Linear Momentum (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9702
Linear momentum
Linear momentum, p, is defined as the product of mass and velocity
Where:
p = linear momentum in kilogram metres per second (kg m s-1)
m = mass in kilograms (kg)
v = velocity in metres per second (m s-1)
Momentum is a vector quantity; it has both magnitude and direction
It can have a positive or negative value which describes its direction in a one dimensional plane
If an object travelling to the right has positive momentum, an object travelling to the left (in the opposite direction) has a negative momentum
Momentum of a ball hitting a wall
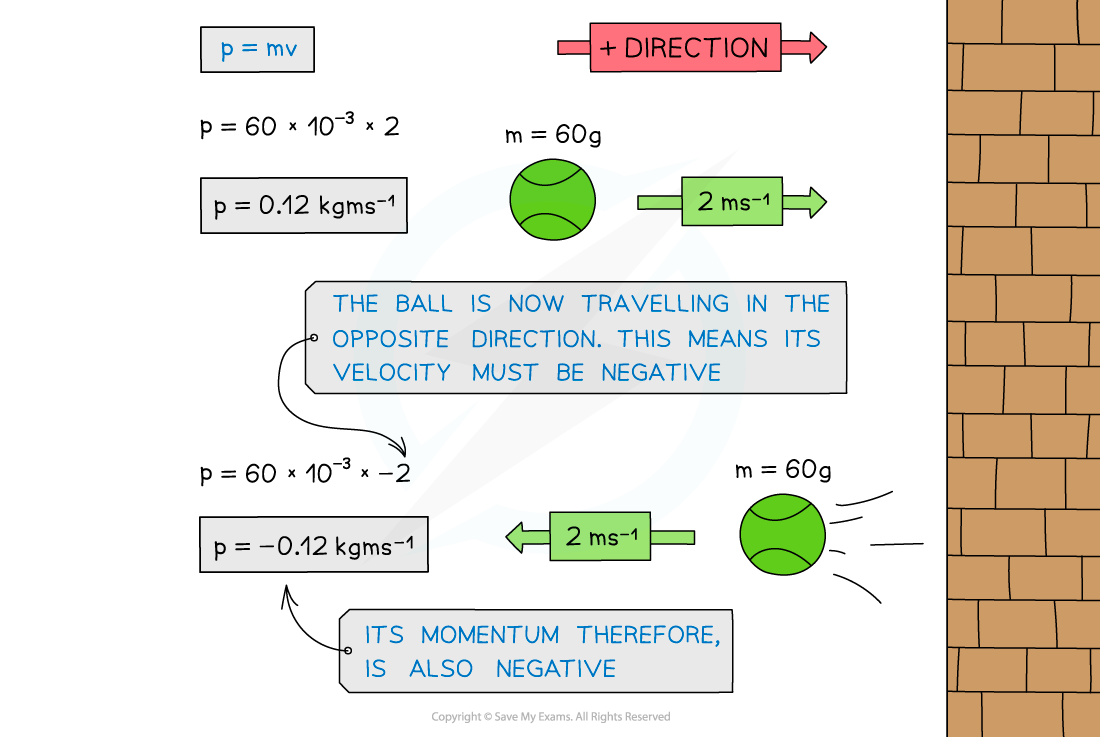
When the ball is travelling in the opposite direction, its velocity is negative. Since momentum = mass × velocity, its momentum is also negative
Worked Example
A tennis ball of mass, m = 60 g travels at a velocity, v = 75 m s-1. A brick of mass, m = 3 kg travels at a velocity, v = 1.5 m s-1.
Determine which object has the most momentum.

Answer:
Step 1: List the known quantities and convert to SI units
Mass of tennis ball,
Velocity of tennis ball,
Mass of brick,
Velocity of brick,
Step 2: Determine the momentum of the tennis ball
Step 3: Determine the momentum of the brick
Step 4: State which object has the most momentum
Both objects have the same momentum
Even though the brick has a greater mass, it has a much lower velocity than the tennis ball
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember to convert the values given into SI units. It is good practice to do this before the calculation.
If the mass is given in grams, convert to kg by dividing the value by 1000
If the velocity is given in km s−1, convert to m s−1 by multiplying the value by 1000
Like with Force and Acceleration, the direction you consider positive is your choice, as long you are consistent throughout the calculation.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?