Precision, Accuracy & Experimental Limitations (OCR A Level Physics) : Revision Note
Limitations in Experimental Procedures
Even if the experimental result is close to the true value, there are always potential limitations of experimental methods such as the presence of random errors
Random errors cannot be completely removed but their effect can be reduced by taking as many repeats as possible and using the average of the repeats
There are always opportunities to identify limitations of the procedure, some common examples include:
Parallax error when reading scales
Not using a fiducial marker (eg. when measuring the time period of a pendulum using a stopwatch)
Not repeating measurements to reduce random errors
Not checking for zero errors to reduce systematic errors
The equipment not working properly or not checking beforehand with small tests
Equipment with poor precision and resolution (eg. a ruler over a micrometer)
Difficult to control variables (eg. the temperature of the classroom)
Unwanted heating effects eg. in circuits
Precision, Accuracy & Error Margins
Precision
Precision is how close the measured values are to each other
If a measurement is repeated several times, then they can be described as precise when the values are very similar to, or the same as, each other
The precision of a measurement is reflected in the values recorded
Measurements to a greater number of decimal places are said to be more precise than those to a whole number
Accuracy
Accuracy is how close a measured value is to the true value
The accuracy can be increased by repeating measurements and finding a mean average

The difference between precise and accurate results
Measurements of quantities are made with the aim of finding the true value of that quantity
In reality, it is impossible to obtain the true value of any quantity, there will always be a degree of uncertainty
The uncertainty is an estimate of the difference between a measurement reading and the true value
Random and systematic errors are two types of measurement errors which lead to uncertainty
Random Error
Random errors cause unpredictable fluctuations in an instrument’s readings as a result of uncontrollable factors, such as environmental conditions
This affects the precision of the measurements taken, causing a wider spread of results about the mean value
To reduce random error:
Repeat measurements several times and calculate an average from them
Systematic Error
Systematic errors arise from the use of faulty instruments used or from flaws in the experimental method
This type of error is repeated every time the instrument is used or the method is followed, which affects the accuracy of all readings obtained
To reduce systematic errors:
Instruments should be recalibrated or the technique being used should be corrected or adjusted

Representing precision and accuracy on a graph
Zero Error
This is a type of systematic error which occurs when an instrument gives a reading when the true reading is zero
This introduces a fixed error into readings which must be accounted for when the results are recorded
Margin of Error
Most items of apparatus will have a margin of error that can be used in percentage error calculations
This percentage error will then give an idea of the magnitude of any error and therefore how much of an impact it may have had on the results
If the percentage error is too high, any conclusions drawn may be rejected or further testing may be required by making improvements to the apparatus used or to the experimental procedure in order to reduce the percentage error
Percentage Uncertainty in Apparatus
The uncertainty in a measurement is related to the resolution or smallest scale division of the measuring instrument
When measuring with analogue instruments, the reading must be rounded up or down to the nearest scale division
The uncertainty in the measurement is, therefore, half the smallest scale division
For a protractor:
Angles are measured to the nearest degree
The uncertainty is half a degree, 0.5°
For a ruler:
Lengths are measured to the nearest millimetre
The uncertainty is half a millimetre, 0.5 mm
For a stopwatch:
Time is measured to the nearest 0.01 s
However, reaction time is 0.1 – 0.5 s so a degree of precision of 0.1 – 0.5 s is much more reasonable
In this case, the uncertainty would be 0.05 – 0.25 s
The percentage of uncertainty in any single reading taken using the equipment is found using:
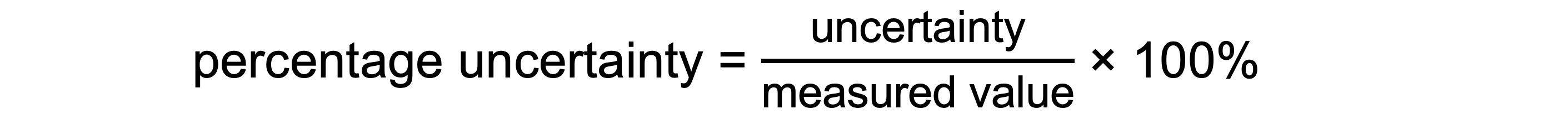
It is important to note that for a particular piece of apparatus, the larger the value measured, the smaller the percentage error
For example, when measuring the length of a piece of wire there will be a greater percentage error in measuring a length of 7.6 cm than in measuring a length of 38.9 cm using the same ruler
Examiner Tips and Tricks
It is very common for students to confuse precision with accuracy - measurements can be precise but not accurate if each measurement reading has the same error. Precision refers to the ability to take multiple readings with an instrument that are close to each other, whereas accuracy is the closeness of those measurements to the true value.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
