Electric Current & Charge (OCR A Level Physics) : Revision Note
Electric Current
Electric Current
Electric current is defined as the rate of flow of charge
It is measured in units of amperes (A) or amps
The symbol for current is I
By convention, current is considered to flow in the direction from positive to negative, even though the actual charge carriers in a metal (electrons) flow from negative to positive
This is known as conventional current direction
The charge, current and time are related by the equation:
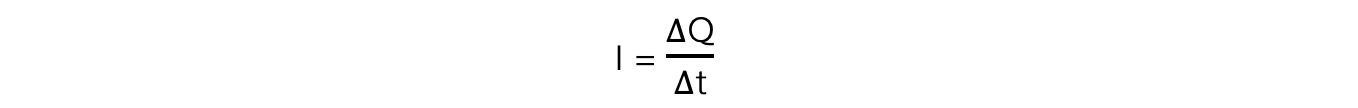
Where:
I = current (A)
ΔQ = change in charge (Q)
Δt = time interval (s)
When two oppositely charged conductors are connected together (by a length of wire), charge will flow between the two conductors, causing a current

Charge can flow between two conductors. The direction of conventional current in a metal is from positive to negative
There are several examples of electric currents, including in household wiring and electrical appliances
Current is measured using an ammeter
Ammeters should always be connected in series with the part of the circuit you wish to measure the current through

An ammeter can be used to measure the current around a circuit and always connected in series
Worked Example
When will 8 mA of current pass through an electrical circuit?
A. When 1 J of energy is used by 1 C of charge
B. When a charge of 4 C passes in 500 s
C. When a charge of 8 C passes in 100 s
D. When a charge of 1 C passes in 8 s
Answer: B
Step 1: Write out the equation relating current, charge and time, rearranging for charge Q
Q = It
Step 2: Rule out any obviously incorrect options
Option A does not contain charge or time, so can be ruled out
Step 3: Try the rest of the options to determine the correct answer
Consider option B:
I = 4 / 500 = 8 × 10–3 = 8 mA
Consider option C:
I = 8 / 100 = 80 × 10–3 = 80 mA
Consider option D:
I = 1 / 8 = 125 × 10–3 = 125 mA
Therefore, the correct answer is B
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Although electric charge can be positive or negative, since the conventional direction of current is the flow of positive charge the current should always be a positive value for your exam answers.
Electric Charge
Charge is a property certain particles have. It can either be:
A positive charge (+) (eg. proton)
A negative charge (–) (eg. electron)
A neutral (no) charge (eg. neutron)
An atom is neutral. This is because it has an equal number of protons (positive charge) and electrons (negative) charge
However, just the nucleus which is made up of protons and neutrons is positively charged
In physics, the charge is represented by the symbol Q or q
The Coulomb
The unit of charge is the Coulomb (C)
This is defined as the quantity of charge that passes a fixed point per second when a current of 1 A is flowing
The coulomb (C), in SI base units, is equal to the quantity of electricity conveyed in one second by a current of one ampere i.e. 1 C = 1 A s

Definition of the Coulomb
Quantisation of Charge
The charge on charge carriers is quantised
This means the charge comes in definite, finite quantities
In this way, the quantity of charge can be quantised depending on how many protons or electrons are present
Positive and negative charge has a definite minimum magnitude and comes in multiples of that magnitude
This magnitude is the elementary charge, e = 1.60 × 10-19 C
The magnitude of the charge just refers to its value, rather than whether it is positive or negative
The net charge on a particle can be quantised, meaning it is always a multiple of the charge of an electron by convention
The charge of an electron, e is -1.60 × 10-19 C
The charge of a proton, +e is +1.60 × 10-19 C
Worked Example
Determine the charge of an ion with charge 3e. State an appropriate unit for your answer.
Answer:
Step 1: Calculate the charge
1e = –1.60 × 10–19
3e = 3 × (–1.60 × 10–19) = –4.8 × 10–19
Step 2: Include the unit for charge
The units of charge is coulombs (C)
Therefore 3e = –4.8 × 10–19 C
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Although the charge of the electron is given on your data sheet, you will be expected to remember that the charge of the proton has the same magnitude

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
