Capacitance (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9702
Defining capacitance
Capacitors are electrical devices used to store energy
In electronic circuits, they are commonly used as a backup store of energy in case of power failure
The circuit symbol for a parallel plate capacitor is two parallel lines
Capacitor circuit symbol

The circuit symbol for a capacitor consists of two parallel lines perpendicular to the wires on either side
Capacitors possess capacitance, which is defined as:
The charge stored per unit potential
The greater the capacitance, the greater the charge stored on the capacitor
Capacitors come in different forms, such as:
isolated spherical conductors
parallel plates
Isolated spherical conductors
An isolated spherical conductor can store charge on its surface, which means it can act as a capacitor
When the conducting sphere is connected to a high-voltage supply:
electrons move on to, or off of, the surface of the sphere
the remaining charges are of the same type, so they repel
the surface is conducting, allowing them to move and become evenly distributed
As the potential difference of the supply increases, the charge on the conductor also increases
The capacitance of the sphere is equal to the ratio of the charge to the potential
Capacitance of an isolated spherical conductor
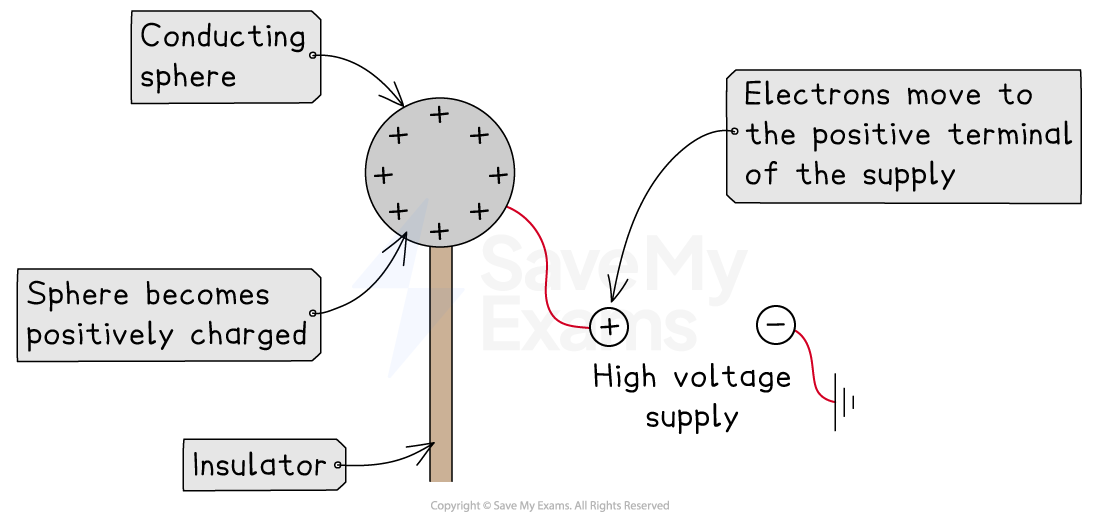
Conducting spheres act like capacitors due to their ability to store charge on their surfaces
Parallel plate capacitors
A parallel plate capacitor is made up of two conducting metal plates connected to a voltage supply
The negative terminal of the voltage supply pushes electrons onto one plate, making it negatively charged
The electrons are repelled from the opposite plate, making it positively charged
There is a dielectric between the plates which ensures charge does not flow freely between the plates
Capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor
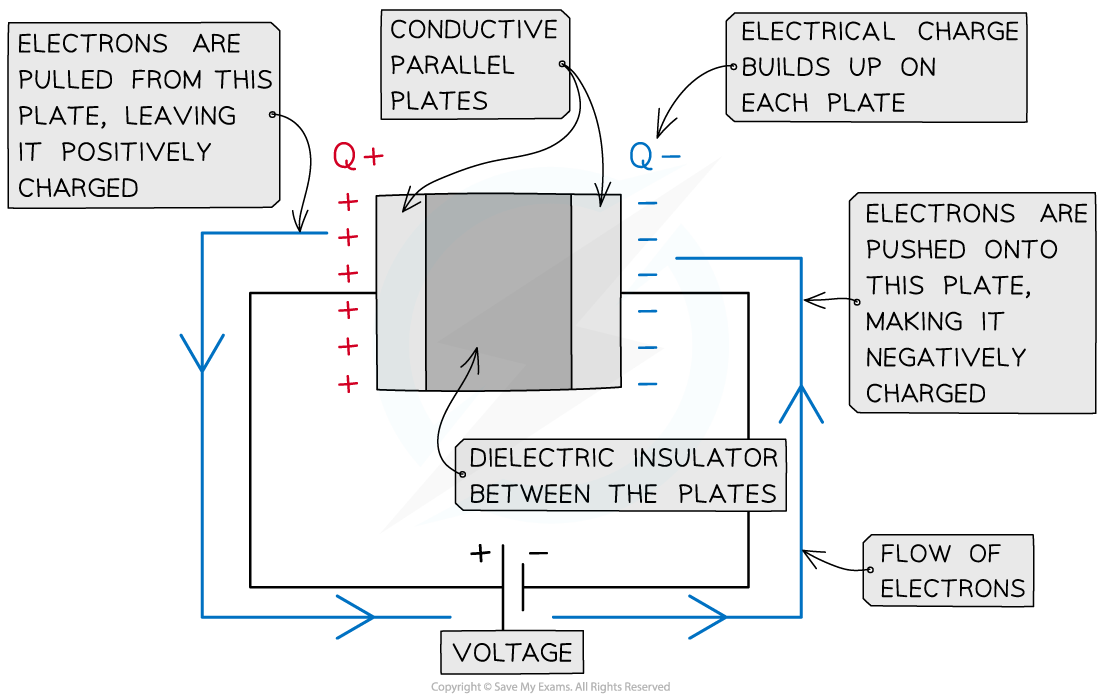
A parallel plate capacitor is made up of two conductive plates with opposite charges building up on each plate
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The ‘charge stored’ by a capacitor refers to the magnitude of the charge stored on each plate in a parallel plate capacitor or on the surface of a spherical conductor. The capacitor itself does not store charge.
Calculating capacitance
The capacitance of a capacitor is defined by the equation:
Where:
C = capacitance (F)
Q = charge (C)
V = potential difference (V)
The unit of capacitance is the farad (F), where one farad is equivalent to one coulomb per volt
In practice, 1 F, or 1 C V–1, is a very large unit
As a result, capacitance values are often quoted in microfarads (μF), nanofarads (nF) or picofarads (pF)
A typical capacitor
A capacitor of capacitance 47 μF might typically be used in a simple circuit
For a parallel plate conductor, Q is the charge on the plates and V is the potential difference across the capacitor
Note: The charge Q is not the charge of the capacitor itself, it is the charge stored on the plates
This capacitance equation shows that an object’s capacitance is the ratio of the charge on an object to its potential
Capacitance of a spherical conductor
The capacitance of an isolated spherical conductor is equal to the charge per unit potential at the surface of the sphere
This is because the charge on the surface of a spherical conductor can be considered as a point charge at its centre
The potential V of an isolated point charge is given by:
Where:
R = radius of the sphere (m)
ε0 = permittivity of free space
Combining these equations gives an expression for the capacitance of an isolated spherical conductor:
C = 4πε0R
Note: The charge Q is not the charge of the capacitor itself, it is the charge stored on the surface of the spherical conductor
Worked Example
A parallel plate capacitor has a capacitance of 1 nF and is connected to a voltage supply of 0.3 kV.
Calculate the charge on the plates.
Answer:
Step 1: Write down the known quantities
Capacitance, C = 1 nF = 1 × 10–9 F
Potential difference, V = 0.3 kV = 0.3 × 103 V
Step 2: Write out the equation for capacitance
Step 3: Rearrange for charge Q
Q = CV
Step 4: Substitute in values
Q = (1 × 10–9) × (0.3 × 103) = 3 × 10–7 C = 300 nC
Worked Example
Lightning can be simulated in a laboratory using an isolated metal sphere to investigate electrical discharge.
A spherical conductor with a radius of 75 cm is charged to a potential of 1.5 MV.
Calculate the capacitance of the sphere, in pF.
Answer:
Step 1: List the known quantities
Radius of sphere, R = 75 cm = 75 × 10−2 m
Permittivity of free space, ε0 = 8.85 × 10−12 F m−1
Step 2: Write out the equation for the capacitance of a charged spherical conductor
C = 4πε0R
Step 3: Calculate the capacitance
C = 4π × (8.85 × 10−12) × (75 × 10−2)
C = 8.34 × 10−11 F = 83 pF (2 s.f.)
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The letter ‘C’ is used both as the symbol for capacitance as well as the unit of charge (coulombs). Take care not to confuse the two!

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?