, C & D can be ruled out as sound and ultrasound are both longitudinal waves
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You may be expected to describe the intensity, or even draw the graph of intensity v angle, for light with two polarisers.
Observing Polarising Effects
Observing Polarisation of Microwaves
A microwave transmitter can emit naturally polarised waves with a wavelength of around 3 cm
To check whether the microwaves are polarised, place a microwave receiver in front of the transmitter and rotate about the axis through them
The signal, which is detected using an ammeter or audio amplifier and loudspeaker will rise and fall with intensity as the receiver is rotated
When the transmitter and the polarisation axis of the receiver are perpendicular to each other, the signal will be 0
When the receiver has a maximum signal, a metal grille can be placed between the transmitter and receiver, acting as a second polariser
When the grille is rotated (for example, in 10° increments), the signal varies and is 0 when the metal rods are aligned with the electric field vector of the emitted microwaves
If the microwave transmitter is producing vertically plane-polarised radiation:
If the bars of the metal grille are horizontally orientated, very few of the microwaves will be absorbed and the ammeter reading will be high
If the bars of the metal grille are vertically orientated, all of the microwaves will be absorbed and the ammeter reading will be zero

The polarisation of microwaves can be detected using a transmitter and receiver
Radio and television services are broadcast either horizontally-polarised or vertically-polarised
Therefore, the reception aerial needs to be mounted flat (horizontal), or on its side (vertical),
The particular orientation of an aerial will depend on the transmitter it is pointing towards and the polarity of the services being broadcast

Broadcasting towers always transmit either vertically or horizontally polarised signals. This is why aerials must be positioned accordingly otherwise they won't pick up the TV signal correctly
Observing Polarisation of Light
Polarisation of light can be observed by looking through a polarising filter at different light sources (such as the Sun, a light bulb or a laptop screen)
This can be with two filters aligned at different angles to each other
As one of the filters is rotated through different angles with respect to the other, the intensity of transmitted light passing through rises and falls
It can also be observed by looking through a single polarising filter at light reflected at a shallow angle from water, such as a pond, or from shiny surfaces in the lab
Rotating the polarising filter shows the reflected image become dimmer and brighter again
One use of this is in photography

As well as giving a cool look to photographs, polaroid filters are extremely useful for reducing glare in photos and snapping pictures of objects underwater

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?