Young's Modulus (OCR A Level Physics) : Revision Note
Young's Modulus
The Young modulus is defined as
The measure of the ability of a material to withstand changes in length with an added load
This gives information about the elasticity of a material ie. how stiff a material is
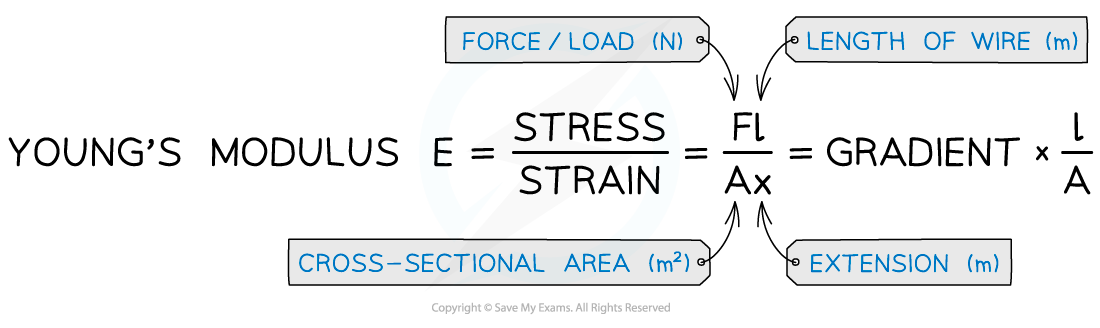
The Young Modulus, E, can be calculated from the ratio of stress and strain
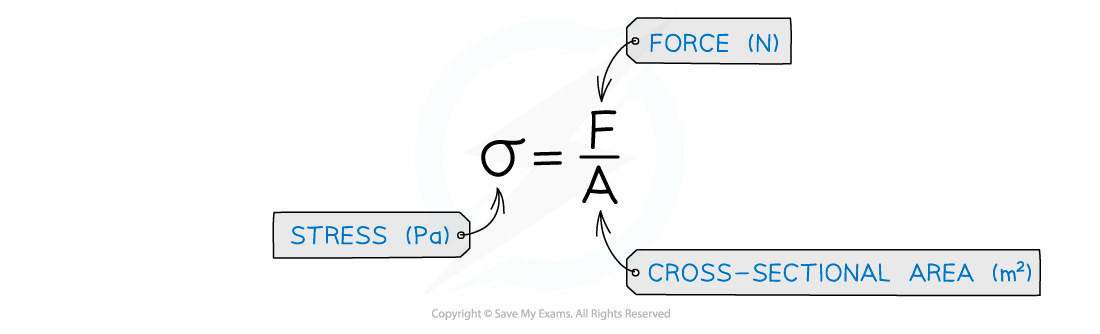


Its unit is the same as stress: Pa (since strain is unitless)
Just like the Force-Extension graph, stress and strain are directly proportional to one another for a material exhibiting elastic behaviour

A stress-strain graph is a straight line with its gradient equal to Young modulus
The gradient of a stress-strain graph when it is linear is equal to the Young Modulus
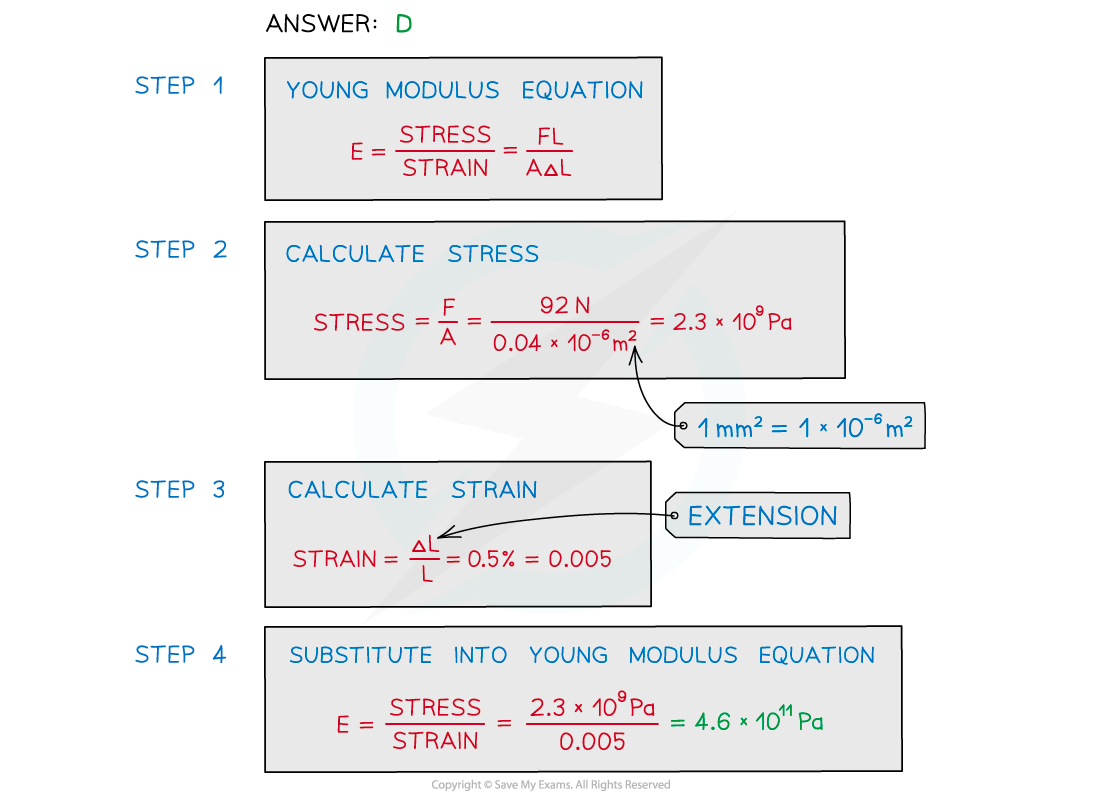
Worked Example
A metal wire that is supported vertically from a fixed point has a load of 92 N applied to the lower end.
The wire has a cross-sectional area of 0.04 mm2 and obeys Hooke’s law.
The length of the wire increases by 0.50%.What is the Young modulus of the metal wire?
A. 4.6 × 107Pa
B. 4.6 × 1012 Pa
C. 4.6 × 109 Pa
D. 4.6 × 1011 Pa
Examiner Tips and Tricks
To remember whether stress or strain comes first in the Young modulus equation, try thinking of the phrase ‘When you’re stressed, you show the strain’ ie. Stress ÷ strain.
Determining the Young Modulus
Aims of the Experiment
The aim of the experiment is to measure the Young Modulus of a metal wire
This requires a clamped horizontal wire over a pulley
This experiment can also be done with a vertical wire attached to the ceiling with a mass attached
Variables
Independent variable = Force (or load) (N)
Dependent variable = Extension (m)
Control variables:
The original length of wire
The thickness of the wire
The metal used for the wire
Equipment List
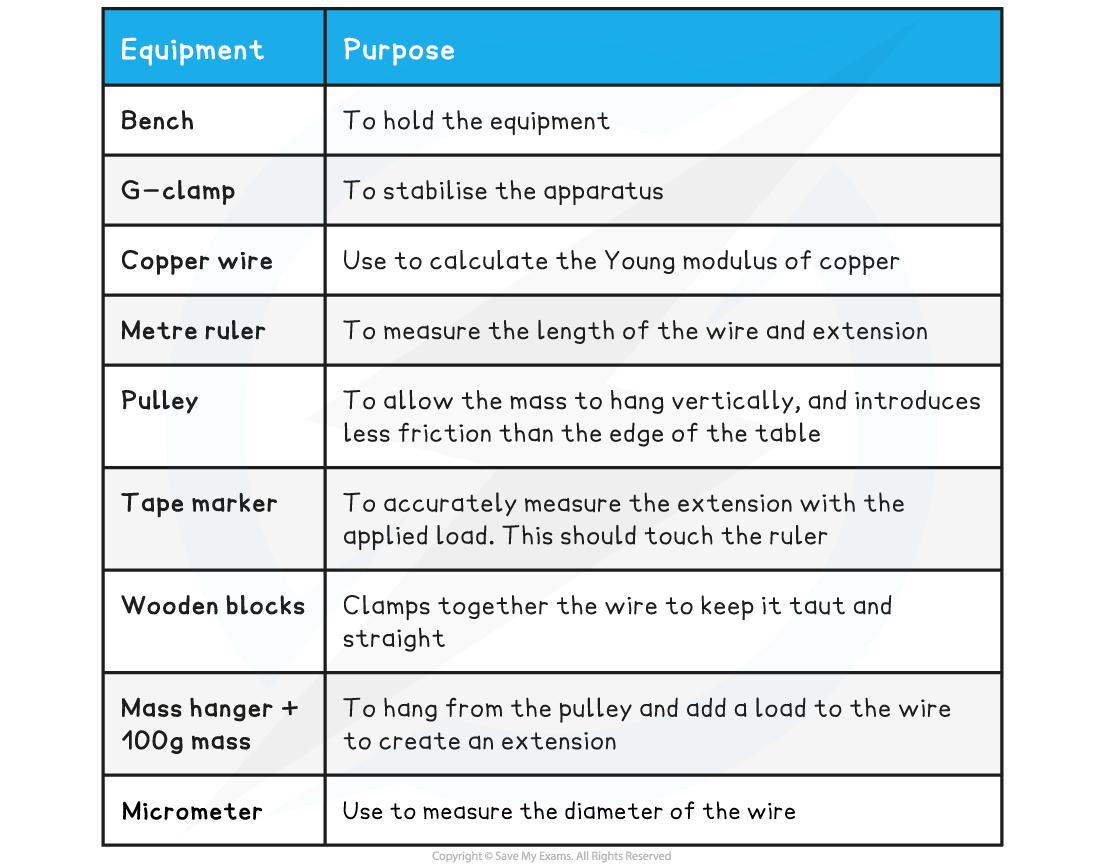
Resolution of measuring equipment:
Metre ruler = 1 mm
Method
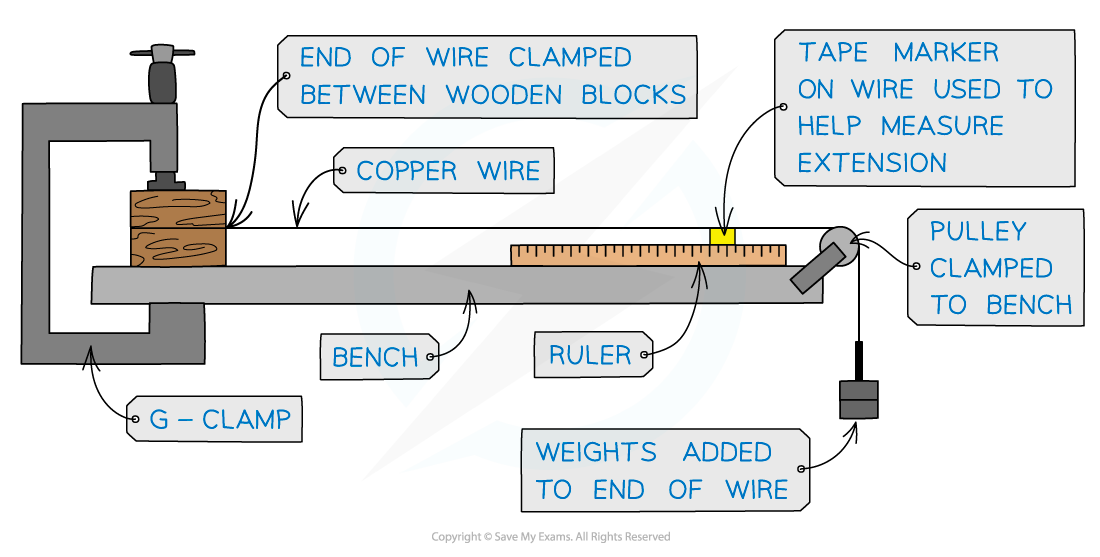
This method is an example of the procedure for varying load and measuring the extension of a copper wire. This is just one way of measuring the relationship between them
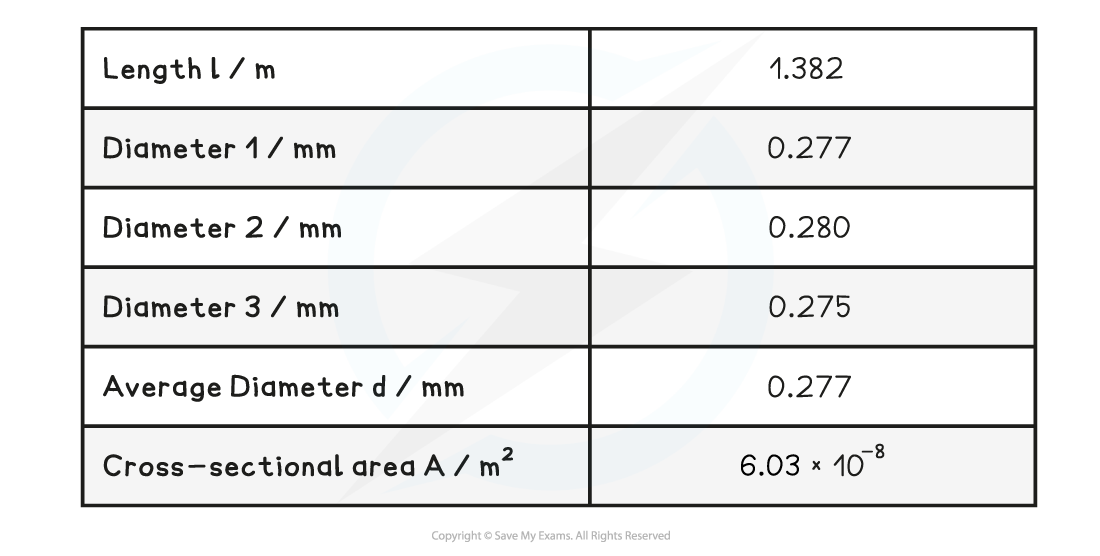
Measure the diameter of the wire with a micrometre screw gauge or digital callipers. Take at least 3 readings and find an average
Set up the apparatus so the wire is taut. No masses should be on the mass hanger just yet
Measure the original length of the wire using a metre ruler and mark a reference point with tape preferably near the beginning of the scale eg. at 1 cm
Record initial reading on the ruler of the reference point
Add a 100 g mass onto the mass hanger
Read and record the new reading of the tape marker from the meter ruler
Repeat this method by adding a 100 g mass (at least 5 – 10 times) and record the new scale reading from the metre ruler
An example of a table with some possible loads and extensions might look like:

Analysis of Results
1. Determine extension x from final and initial readings
Example table of results:

Table with additional data
2. Plot a graph of force against extension and draw line of best fit
3. Determine gradient of the force v extension graph

4. Calculate cross-sectional area from:

5. Calculate the Young’s modulus from:
Evaluating the Experiment
Systematic Errors:
Use a vernier scale for more precise readings
This is more likely to produce an accurate value for the extension
If the wire is extended past its elastic limit, it will be permanently deformed
To reduce the risk of this, remove the load and check the wire returns to its original length before taking any new readings
Random Errors:
Parallax error from reading the marker on the ruler
Random errors are reduced by repeating the experiment for all the loads and finding an average extension
Reduce the uncertainty on the cross-sectional area by measuring the diameter in several places and calculating an average
Safety Considerations
Wear safety goggles at all times in case the wire snaps
Make sure a cushion or soft surface is kept directly below the mass hanger, in case it falls off
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Although every care should be taken to make the experiment as reliable as possible, you will be expected to suggest improvements in producing more accurate and reliable results (e.g. repeat readings and use a longer length of wire)

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
