Simple Harmonic Motion (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9702
Conditions for simple harmonic motion
Simple harmonic motion (SHM) is a specific type of oscillation that occurs when acceleration is proportional to displacement from a fixed point and in the opposite direction
An object is said to perform simple harmonic oscillations when all of the following apply:
The oscillations are periodic (repeating)
There is a central equilibrium point known as the fixed point
The object's displacement, velocity and acceleration change continuously
There is a restoring force always directed towards the fixed point
The magnitude of the restoring force is proportional to the displacement
The restoring force causes the acceleration
The restoring force and the acceleration must always be:
Directed towards the equilibrium position, and hence, in the opposite direction to the displacement
Directly proportional to the displacement
a ∝ −x
Where:
a = acceleration (m s−2)
x = displacement (m)
Restoring force, acceleration and displacement
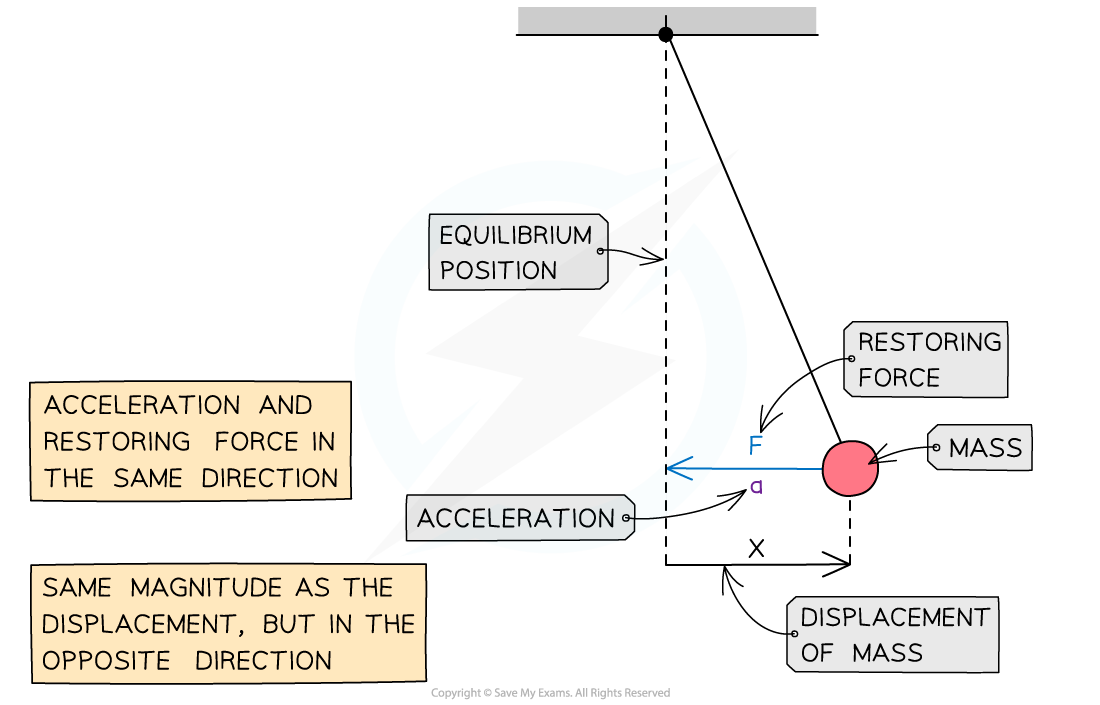
Force, acceleration and displacement of a simple pendulum in SHM
Examples of simple harmonic motion
Examples of oscillators that undergo SHM are:
The pendulum of a clock
A child on a swing
The vibrations of a bowl
A bungee jumper reaching the bottom of his fall
A mass on a spring
Guitar strings vibrating
A ruler vibrating off the end of a table
The electrons in alternating current flowing through a wire
The movement of a swing bridge when someone crosses
A marble dropped into a bowl
Examples of simple harmonic motion
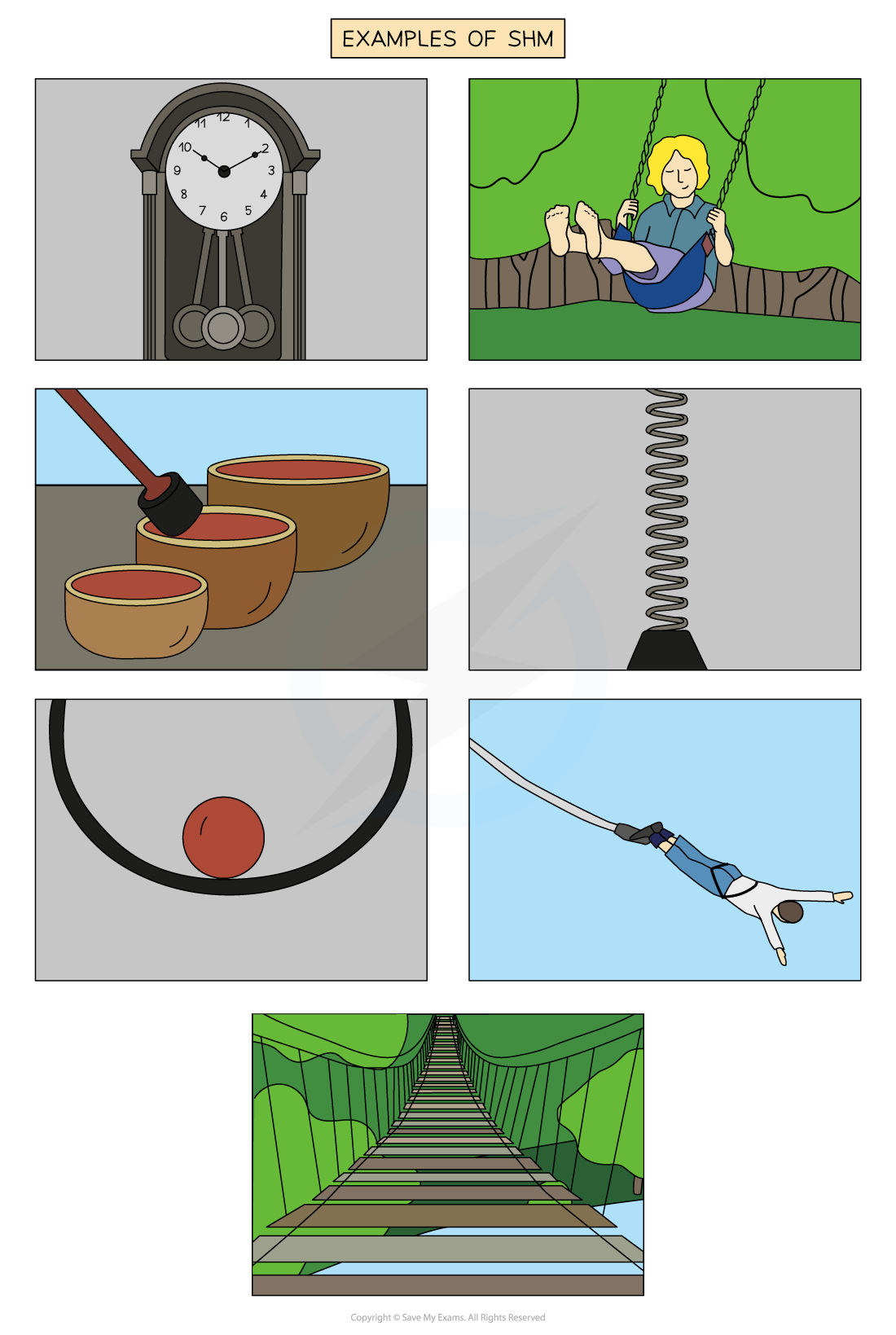
A pendulum, bungee jumper, swing bridge, vibrations in a prayer bowl, a swing, a ball rolling up and down the sides of a bowl and a spring are all examples of simple harmonic oscillations.
An example of not SHM
A person jumping on a trampoline is not an example of simple harmonic motion because:
The restoring force on the person is not proportional to their displacement from the equilibrium position and always acts down
When the person is not in contact with the trampoline, the restoring force is equal to their weight, which is constant
This does not change, even if they jump higher
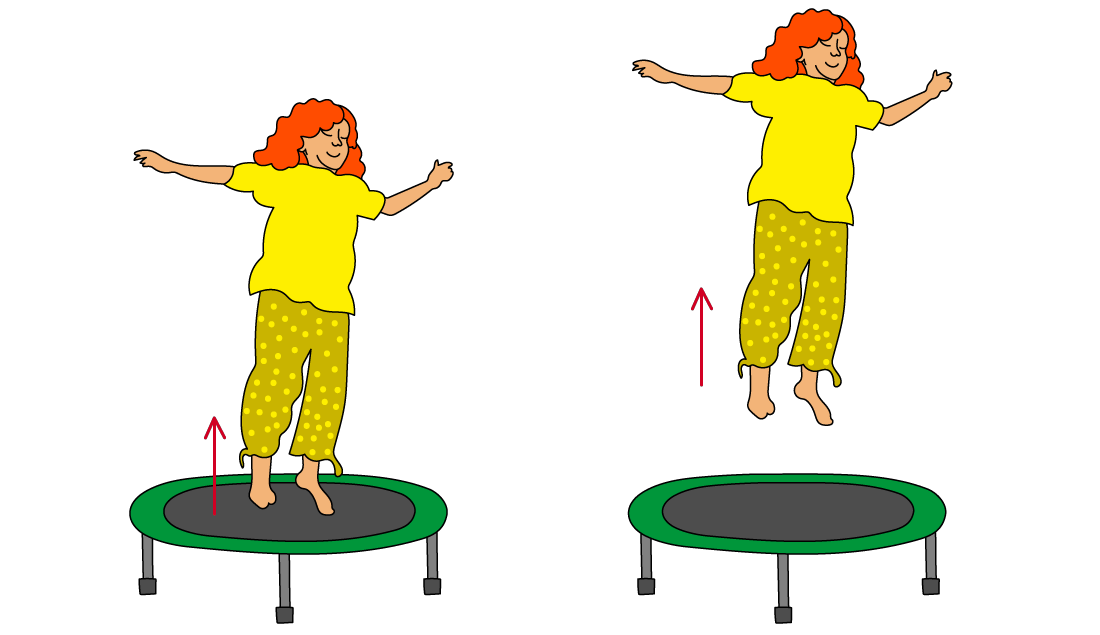
The restoring force of the person bouncing is equal to their weight and always acts downwards

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
