I-V Characteristics (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Physics) : Revision Note
I–V characteristics
As the potential difference (voltage) across a component is increased, the current also increases (in accordance with Ohm’s law)
The precise relationship between potential difference and current is different for different components and can be shown on an I-V graph:
I-V Characteristics of different components
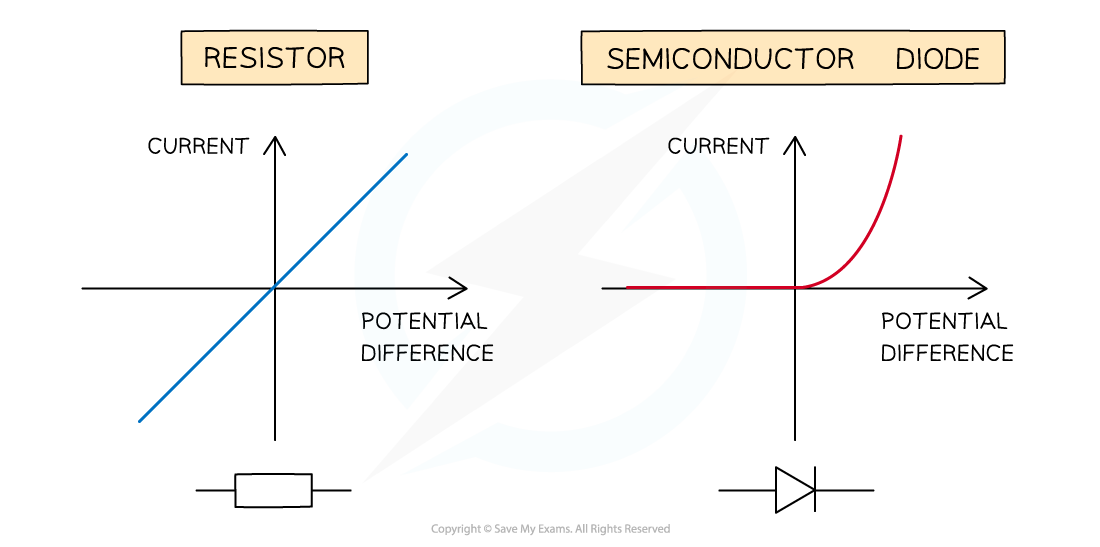
I-V characteristics for metallic conductor (e.g. resistor) and semiconductor diode
The I-V graph for a metallic conductor at constant temperature e.g. a resistor, is very simple:
The current is directly proportional to the potential difference
This is demonstrated by the straight line graph through the origin
The I-V graph for a semiconductor diode is slightly different. A diode is used in a circuit to allow current to flow only in a specific direction:
When the current is in the direction of the arrowhead symbol, this is forward bias. This is shown by the sharp increase in potential difference and current on the right side of the graph
When the diode is switched around, it does not conduct and is called reverse bias. This is shown by a zero reading of current or potential difference on the left side of the graph
Worked Example
The I–V characteristic of two electrical component X and Y are shown.

Which statement is correct?
A. The resistance of X increases as the current increases
B. At 2 V, the resistance of X is half the resistance of Y
C. Y is a semiconductor diode and X is a resistor
D. X is a resistor and Y is a filament lamp
Answer: C
The I-V graph X is linear
This means the graph has a constant gradient. I/V and the resistance is therefore also constant (since gradient = 1/R)
This is the I-V graph for a conductor at constant temperature e.g. a resistor
The I-V graph Y starts with zero gradient and then the gradient increases rapidly
This means it has infinite resistance at the start which then decreases rapidly
This is characters of a device that only has current in one direction e.g a semiconductor diode
Therefore the answer is C
Resistance in a filament lamp
The I-V graph for a filament lamp has a distinctive shape
I-V characteristics for a filament lamp
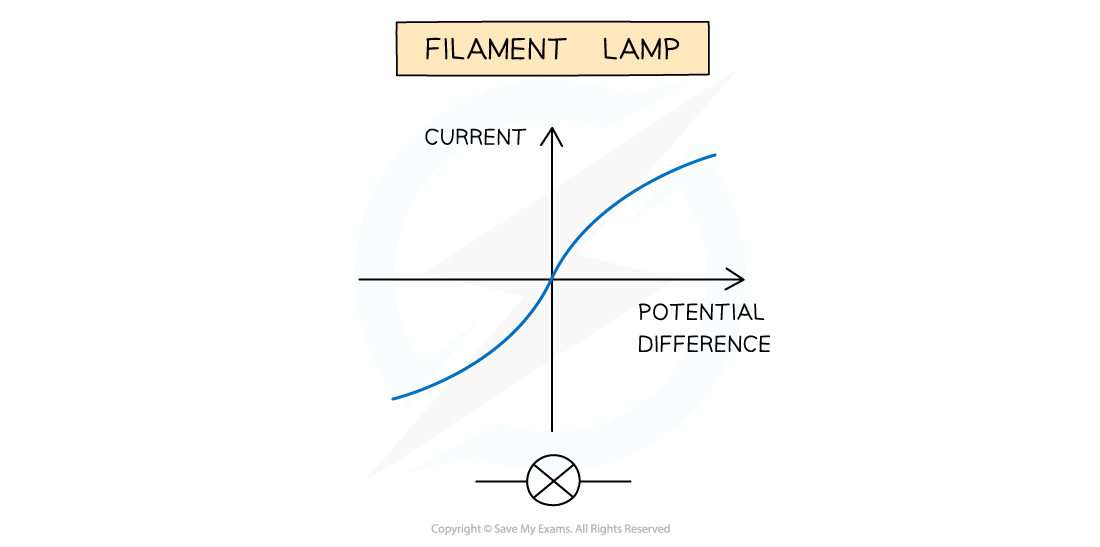
A graph showing the I-V characteristics for a filament lamp.
This is because:
As the current increases, the temperature of the filament in the lamp increases
The higher temperature causes an increase in resistance
Resistance opposes current, causing the current to increase at an increasingly slower rate
Where the graph is a straight line, the resistance is constant
The resistance increases as the graph curves
Resistance and temperature
All solids are made up of vibrating atoms
The higher the temperature, the faster these atoms vibrate
Electric current is the flow of free electrons through a conductor
The electrons collide with the vibrating metal ions that make up the wire
The vibrating ions impedes the flow of electrons (charge)
Therefore, the current decreases
As the temperature increases, the resistance increases
And as the resistance increases, the current decreases

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
