Pressure (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9702
Pressure
Pressure tells us how concentrated a force is
Pressure is defined as:
The force per unit area
Pressure is calculated using the following equation:
Where:
p = pressure in pascals (Pa)
1 Pa = 1 N m-2
F = force in newtons (N)
A = area in metres squared (m2)
Pressure, unlike force, is a scalar
Therefore pressure does not have a specific direction
If a force is spread over a large area it will result in a small pressure
If a force is spread over a small area it will result in a large pressure
Pressure of different styles of shoes
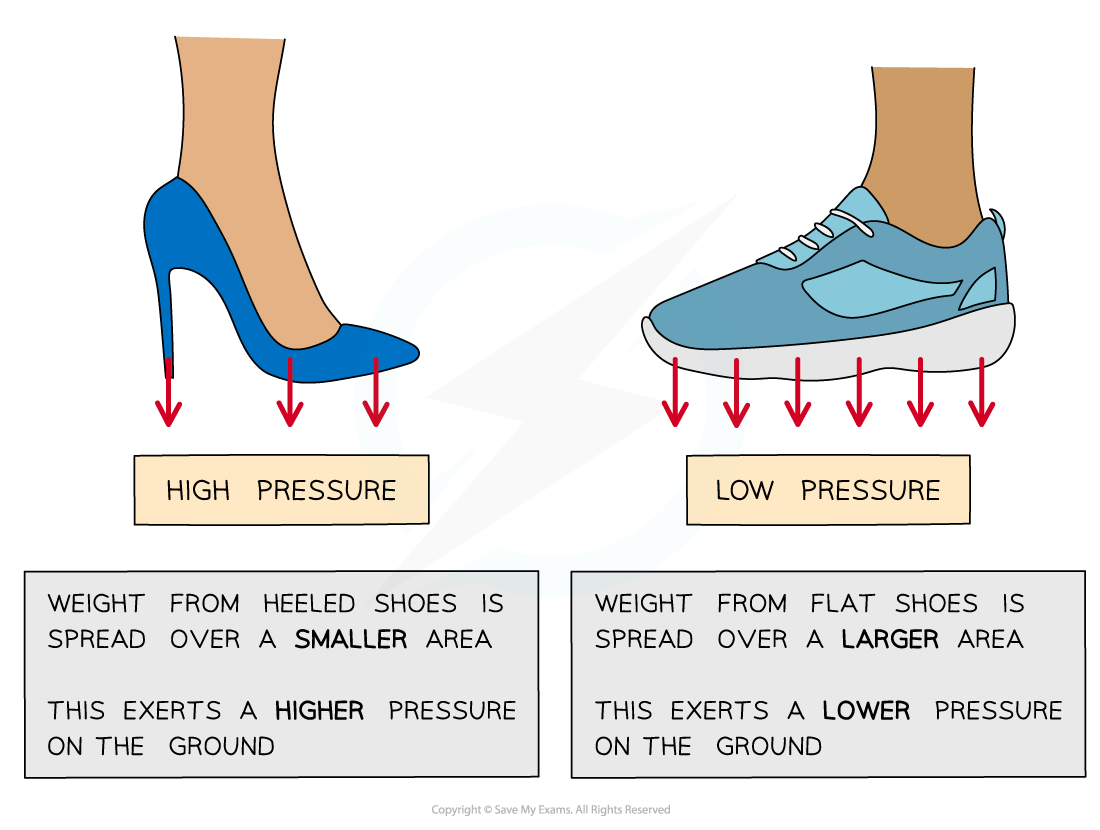
High-heeled shoes exert a greater pressure than flat shoes because the same force (weight) is spread over a smaller area
Worked Example
A cylinder is placed on a horizontal surface as shown below.

The mass of the cylinder is 4.7 kg and the diameter is 8.4 cm.
Calculate the pressure produced by the cylinder on the horizontal surface.
Answer:
Step 1: List the known quantities and convert to SI units
Mass, m = 4.7 kg
Diameter of cylinder, d = 0.084 m
Step 2: State the pressure equation
Step 3: Calculate the force exerted by the cylinder
The force is the weight acting on the cylinder
Acceleration of free fall, g = 9.81 m s-2
Step 4: Calculate the area
Only the base of the cylinder is in contact with the surface
Step 5: Substitute the known values into the pressure equation to calculate
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The area referred to is the ‘cross-sectional’ area of a 3D object. This is the area of the base that the force is applied on. For a cylinder, this will be a circle.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?