The Wave Equation (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9702
Derivation of v = f λ
Using the definitions of speed, frequency and wavelength, the wave equation v = fλ can be derived
This is an important relationship between three key properties of a wave
The derivation for this is shown below
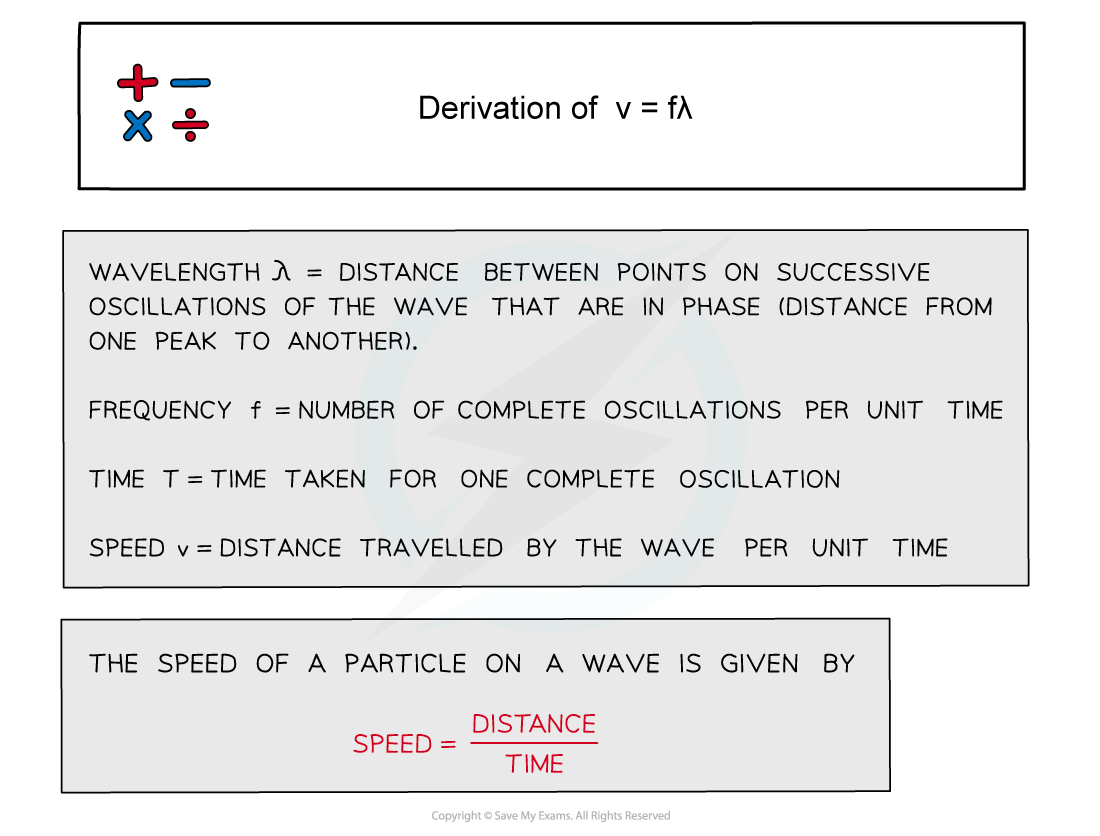

Derivation of v = fλ
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You will be expected to remember all the steps for this derivation (but do not need to write the full definition for each variable). If you are unsure as to where speed = distance/time comes from, make sure to revisit chapter “2. Kinematics”.
The wave equation
The wave equation links the speed, frequency and wavelength of a wave
This is relevant for both transverse and longitudinal waves
Where
v is wave speed in m s−1
f is frequency in Hz
λ is wavelength in m
The wave equation tells us that for a wave at constant speed:
As the wavelength increases, the frequency decreases
As the wavelength decreases, the frequency increases
So wavelength and frequency are inversely proportional to each other
Wavelength and frequency are inversely proportional
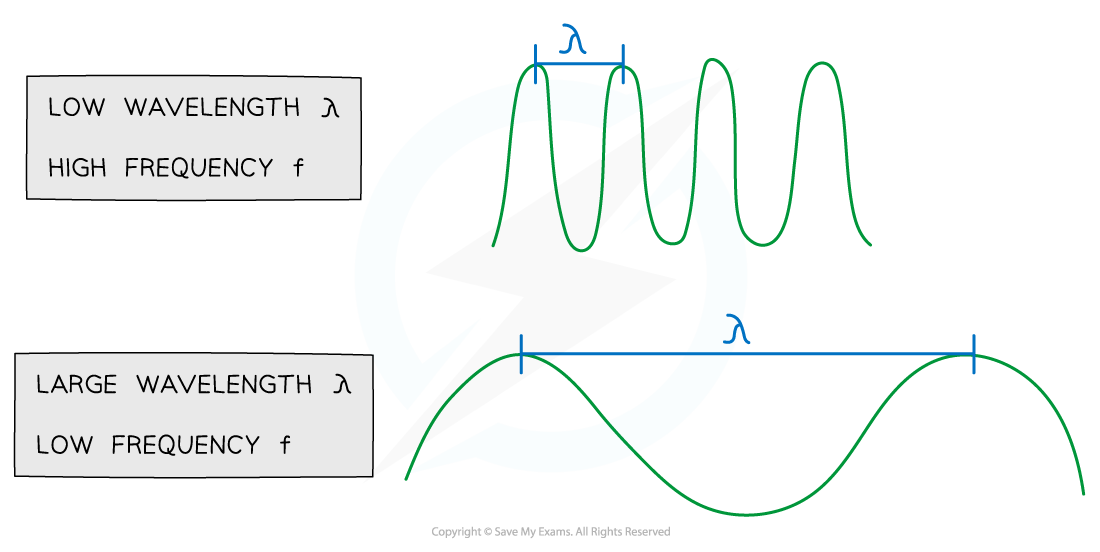
The relationship between frequency and wavelength of a wave
Worked Example
The wave in the diagram below has a speed of 340 m s–1.
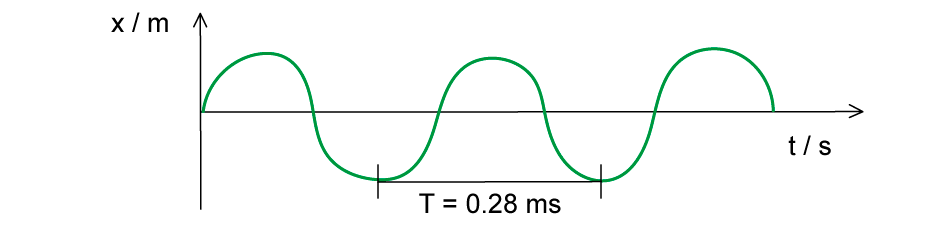
What is the wavelength of the wave?
Answer:
Step 1: Determine the frequency of the wave:
Convert the period T into seconds and substitute into the frequency equation
Step 2: Determine wavelength:
Rearrange the wavelength equation and substitute speed and frequency
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You may also see the wave equation be written as c = fλ where c is the wave speed. However, c is often used to represent the speed of light (3 x 108 ms-1). Only electromagnetic waves travel at this speed, therefore it’s best practice to use v for any speed that isn’t the speed of light instead.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
