Hubble's Law & the Big Bang Theory (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9702
Hubble's law & the Big Bang theory
Edwin Hubble investigated the light spectra emitted from a large number of galaxies
He used redshift data to determine the recession velocities of these galaxies, and standard candles to determine the distances
From these measurements, he formulated a relationship, now known as Hubble’s law, which states:
The recession speed of galaxies moving away from Earth is proportional to their distance from the Earth
This can be calculated using:
Where:
v = the galaxy's recessional velocity (m s-1)
d = distance between the galaxy and Earth (m)
H0 = Hubble's constant, or the rate of expansion of the universe (s-1)
This equation tells us:
The further away a galaxy is, the faster its recession velocity
The gradient of a graph of recession velocity against distance is equal to the Hubble constant
Hubble's law graph
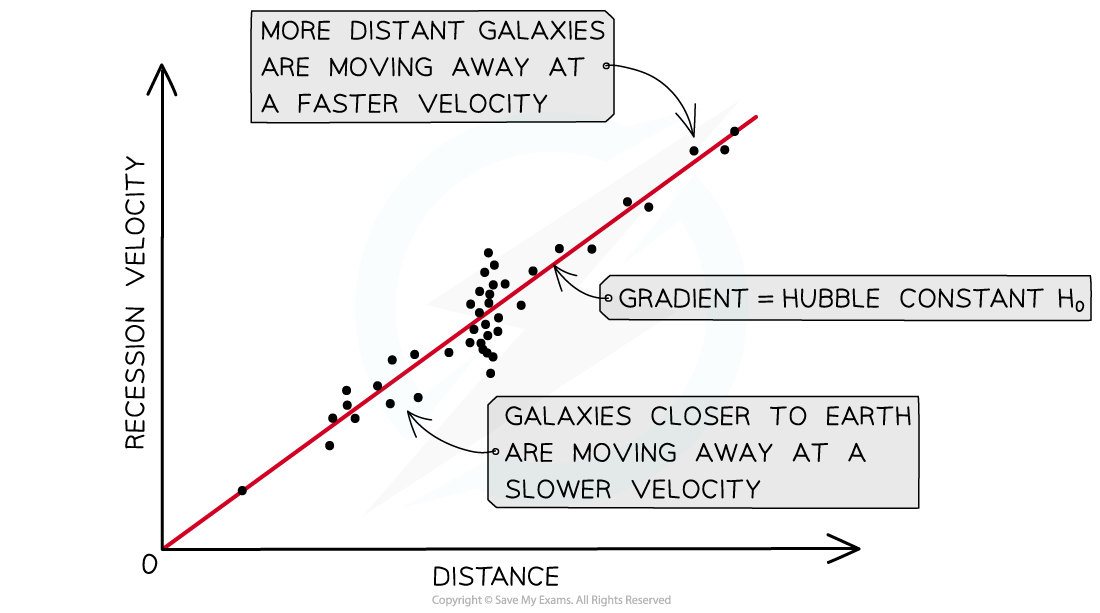
A key aspect of Hubble’s law is that the furthest galaxies appear to move away the fastest
Age of the Universe
If the galaxies are moving away from each other, then they must’ve started from the same point at some time in the past
If this is true, the universe likely began in an extremely hot, dense singular point which subsequently began to expand very quickly
This idea is known as the Big Bang Theory
The redshift of galaxies and the expansion of the universe are now some of the most prominent pieces of evidence to suggest this theory is true
The data from Hubble’s law can be extrapolated back to the point that the universe started expanding i.e. the beginning of the Universe
Therefore, the age of the universe T0 is equal to:
Current estimates of the age of the universe range from 13 – 14 billion years
There is still some discussion about the exact age of the universe, therefore, obtaining accurate measurements for the Hubble constant is a top priority for cosmologists
Expansion of the Universe

Tracing the expansion of the universe back to the beginning of time leads to the idea the universe began with a “big bang”
Worked Example
A galaxy is found to be moving away with a speed of 2.1 × 107 m s-1. The galaxy is at a distance of 9.5 × 1024 m from Earth.
Assuming the speed has remained constant, what is the age of the universe in years?
Answer:
Step 1: Write down Hubble’s Law
Step 2: Rearrange for the Hubble constant H0, and calculate
Step 3: Write the equation for the age of the universe T0, and calculate
Step 4: Convert from seconds into years
Therefore, the age of the universe is estimated to be about 14.3 billion years

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?