Specific Acoustic Impedance (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9702
Written by: Ashika
Updated on
Specific acoustic impedance
The acoustic impedance, Z, of a medium is defined as:
The product of the speed of the ultrasound in the medium and the density of the medium
This quantity describes how much resistance an ultrasound beam encounters as it passes through a tissue
Acoustic impedance can be calculated using the equation:
Where:
Z = acoustic impedance (kg m-2 s-1)
ρ = the density of the material (kg m-3)
c = the speed of sound in the material (m s-1)
This equation tells us:
The higher the density of a tissue, the greater the acoustic impedance
The faster the ultrasound travels through the material, the greater the acoustic impedance also
This is because sound travels faster in denser materials
Sound is fastest in solids and slowest in gases
This is because the closer the particles in the material, the faster the vibrations can move through the material
At the boundary between media of different acoustic impedances, some of the wave energy is reflected and some is transmitted
The greater the difference in acoustic impedance between the two media, the greater the reflection and the smaller the transmission
Two materials with the same acoustic impedance would give no reflection
Two materials with a large difference in values would give much larger reflections
Air has an acoustic impedance of Zair = 400 kg m-2 s-1
Skin has an acoustic impedance of Zskin = 1.7 × 106 kg m-2 s-1
The large difference means ultrasound would be significantly reflected, hence a coupling gel is necessary
The coupling gel used has a similar Z value to the skin, meaning that very little ultrasound is reflected
Light travelling through two materials with different acoustic impedance
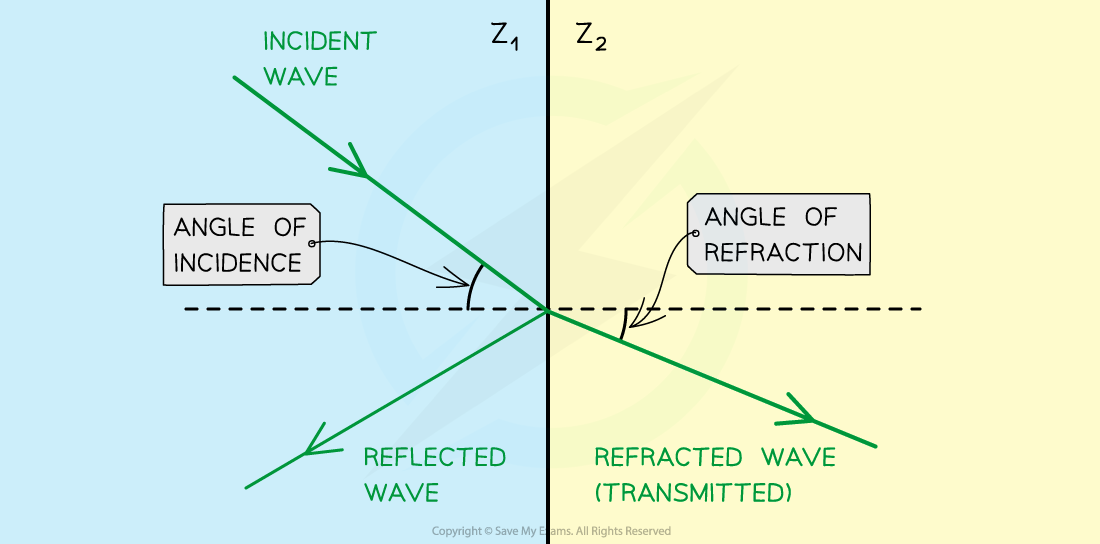
Refraction and reflection of ultrasound waves at a boundary between two materials with different acoustic impedances (in this case, Z1 < Z2 )
Worked Example
The table shows the speed of sound acoustic impedance in four different materials.
medium | speed of ultrasound / m s–1 | acoustic impedance / kg m–2 s–1 |
air | 330 | 4.3 × 102 |
gel | 1500 | 1.5 × 106 |
soft tisuse | 1600 | 1.6 × 106 |
bone | 4100 | 7.0 × 106 |
Use this information to calculate the value for the density of bone.
Answer:
Step 1: Write down known quantities
Acoustic impedance of bone, Z = 7.0 × 106 kg m-2 s-1
Speed of ultrasound in bone, c = 4100 m s-1
Step 2: Write out the equation for acoustic impedance
Step 3: Rearrange for density and calculate
Examiner Tips and Tricks
A common mistake is to confuse the c in the acoustic impedance equation for the speed of light - don’t do this!

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
