Work Done by a Gas (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9702
Work done by a gas
When a gas expands, it does work on its surroundings by exerting pressure on the walls of its container
The work done when a volume of gas changes at constant pressure is defined as:
W = pΔV
Where:
W = work done (J)
p = external pressure (Pa)
V = volume of gas (m3)
Work done by a gas
An example of work done by a gas is in a steam engine where expanding steam pushes a piston to turn the engine
The gas inside the cylinder is enclosed by a moveable piston
The force of the gas pushes the piston outwards
The work done by the gas on the piston pushes the piston outwards
Work done by a gas on a piston
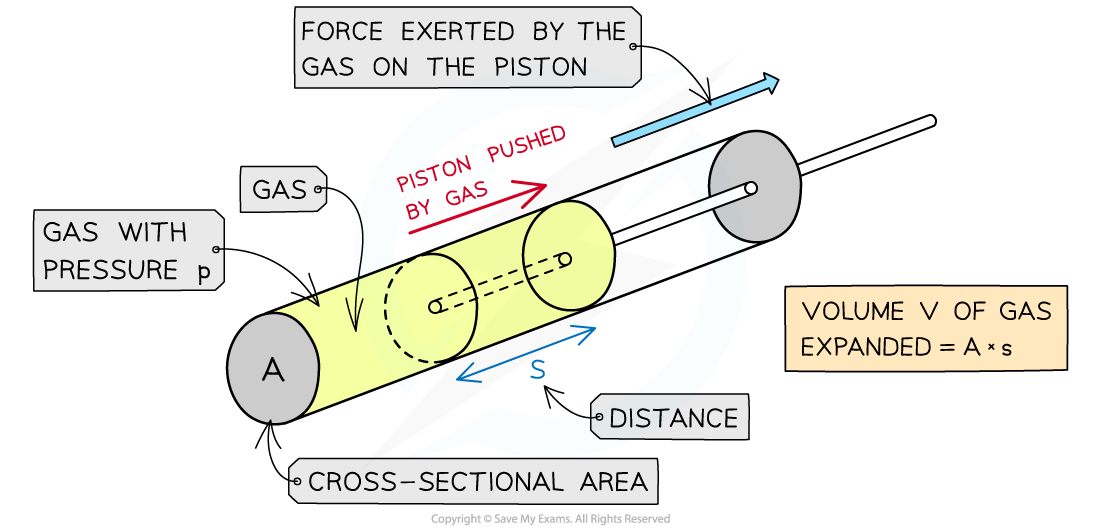
The gas expansion pushes the piston a distance s
Work done on a gas
When work is done on a gas its internal energy is increased which can also cause an increase in temperature
Work can be done on a gas by compression
A force is used to push a piston by a certain distance
This decreases the volume of the gas
The molecules move around faster and therefore have a higher kinetic energy
This increase in kinetic energy also increases its temperature
Work done on a gas

To compress the gas, a force must be used to move the piston a certain distance. This involves doing work.
Differences between work done by or on a gas
When a gas expands, work is done by the gas (-W)
When a gas expands, work done W is negative
When the gas is compressed, work is done on the gas (+W)
When a gas is compressed, work done W is positive
Positive and negative work
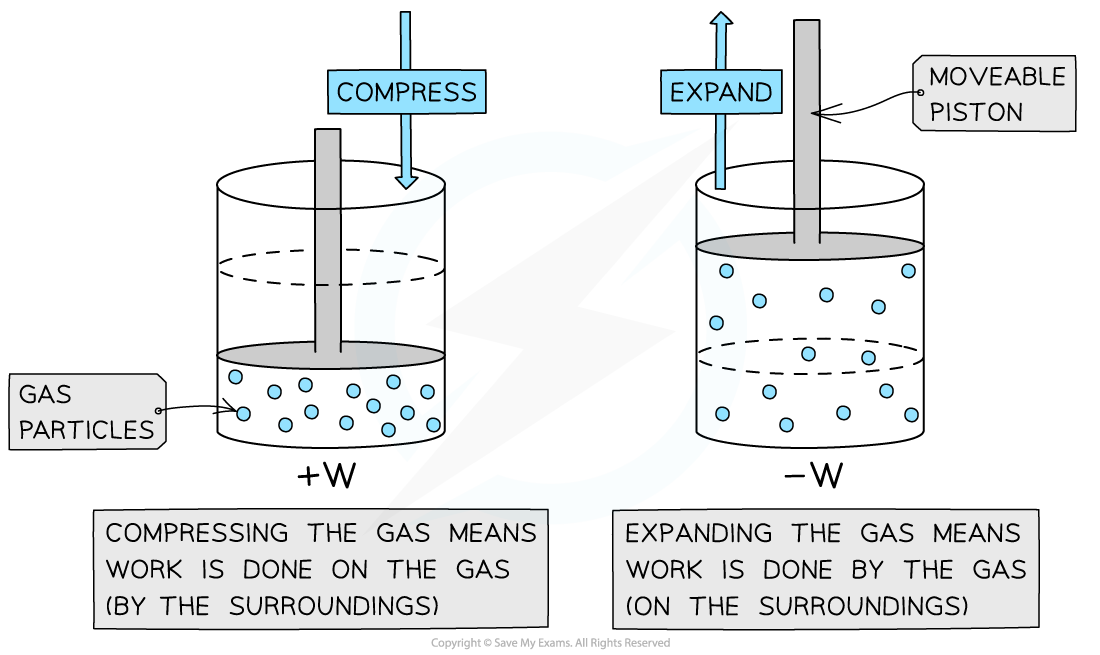
Positive or negative work done depends on whether the gas is compressed or expanded
Worked Example
When a balloon is inflated, its rubber walls push against the air around it.
Calculate the work done when the balloon is blown up from 0.015 m3 to 0.030 m3.
Atmospheric pressure = 1.0 × 105 Pa.
Answer:
Step 1: Write down the equation for the work done by a gas
W = pΔV
Step 2: Substitute in values
ΔV = final volume − initial volume = 0.030 − 0.015 = 0.015 m3
W = (1.0 × 105) × 0.015 = 1500 J
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The pressure p in the work done by a gas equation is not the pressure of the gas but the pressure of the surroundings. This is because when a gas expands, it does work on the surroundings.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?