Work Function & Threshold Frequency (OCR A Level Physics) : Revision Note
Work Function & Threshold Frequency
The photoelectric effect provides important evidence that light is quantised or carried in discrete packets
This is shown by the fact each electron can absorb only a single photon
This means only the frequencies of light above a threshold frequency will emit a photoelectron
Threshold Frequency & Wavelength
The threshold frequency is defined as:
The minimum frequency of incident electromagnetic radiation required to remove a photoelectron from the surface of a metal
The threshold wavelength, related to threshold frequency by the wave equation, is defined as:
The longest wavelength of incident electromagnetic radiation that would remove a photoelectron from the surface of a metal
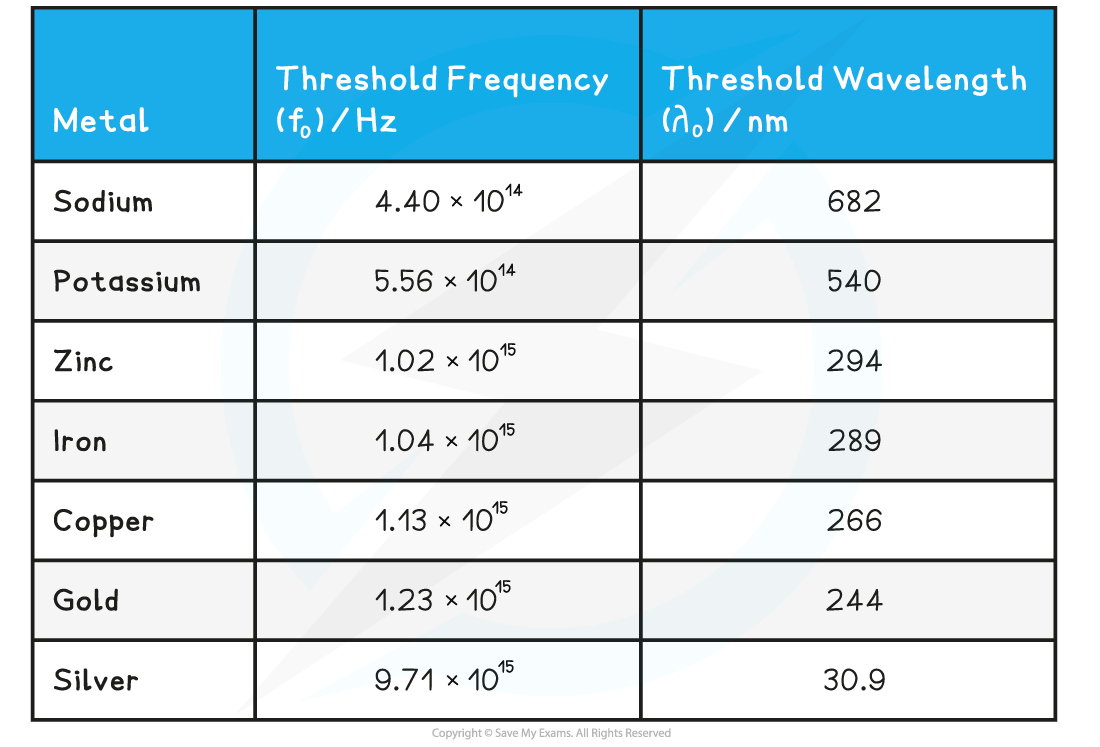
Threshold frequency and wavelength are properties of a material, and vary from metal to metal
Threshold frequencies and wavelengths for different metals
Work Function
The work function Φ, or threshold energy, of a material, is defined as:
The minimum energy required to release a photoelectron from the surface of a metal
Consider the electrons in a metal as trapped inside an ‘energy well’ where the energy between the surface and the top of the well is equal to the work function Φ
A single electron absorbs one photon
Therefore, an electron can only escape from the surface of the metal if it absorbs a photon which has an energy equal to Φ or higher
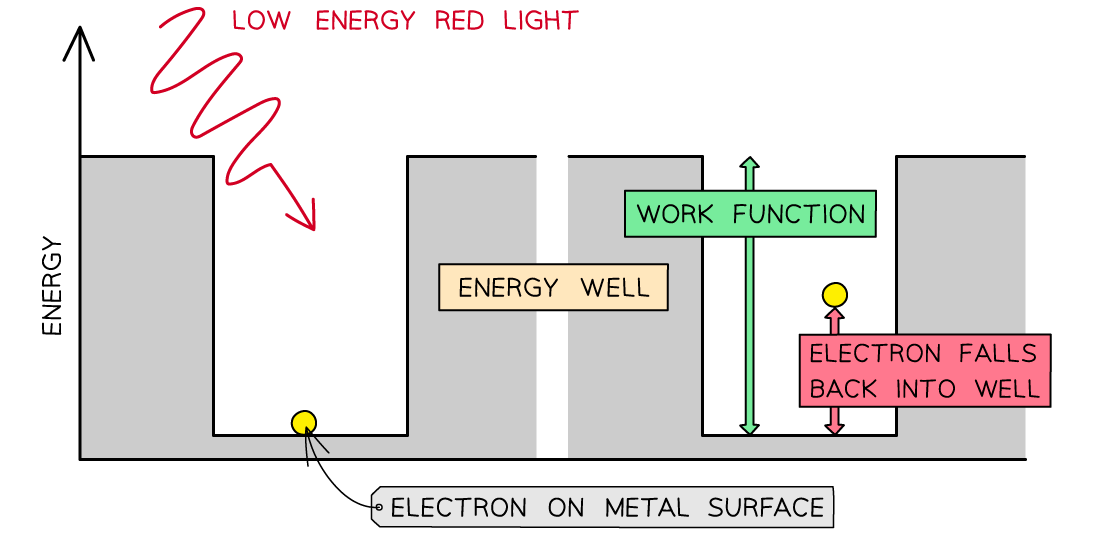

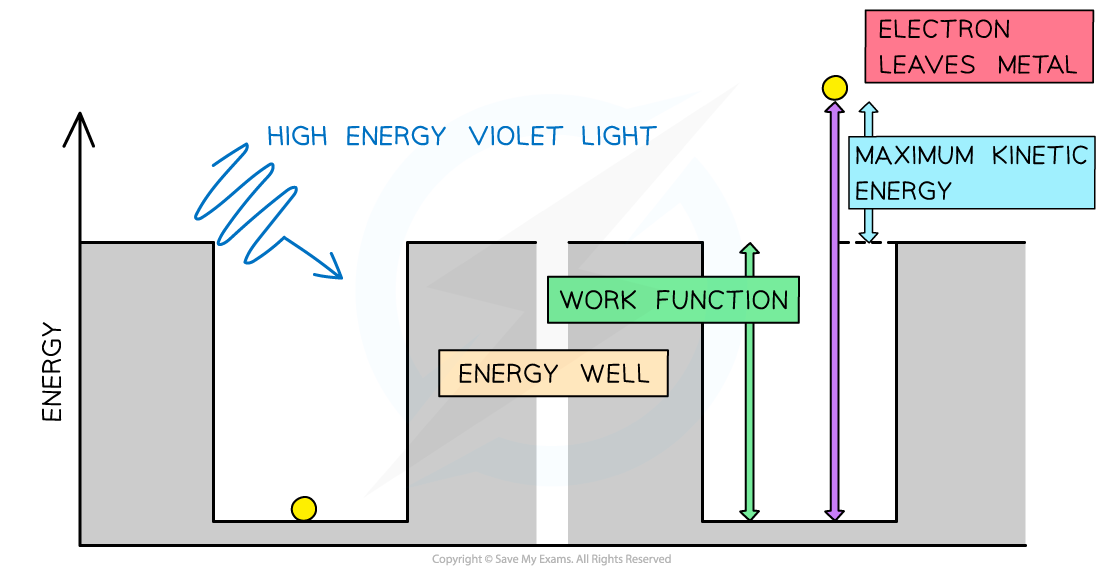
In the photoelectric effect, a single photon may cause a surface electron to be released if it has sufficient energy
Different metals have different threshold frequencies and hence different work functions
Using the well analogy:
A more tightly bound electron requires more energy to reach the top of the well
A less tightly bound electron requires less energy to reach the top of the well
Alkali metals, such as sodium and potassium, have threshold frequencies in the visible light region
This is because the attractive forces between the surface electrons and positive metal ions are relatively weak
Transition metals, such as zinc and iron, have threshold frequencies in the ultraviolet region
This is because the attractive forces between the surface electrons and positive metal ions are much stronger
Examiner Tips and Tricks
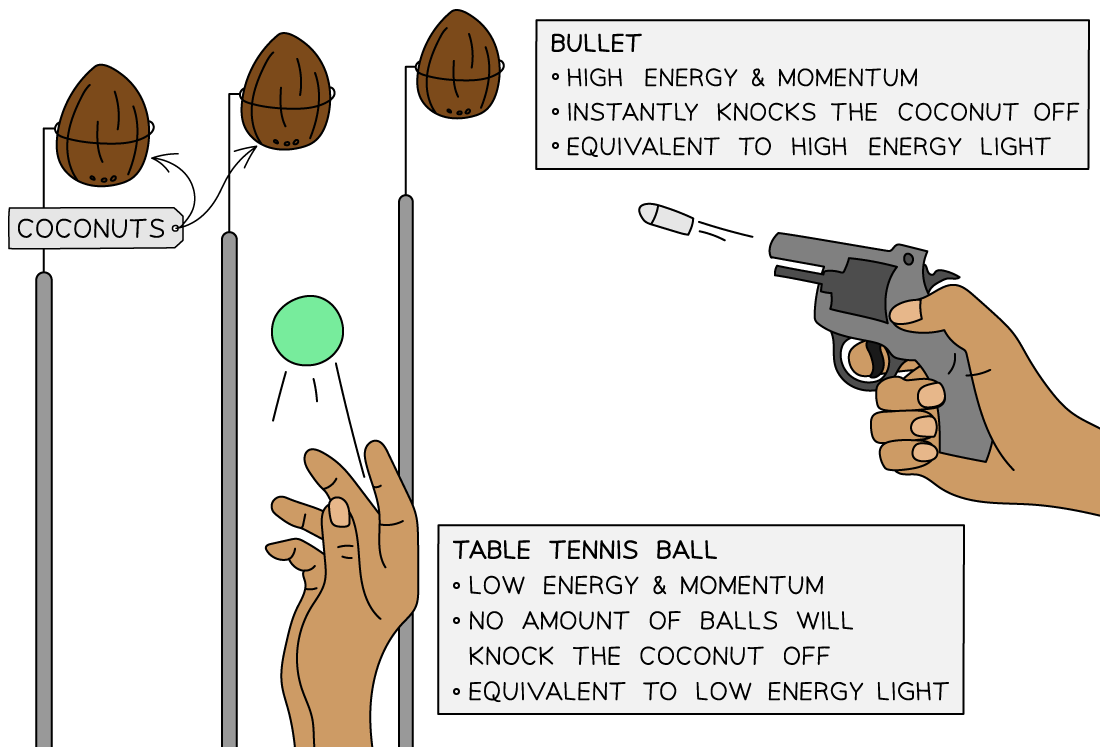
A useful analogy for threshold frequency is a fairground coconut shy:
One person is throwing table tennis balls at the coconuts, and another person has a pistol
No matter how many of the table tennis balls are thrown at the coconut it will still stay firmly in place – this represents the low frequency quanta
However, a single shot from the pistol will knock off the coconut immediately – this represents the high frequency quanta

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
