Calculating Speed in SHM (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9702
Written by: Ann Howell
Updated on
Calculating speed of an oscillator
The speed of an object in simple harmonic motion varies as it oscillates back and forth
Its speed is the magnitude of its velocity
SHM solution equation for speed
The speed of an oscillator released from the equilibrium position in SHM is defined by:
v = v0 cos(⍵t)
Where:
v = speed (m s-1)
v0 = maximum speed (m s-1)
⍵ = angular frequency (rad s-1)
t = time (s)
Interpreting the graph v = v0 cos(⍵t)
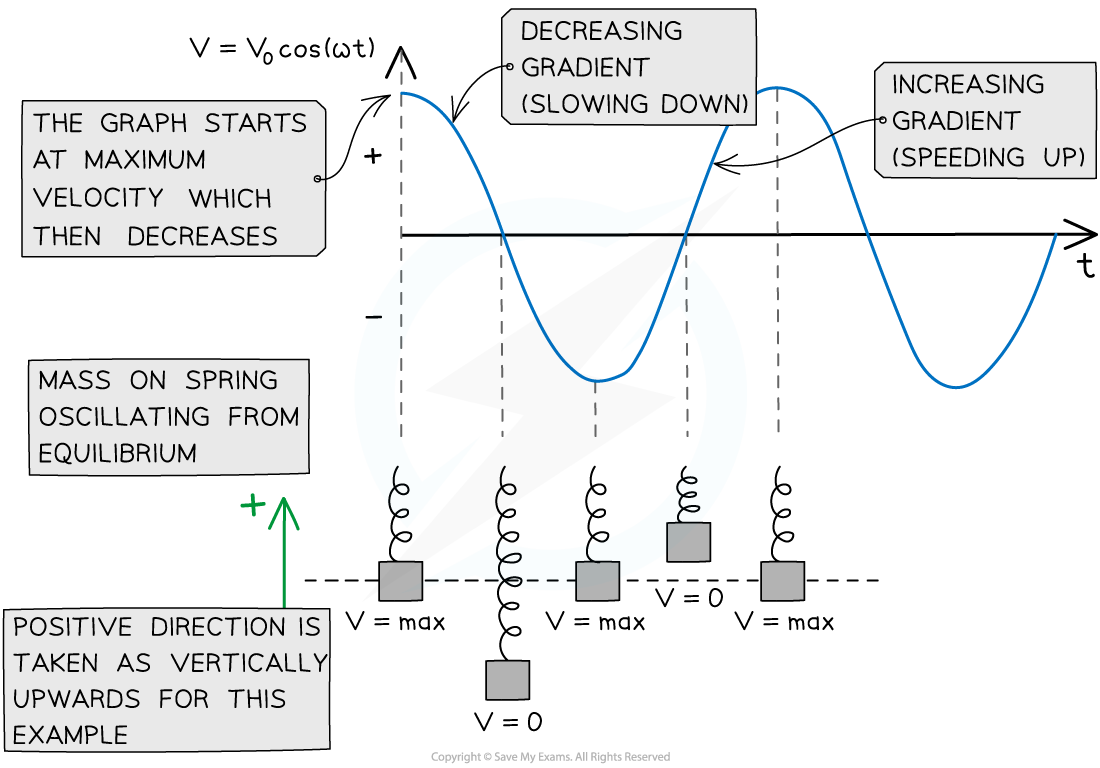
The variation of the speed of a mass on a spring in SHM over one complete cycle
This is a cosine function because the object starts oscillating from the equilibrium position (x = 0 when t = 0)
This is shown on the SHM graphs revision note
Although the symbol v is commonly used to represent velocity, not speed, exam questions focus more on the magnitude of the velocity than its direction in SHM
The maximum speed of an oscillator is the amplitude, v0 of the velocity-time graph
SHM equation for speed
The speed v changes with the oscillator’s displacement x according to the equation:
v = ±ω
Where:
v = speed (m s-1)
x0 = amplitude (m)
± = ‘plus or minus’, this value can be positive or negative
⍵ = angular frequency (rad s-1)
x = displacement (m)
This equation shows that when an oscillator has a greater amplitude x0, it has to travel a greater distance in the same amount of time and hence has greater speed v
Both speed equations will be given on your data sheet in the exam
Maximum speed
An oscillator reaches its greatest speed at the equilibrium position i.e. when its displacement is 0 (x = 0)
At maximum speed the SHM speed equation becomes:
v0 = ⍵x0
Worked Example
A simple pendulum oscillates with simple harmonic motion with an amplitude of 15 cm. The frequency of the oscillations is 6.7 Hz.
Calculate the speed of the pendulum at a position of 12 cm from the equilibrium position.
Answer:
Step 1: Write out the known quantities
Amplitude of oscillations, x0 = 15 cm = 0.15 m
Displacement at which the speed is to be found, x = 12 cm = 0.12 m
Frequency, f = 6.7 Hz
Step 2: Oscillator speed with displacement equation
v = ±ω
Since the speed is being calculated, the ± sign can be removed as direction does not matter in this case
Step 3: Write an expression for the angular frequency
The equation relating angular frequency and normal frequency:
⍵ = 2πf = 2π× 6.7 = 42.097…
Step 4: Substitute in values and calculate
v = 3.789 = 3.8 m s-1 (2 s.f)
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You often have to convert between time period T, frequency f and angular frequency ⍵ for many exam questions – so make sure you revise the equations relating to these.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
