Resistors in Series & Parallel Circuits (OCR A Level Physics) : Revision Note
Combining Resistors in Series
When two or more components are connected in series:
The combined resistance of the components is equal to the sum of individual resistances
For example, for three resistors connected in series:

Combined resistance of two or more resistors in series equation
Worked Example
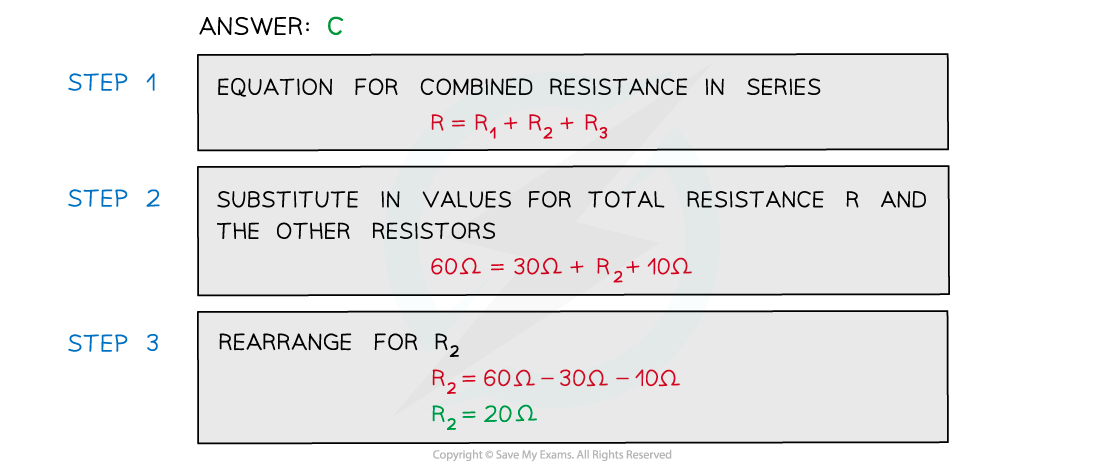
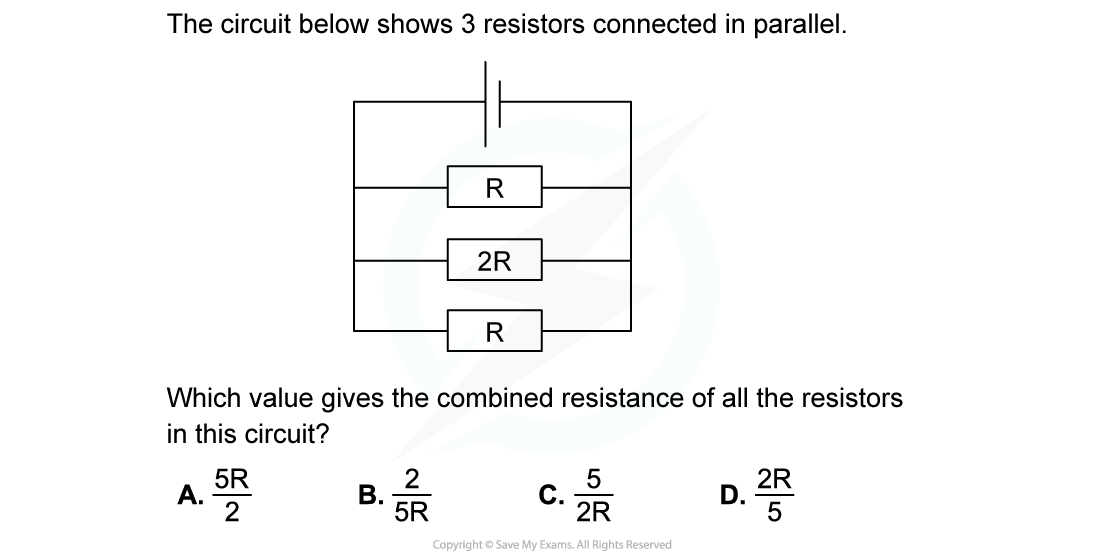
The combined resistance R in the following series circuit is 60 Ω.What is the resistance value of R2?
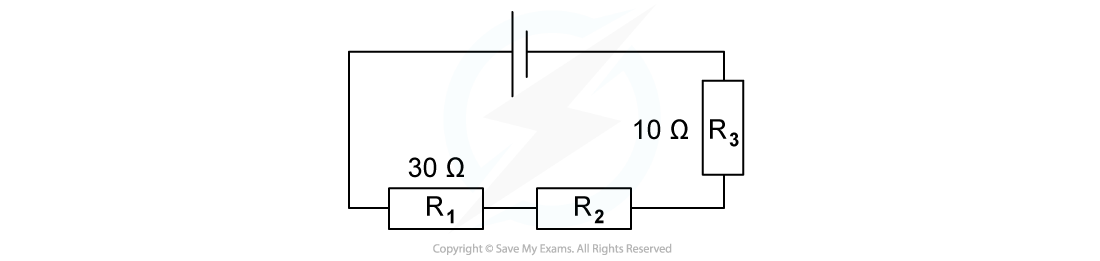
A. 100 Ω
B. 30 Ω
C. 20 Ω
D. 40 Ω
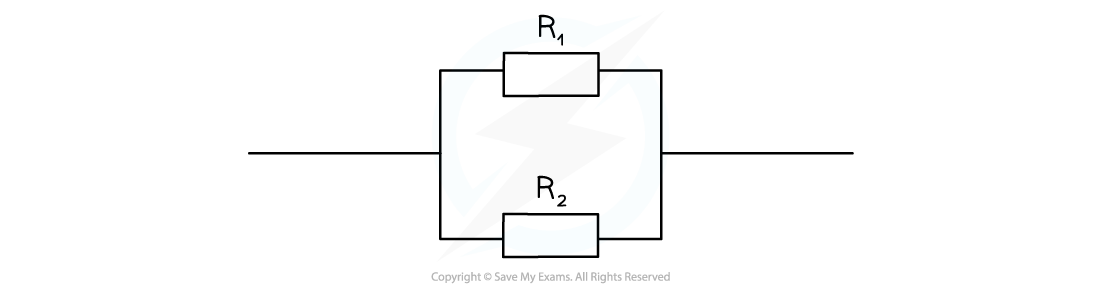
Combining Resistors in Parallel
When two or more component are connected in parallel:
The reciprocal of the combined resistance is the sum of the reciprocals of the individual resistances
For example, for two resistors connected in parallel:

Combined resistance of two or more resistors in parallel equation
This means the combined resistance decreases and is less than the resistance of any of the individual components
For example, If two resistors of equal resistance are connected in parallel, then the combined resistance will halve
Worked Example
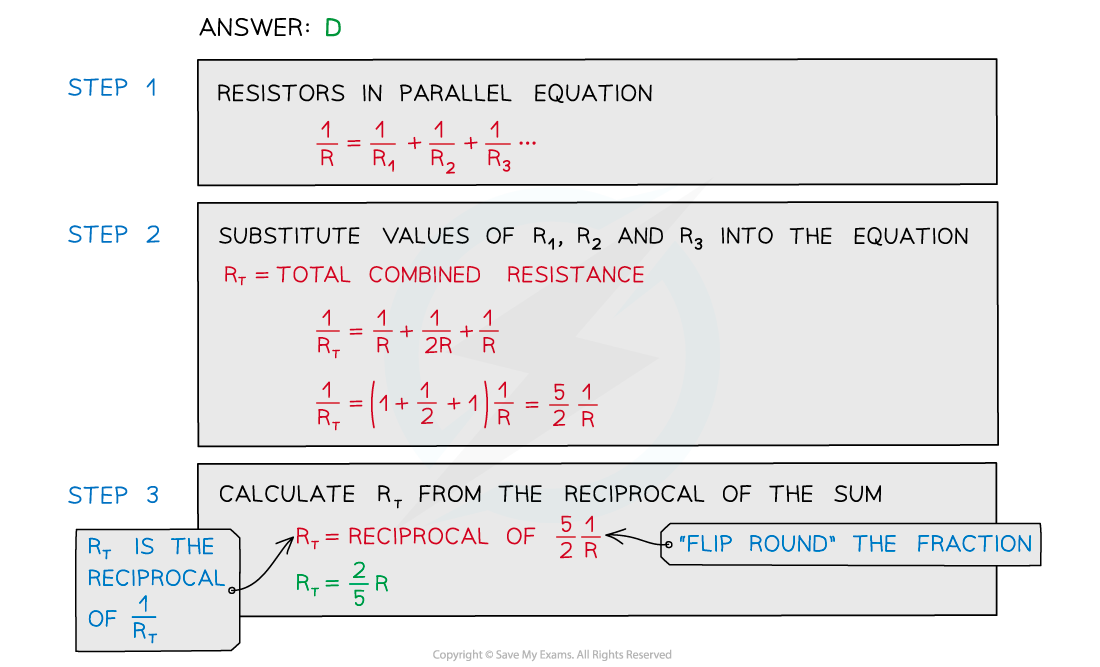
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The most common mistake is to forget to find the reciprocal of RT
The reciprocal of a value is 1 / value
For example, the reciprocal of a whole number such as 2 equals ½
The reciprocal of ½ is 2
If the number is already a fraction, the numerator and denominator are ‘flipped’ round

In the case of the resistance R, this becomes 1/R
To get the value of R from 1/R, you must do 1 ÷ your answer
You can also use the reciprocal button on your calculator (labelled either x-1 or 1/x, depending on your calculator)

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
