Electric Force Between Two Point Charges (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9702
Point charge approximation
When calculating the force between two charges, air is treated as a vacuum
This is why the permittivity of free space ε0 is used
For a point outside a spherical conductor, the charge of the sphere may be considered to be a point charge at its centre
A uniform spherical conductor is one where its charge is distributed evenly
The electric field lines around a spherical conductor are therefore identical to those around a point charge
An example of a spherical conductor is a charged sphere
The field lines are radial and their direction depends on the charge of the sphere
If the spherical conductor is positively charged, the field lines are directed away from the centre of the sphere
If the spherical conductor is negatively charged, the field lines are directed towards the centre of the sphere
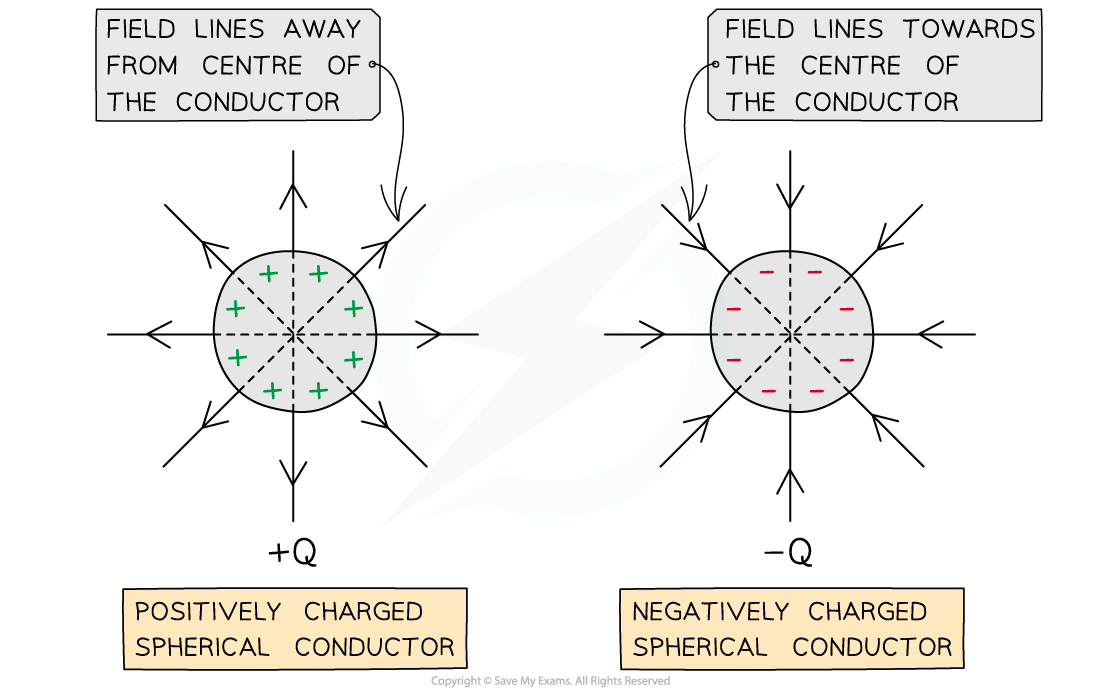
Electric field lines around a uniform spherical conductor are identical to those on a point charge
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You might have noticed that the electric fields share many similarities to the gravitational fields. The main difference being the gravitational force is always attractive, whilst electrostatic forces can be attractive or repulsive.
You should make a list of all the similarities and differences you can find, as this could come up in an exam question.
Coulomb's law
All charged particles generate an electric field
This field exerts a force on charged particles which are nearby
The electric force between two charges is defined by Coulomb’s law, which states that:
The force between two point charges is directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them
This electric force can be calculated using the expression:
Where:
F = electric force between two charges (N)
Q1, Q2 = magnitudes of the charges (C)
r = distance between the centres of the two charges (m)
ε0 = permittivity of free space
Electrostatic attraction between two charges

The attractive electric force FE between two point charges +Q and −Q with a separation of r is defined by Coulomb’s law
The constant ε0 is the permittivity of free space
ε0 = 8.85 × 10–12 C2 N–1 m–2 and refers to charges in a vacuum
The value of the permittivity of air is taken to be the same as ε0
All other materials have a higher permittivity ε > ε0
ε is a measure of the resistance offered by a material in creating an electric field within it
Sometimes Coulomb's law may be written as
Where
is the Coulomb constant
The value of k depends on the material between the charges
In a vacuum, k = 8.99 × 109 N m2 C–2
Repulsive & attractive forces
Unlike the gravitational force between two masses which is only attractive, electric forces can be:
attractive (the charges move closer together)
repulsive (the charges move further apart)

Opposite charges attract, like charges repel
Between two charges of the same type:
The product Q1Q2 is positive, so the electrostatic force is positive
A positive force means the charges experience repulsion
For two opposite charges:
The product Q1Q2 is negative, so the electrostatic force is negative
A negative force means the charges experience attraction
Worked Example
An alpha particle is placed 2.0 mm from a gold nucleus in a vacuum.
Taking them as point charges, calculate the magnitude of the electric force acting between the nuclei.
Proton number of helium = 2
Proton number of gold = 79
Answer:
Step 1: Write down the known quantities
Separation between charges, r = 2.0 mm = 2.0 × 10–3 m
Elementary charge, e = 1.60 × 10–19 C (from the data booklet)
Permittivity of free space, ε0 = 8.85 × 10–12 F m–2 (from the data booklet)
Step 2: Calculate the charges of the alpha particle and gold nucleus
An alpha particle (helium nucleus) has 2 protons, hence it has a charge of:
Q1 = 2e = 2 × (1.60 × 10–19)
A gold nucleus has 79 protons, hence it has a charge of:
Q2 = 79e = 79 × (1.60 × 10–19)
Step 3: Write down Coulomb's law
Step 4: Substitute the values and calculate the magnitude of the electric force
N (2 s.f.)
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You do not need to memorise the value of the permittivity of free space ε0, nor the Coulomb constant 1/4πε0, as these are both given on the data sheet.
Unless specified in the question, you should assume that charges are located in a vacuum.
You should note that Coulomb's law can only be applied to charged spheres whose size is much smaller than their separation. Only in this case, the point charge approximation is valid. You must remember that the separation r must be taken from the centres of the spheres.
You cannot use Coulomb's law to calculate the force between charges distributed on irregularly shaped objects.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?