Efficiency (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9702
Efficiency of a system
The efficiency of a system is the ratio of the useful energy output from the system to the total energy input
If a system has high efficiency, this means most of the energy transferred is useful
If a system has low efficiency, this means most of the energy transferred is wasted
Multiplying this ratio by 100 gives the efficiency as a percentage
The efficiency is calculated using the equation:
Efficiency can also be written in terms of power (the energy transferred per second):
Worked Example
An electric motor has an input power, Pin, useful output power, Pout, power lost Plost, and an efficiency η.
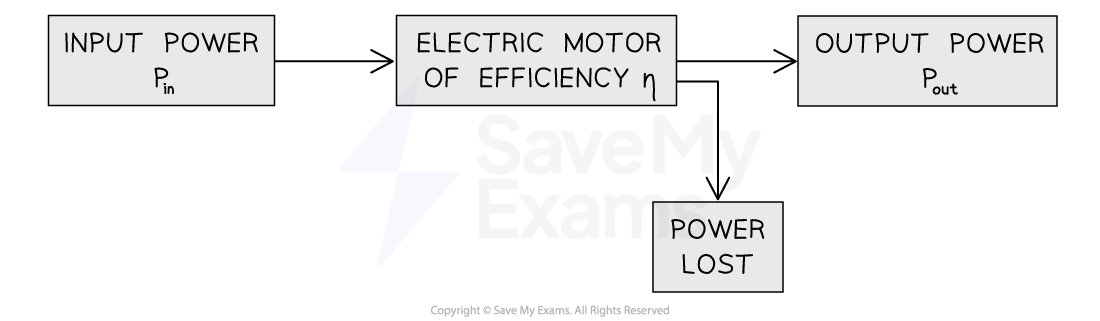
What is the output power of the motor?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Answer: B
Step 1: State the efficiency equation
Step 2: Substitute the terms given in the question
Step 3: Manipulate the equation
Multiply by Pout + Plost on both sides
Expand the brackets
Minus Pout from both sides
It is helpful to first minus ηPlost
Factor out Pout
Divide by η − 1
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Efficiency can be in a ratio or percentage format. If the question asks for an efficiency as a ratio, give your answer as a fraction or decimal. If the answer is required as a percentage, remember to multiply the ratio by 100 to convert it, e.g. Ratio = 0.25, Percentage = 0.25 × 100 = 25 %
Solving problems involving efficiency
Efficiency calculations are often part of a larger multi-step problem
Since efficiency deals with energy and power, questions will often involve energy or power calculations
Worked Example
The diagram shows a pump called a hydraulic ram.
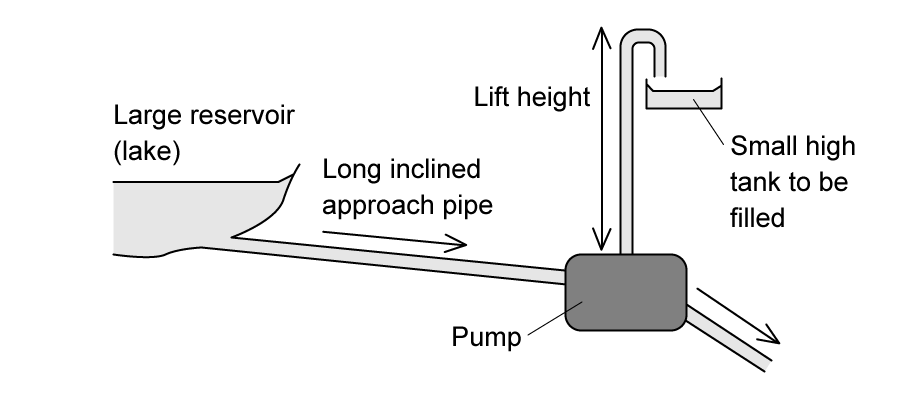
In one such pump, the long approach pipe holds 700 kg of water. A valve shuts when the speed of this water reaches 3.5 m s-1. The kinetic energy of this water is used to lift a small quantity of water by a height of 12m. The efficiency of the pump is 20%.
Which mass of water could be lifted 12 m?
A. 6.2 kg
B. 4.6 kg
C. 7.3 kg
D. 0.24 kg
Answer: C
Step 1: List the known quantities
Mass of water in approach pipe = 700 kg
Speed of water in approach pipe, v = 3.5 m s-1
Height of lifted water, h = 12 m
Step 2: Consider the energy transfer taking place
Energy is transferred from the kinetic store of the water to its gravitational potential store
Step 3: Consider the efficiency of the energy transfer
The transfer is 20% efficient
Therefore, 20% of the kinetic input energy is output as gravitational potential energy
Step 4: Calculate the mass of water lifted water
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Equations for kinetic and potential energies are important for these types of questions. Also, familiarise yourself with the different equations for power depending on what quantities are given.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?