Capacitors in Series & Parallel (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9702
Capacitors in series & parallel
The combined capacitance of capacitors in a circuit depends on whether they are connected in series or parallel
Capacitors in series
Consider two parallel plate capacitors C1 and C2 connected in series, with a potential difference (p.d) V across them
Potential difference of capacitors in series
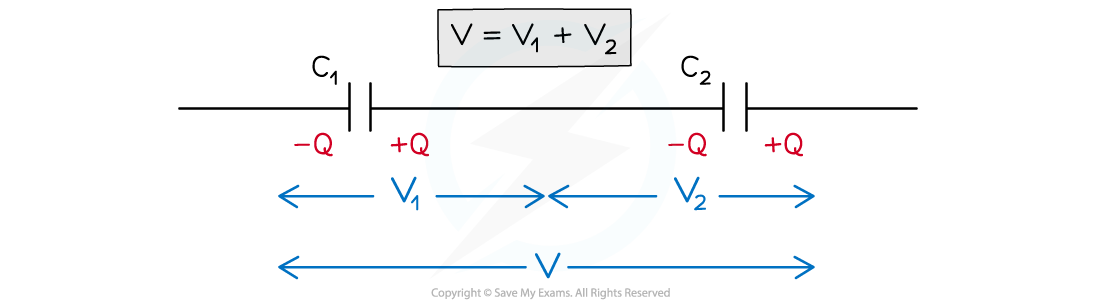
Capacitors connected in series have different p.d across them but have the same charge
In a series circuit, p.d. is shared between all the components in the circuit
Therefore, if the capacitors store the same charge on their plates but have different p.d.s, the p.d across C1 is V1 and across C2 is V2
The total potential difference V is the sum of V1 and V2
V = V1 + V2
Rearranging the capacitance equation for the p.d. V means V1 and V2 can be written as:
and
Where the total p.d. V is defined by the total capacitance
Substituting these into the equation V = V1 + V2 equals:
Since the current is the same through all components in a series circuit, the charge Q is the same through each capacitor and cancels out
Therefore, the equation for the combined capacitance of capacitors in series is:
Capacitors in parallel
Consider two parallel plate capacitors C1 and C2 connected in parallel, each with p.d, V
Potential difference of capacitors in parallel
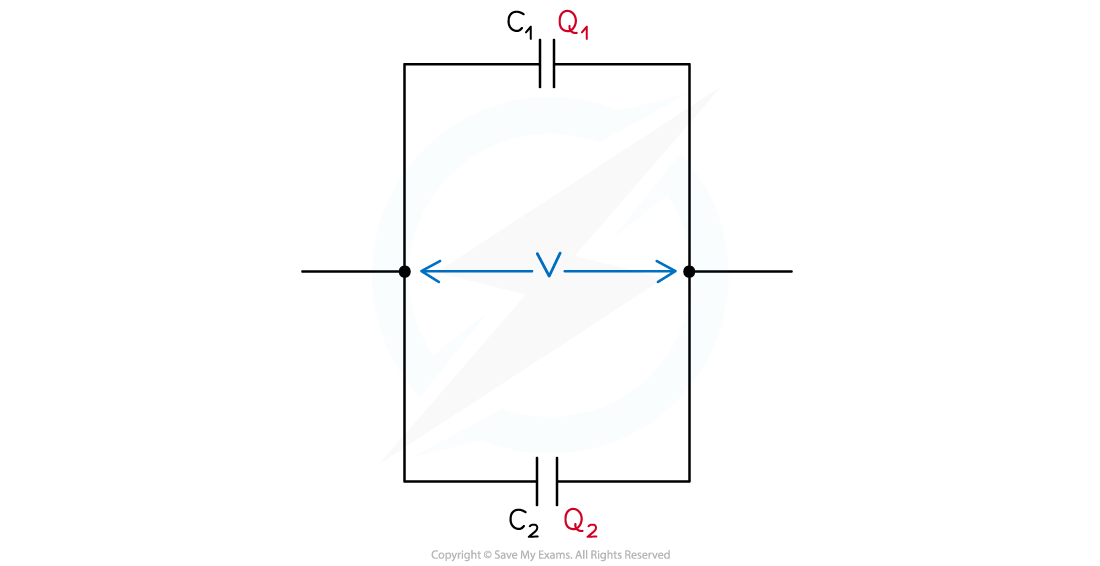
Capacitors connected in parallel have the same p.d across them, but different charge
Since the current is split across each junction in a parallel circuit, the charge stored on each capacitor is different
Therefore, the charge on capacitor C1 is Q1 and on C2 is Q2
The total charge Q is the sum of Q1 and Q2
Q = Q1 + Q2
Rearranging the capacitance equation for the charge Q means Q1 and Q2 can be written as:
Q1 = C1V and Q2 = C2V
Where the total charge Q is defined by the total capacitance:
Q = CtotalV
Substituting these into the Q = Q1 + Q2 equals:
CtotalV = C1V + C2V = (C1 + C2) V
Since the p.d is the same across all components in each branch of a parallel circuit, the p.d V cancels out
Therefore, the equation for the combined capacitance of capacitors in parallel is:
Ctotal = C1 + C2 + C3 ...
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Make sure you learn the equation for the combined capacitance of capacitors in both series and parallel circuits. Both the combined capacitance equations look similar to the equations for combined resistance in series and parallel circuits. However, take note that they are the opposite way around to each other!

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?