The Principle of Superposition (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9702
The principle of superposition
When two or more waves arrive at the same point and overlap, their amplitudes combine
This is called superposition
The principle of superposition states that:
When two or more waves overlap at a point, the displacement at that point is equal to the sum of the displacements of the individual waves
The superposition of surface water waves shows the effect of this overlap
There are areas of zero displacement, where the water is flat
There are areas of increased displacement, where the water waves are higher
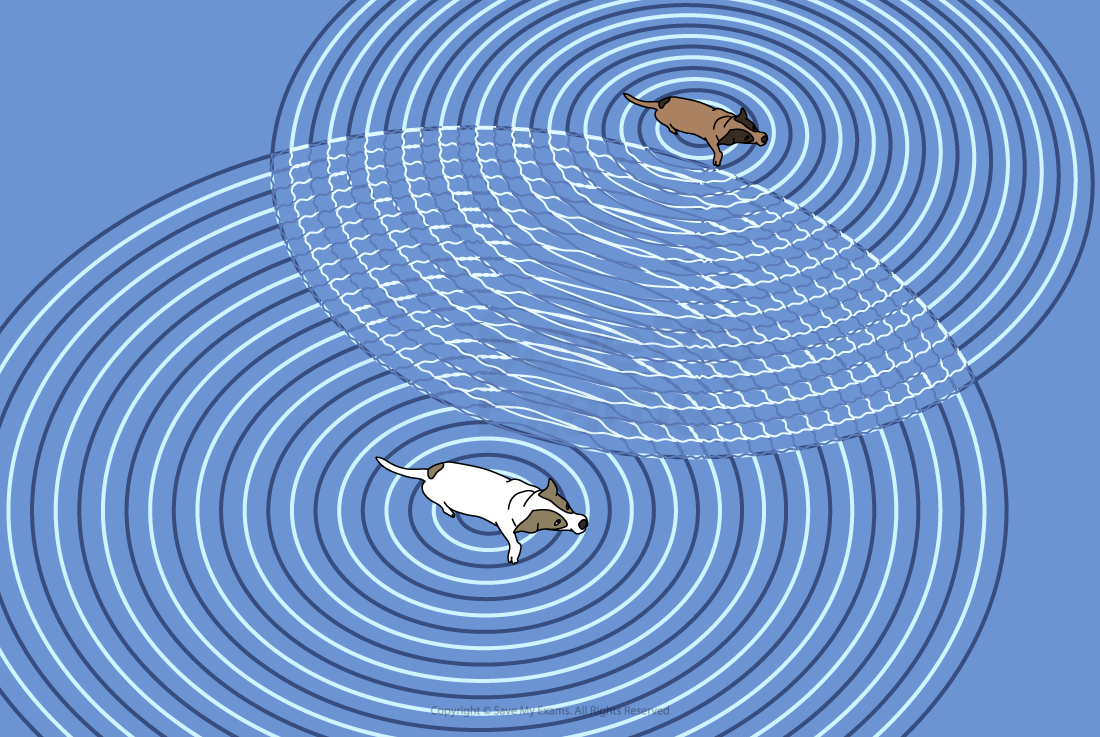
The dogs make waves in the water which superimpose to give areas of both zero and increased displacement.
It is possible to analyse superposition clearly when the waves are drawn on a vertical displacement (amplitude)-displacement graph
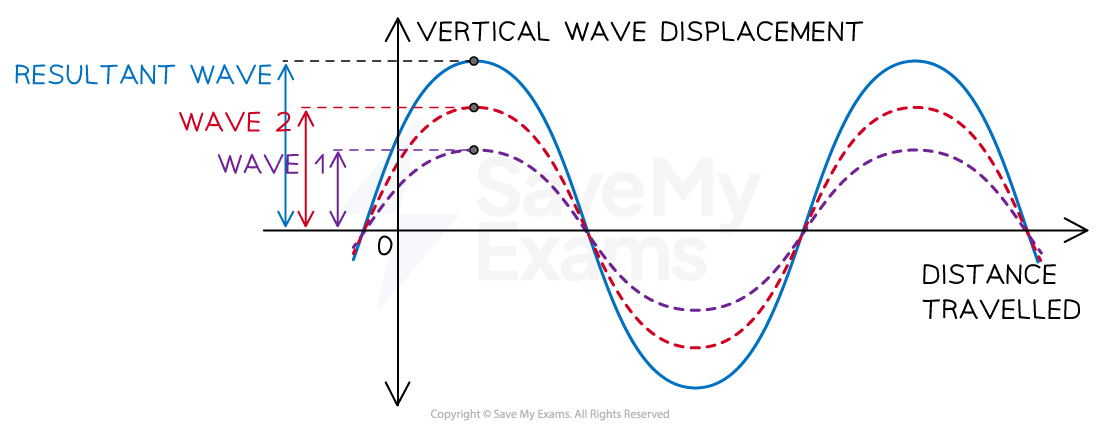
Waves can superimpose so their amplitudes are added together often creating a larger resultant amplitude
Interference is the effect of this overlap
This is explained in the next revision note on Interference & coherence
Individual wave displacements may be positive or negative and are combined in the same way as other vector quantities
It is possible to analyse superposition clearly when the waves are drawn on a displacement-time graph
Superposition can also be demonstrated with two pulses
When the pulses meet, the resultant displacement is also the algebraic sum of the displacement of the individual pulses
After the pulses have interacted, they then carry on as normal
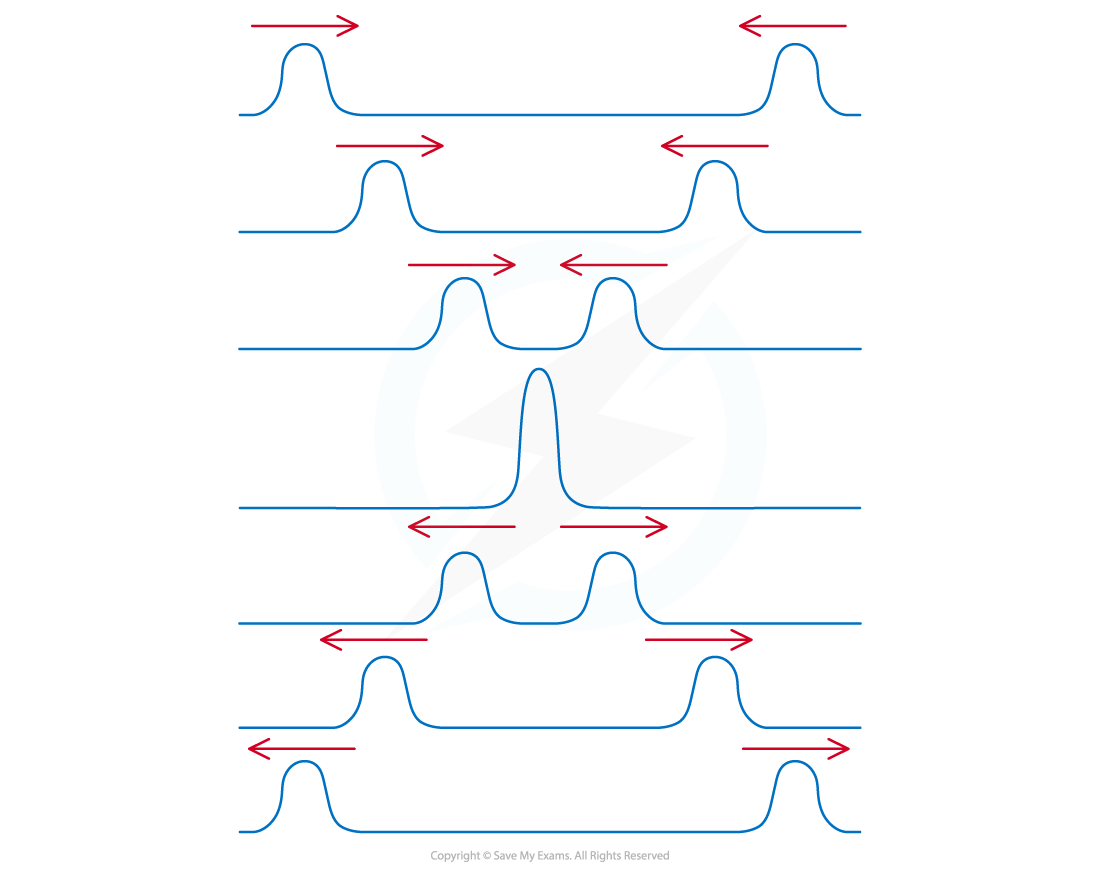
When two pulses overlap their displacements combine to form a resultant displacement
Worked Example
Two overlapping waves of the same types travel in the same direction. The variation with x and y displacement of the wave is shown in the figure below.
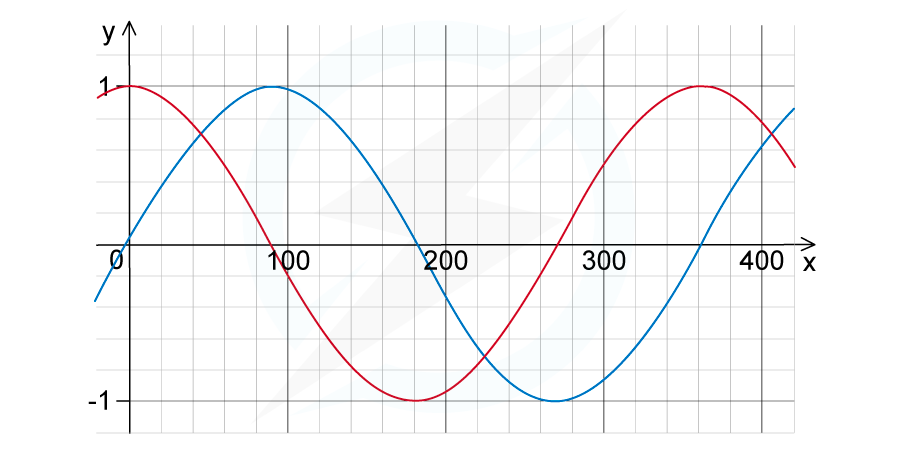
Use the principle of superposition to sketch the resultant wave.
Answer:
The graph of the superposition of both waves is in black:

To plot the correct amplitude at each point, sum the amplitude of both graphs at that point
E.g. at point A, each graph has a value of 0.7. Therefore, the same point with the resultant superposition is 2 × 0.7 = 1.4
Each square on the y-axis represents 0.2
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The best way to draw the superposition of two waves is to find where the superimposed wave has its maximum and minimum amplitudes. It is then a case of joining them up to form the wave. Where the waves intersect determines how much constructive or destructive interference will occur.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?