Radioactive decay is often described as a spontaneous and random process.
State what is meant by
(i) radioactive decay
[2]
(ii) a spontaneous process
[2]
(iii) a random process
[2]
The graph in Fig. 1.1 shows the count rate of a radioactive substance measured by a Geiger-Müller tube.
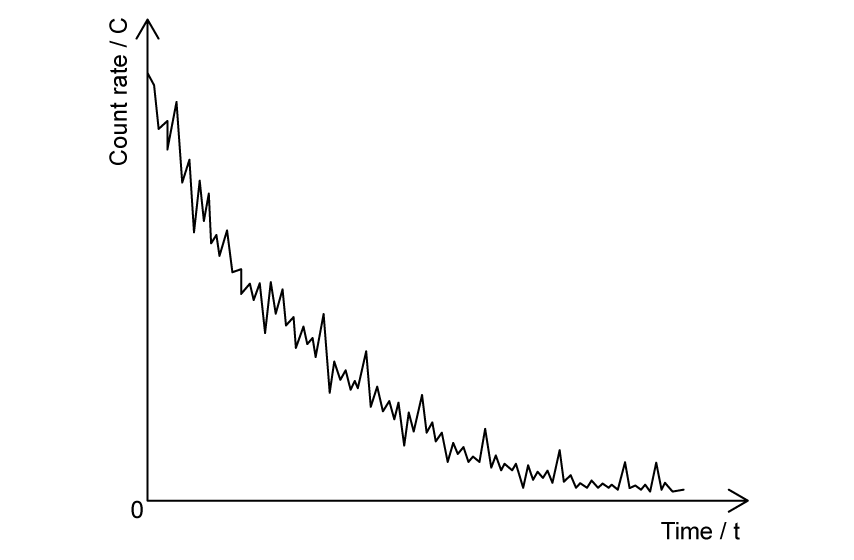
Fig. 1.1
State the feature of Fig. 1.1 which provides evidence for
(i) the random nature of radioactive decay
[1]
(ii) the spontaneous nature of radioactive decay
[1]
The element neptunium has at least 24 isotopes. One of the isotopes is neptunium-231 , which has a half-life of 49 minutes.
(i) State what is meant by isotopes and circle the possible isotopes of neptunium
|
|
[3]
(ii) Define half-life and circle the correct expression for calculating the probability per second of decay of a nucleus of neptunium-231.
|
|
[3]
Fig. 1.2 shows a diagram in which nucleon number A is plotted against proton number Z.
The diagram shows the position of three isotopes of neptunium and their respective decay products.
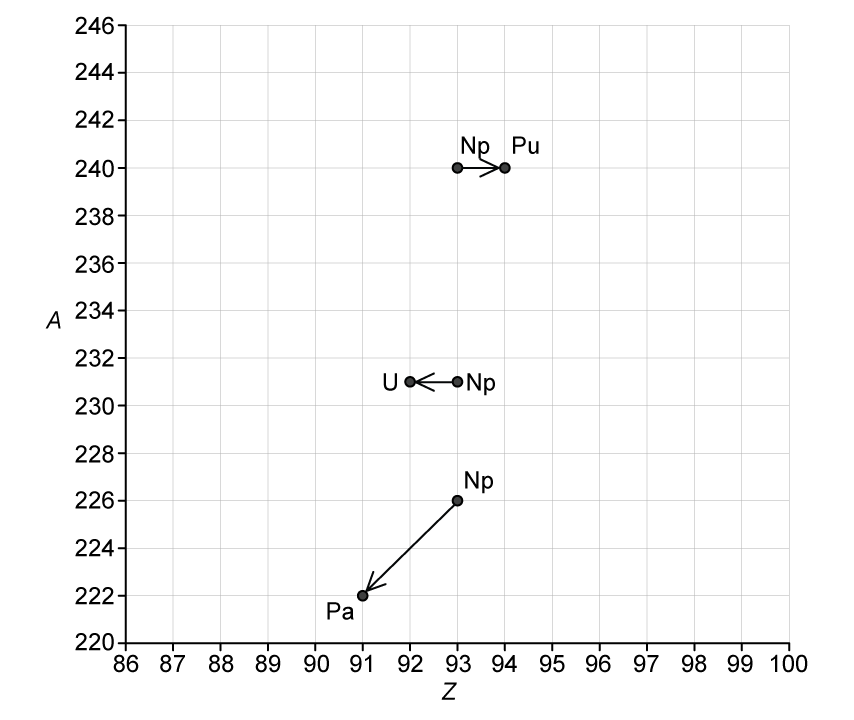
Fig. 1.2
Use Fig. 1.2 to complete the following nuclear decay equations
Did this page help you?





