Displacement, Velocity & Acceleration (OCR A Level Physics) : Revision Note
Displacement, Speed, Velocity & Acceleration
Scalar quantities
Scalar quantities only have a magnitude (size)
Distance: the total length between two points
Speed: the total distance travelled per unit of time
Vector quantities
Vector quantities have both magnitude and direction
Displacement: the distance of an object from a fixed point in a specified direction
Velocity: the rate of change of displacement of an object
Acceleration: the rate of change of velocity of an object
Equations for Velocity & Acceleration
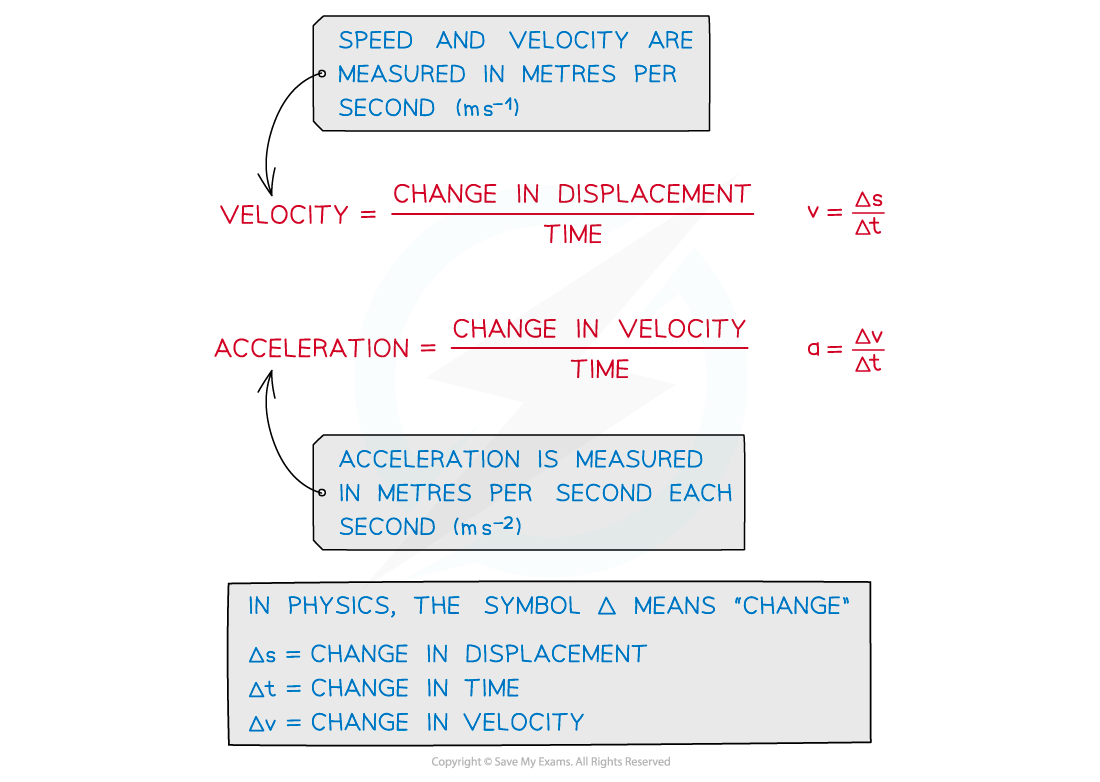
Equations linking displacement, velocity and acceleration
Worked Example
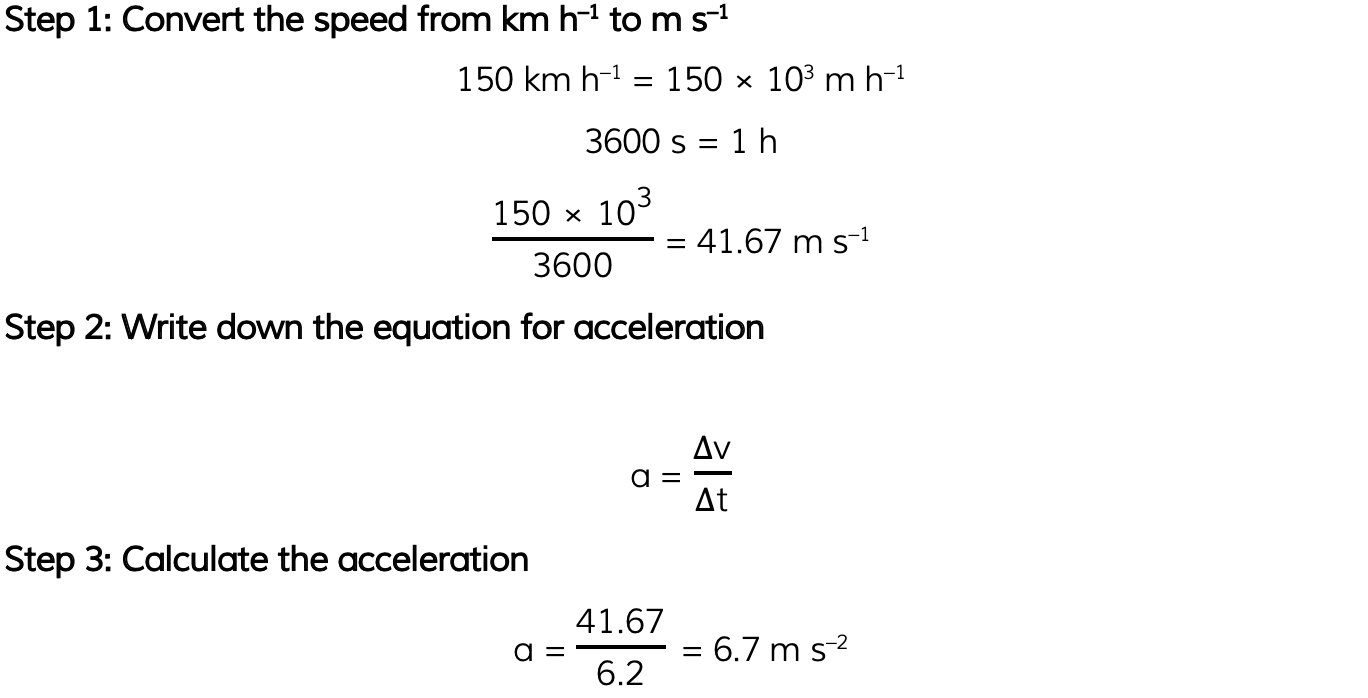
A car accelerates uniformly from rest to a speed of 150 km h–1 in 6.2 s. Calculate the magnitude of the acceleration of the car in m s–2.
Answer:
Instantaneous Speed / Velocity
The instantaneous speed (or velocity) is the speed (or velocity) of an object at any given point in time
This could be for an object moving at a constant velocity or accelerating
An object accelerating is shown by a curved line on a displacement – time graph
An accelerating object will have a changing velocity
To find the instantaneous velocity on a displacement-time graph:
Draw a tangent at the required time
Calculate the gradient of that tangent
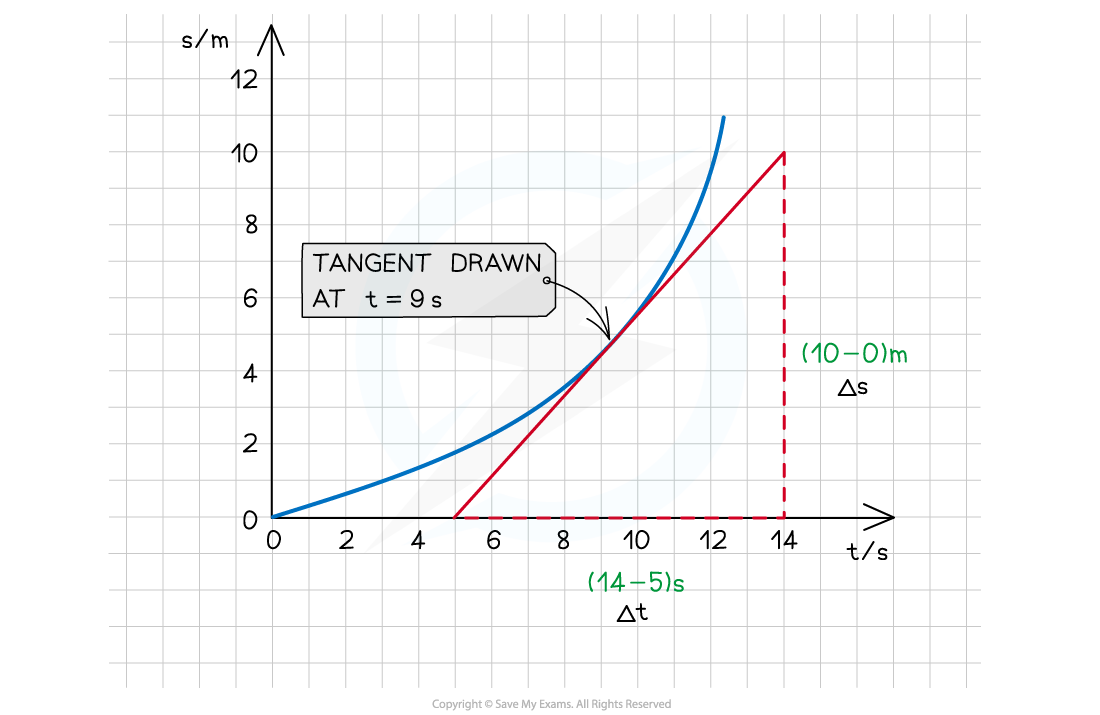
The instantaneous velocity is found by drawing a tangent on the displacement time graph
Average Speed / Velocity
The average speed (or velocity) is the total distance (or displacement) divided by the total time
To find the average velocity on a displacement-time graph, divide the total displacement (on the y-axis) by the total time (on the x-axis)
This method can be used for both a curved or a straight line on a displacement-time graph
Worked Example
A cyclist travels a distance of 20 m at a constant speed then decelerates to a traffic light 5 m ahead. The whole journey takes 3.5 s. Calculate the average speed of the cyclist.
Answer:
Step 1: Write the average speed equation
Average speed = total distance ÷ total time
Step 2: Calculate the total distance
Total distance = 20 + 5 = 25 m
Step 3: Calculate the average speed
Average speed = 25 ÷ 3.5 = 7.1 m s-1

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
