A brick of mass 2 kg is resting on the floor as shown in Fig. 1.1.
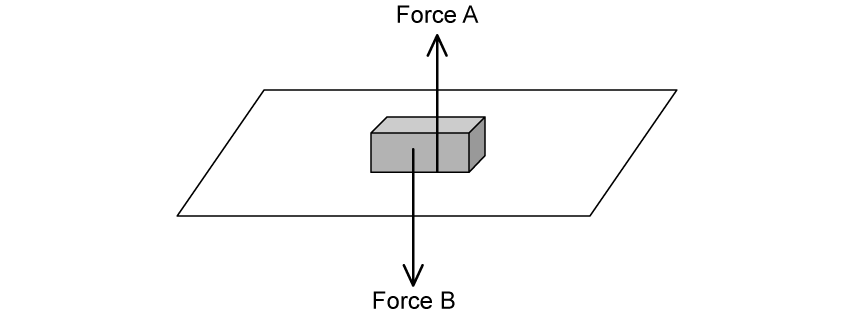
Fig. 1.1
(i) Define equilibrium.
[1]
(ii) State the names of forces A and B.
[1]
(i) State Newton’s first law of motion.
[1]
(ii) Explain how Newton’s first law applies to the brick in Fig. 1.1.
[2]
(i) State Newton’s third law of motion.
[1]
(ii) Explain how Newton’s third law can be applied to one of the forces acting on the brick.
[3]
The surface is raised at one end to form a slope as shown in Fig. 1.2. This causes the brick to accelerate at a constant rate of 0.25 m s−2.
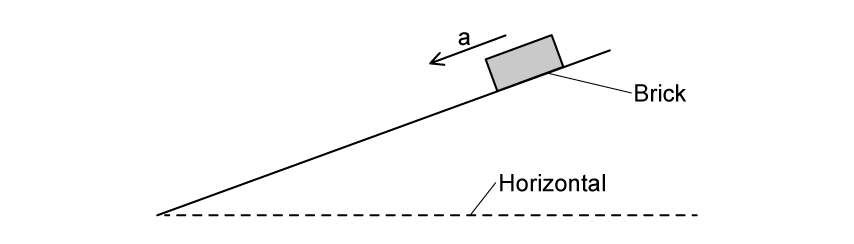
Fig. 1.2
(i) State Newton's second law of motion.
[1]
(ii) Use Newton's second law to determine the magnitude of the resultant force on the brick.
[2]
Did this page help you?















