Equilibrium (OCR A Level Physics) : Revision Note
Equilibrium
A system is in equilibrium when all the forces are balanced. This means:
There is no resultant force
There is no resultant torque
An object in equilibrium will therefore remain at rest, or at a constant velocity, and not rotate
The system is in an equilibrium state when applying the principle of moments
Worked Example
Four beams of the same length each have three forces acting on them.
Which beam has both zero resultant force and zero resultant torque acting?


Conditions for Equilibrium
Coplanar forces can be represented by vector triangles
Forces are in equilibrium if an object is either
At rest
Moving at constant velocity
In equilibrium, coplanar forces are represented by closed vector triangles
The vectors, when joined together, form a closed path
The most common forces on objects are
Weight
Normal reaction force
Tension (from cords and strings)
Friction
The forces on a body in equilibrium are demonstrated below:
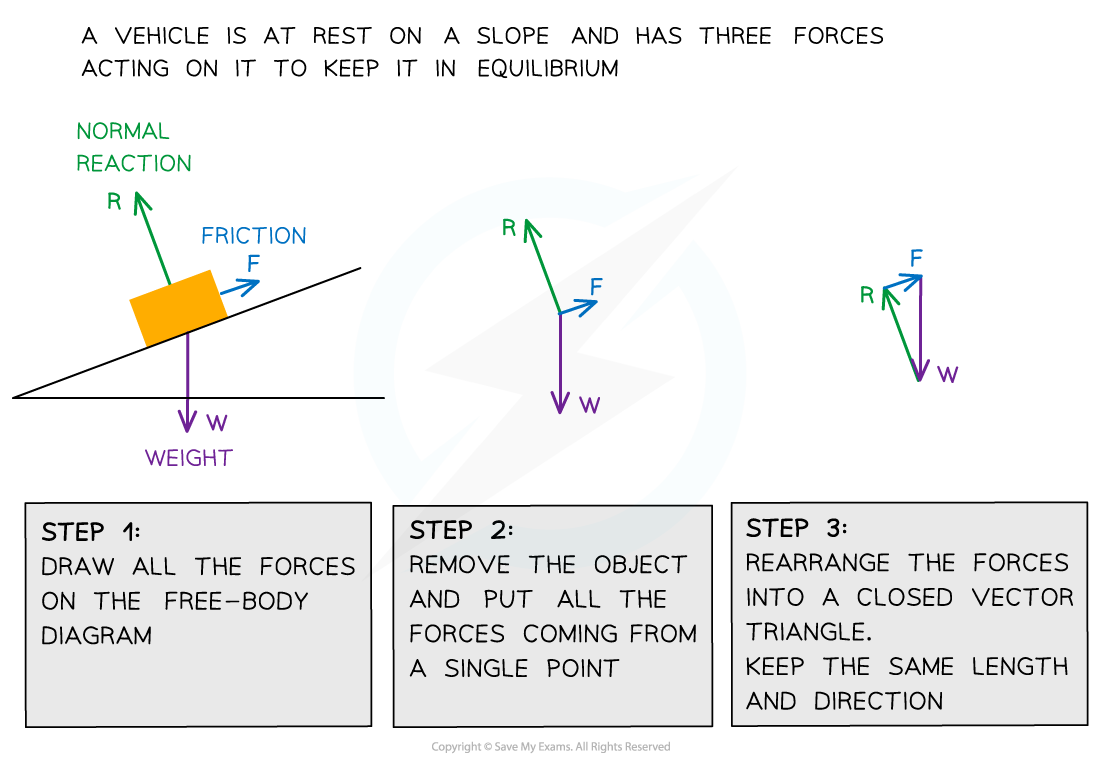
Three forces on an object in equilibrium form a closed vector triangle
Worked Example
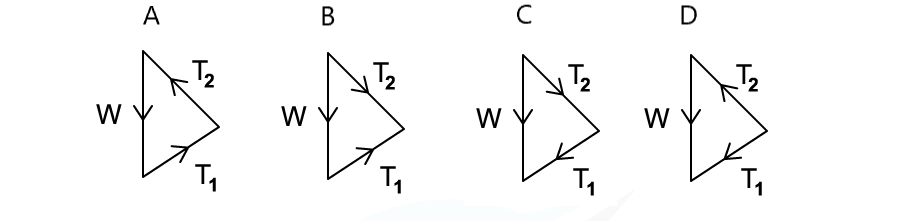
A weight hangs in equilibrium from a cable at point X. The tensions in the cables are T1 and T2 as shown.

Which diagram correctly represents the forces acting at point X?
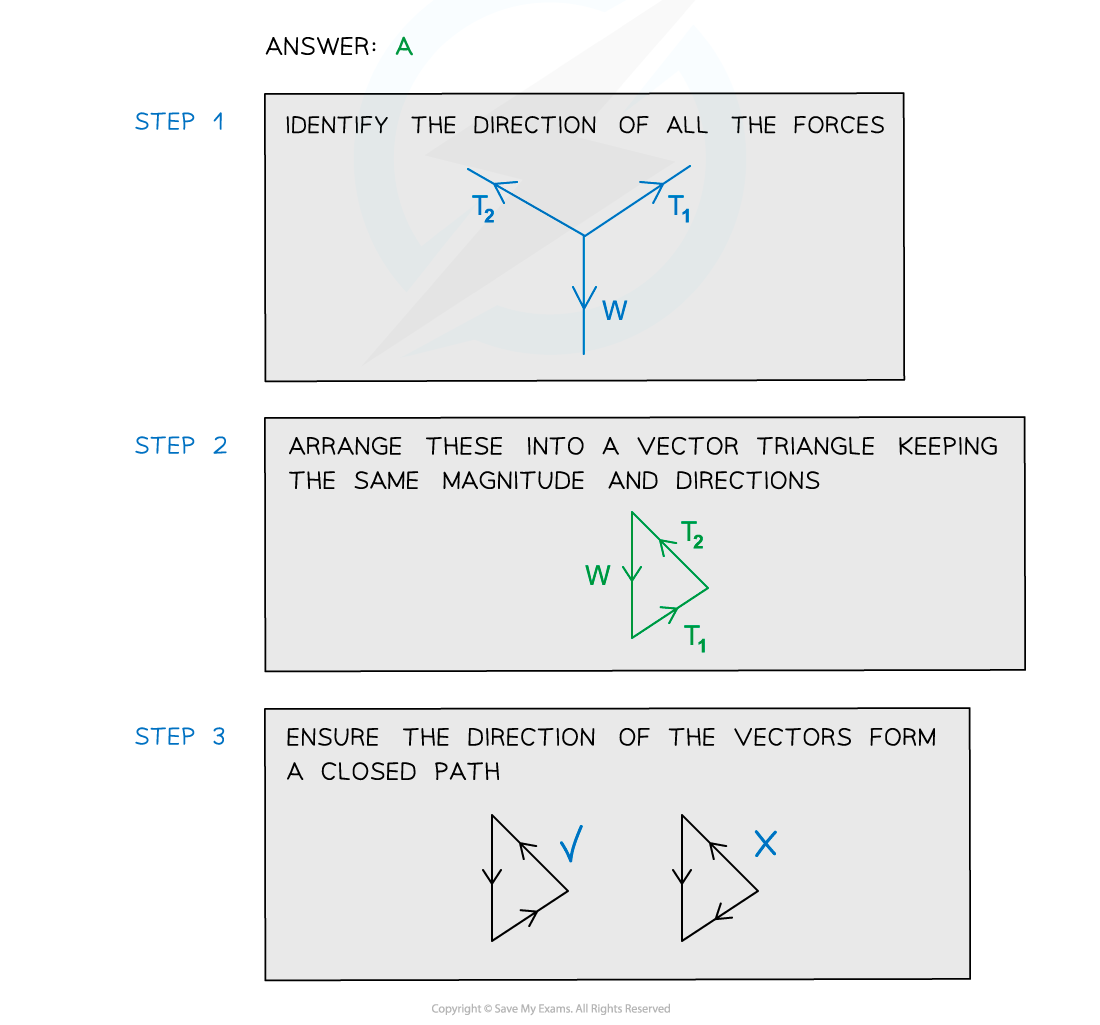
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The diagrams in exam questions about this topic tend to be drawn to scale, so make sure you have a ruler handy!

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
