Specific Latent Heat Capacity (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Physics) : Revision Note
Defining latent heat capacity
Energy is required to change the state of a substance
Examples of changes of state are:
Melting = solid to liquid
Evaporation/vaporisation/boiling = liquid to gas
Sublimation = solid to gas
Freezing = liquid to solid
Condensation = gas to liquid
Changes of state
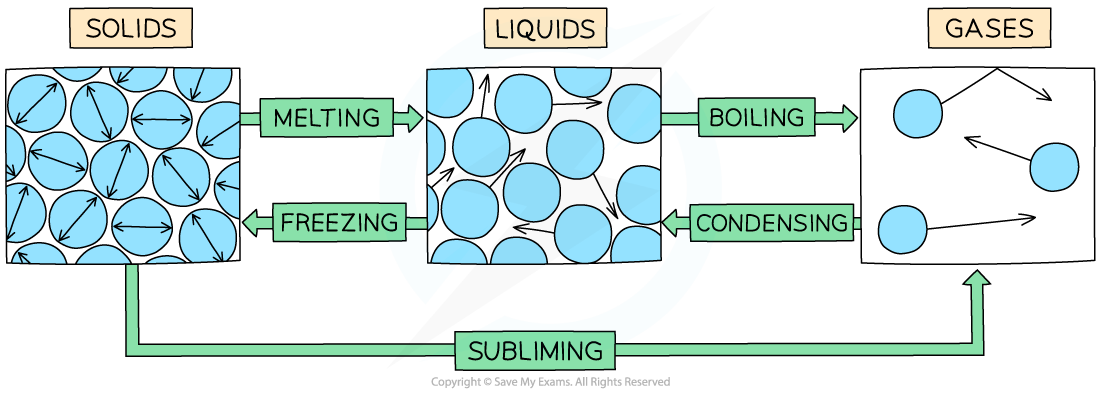
The example of changes of state between solids, liquids and gases
When a substance changes state, there is no temperature change
The energy supplied to change the state is called the specific latent heat and is defined as:
The thermal energy required to change the state of 1 kg of mass of a substance without any change of temperature
There are two types of latent heat:
Specific latent heat of fusion (melting)
Specific latent heat of vaporisation (boiling)
It is important to recognise the difference between latent heat and specific latent heat
latent heat is the energy required to change a materials state
specific latent heat is the energy required to change the state of 1 kg of a material
Types of latent heat
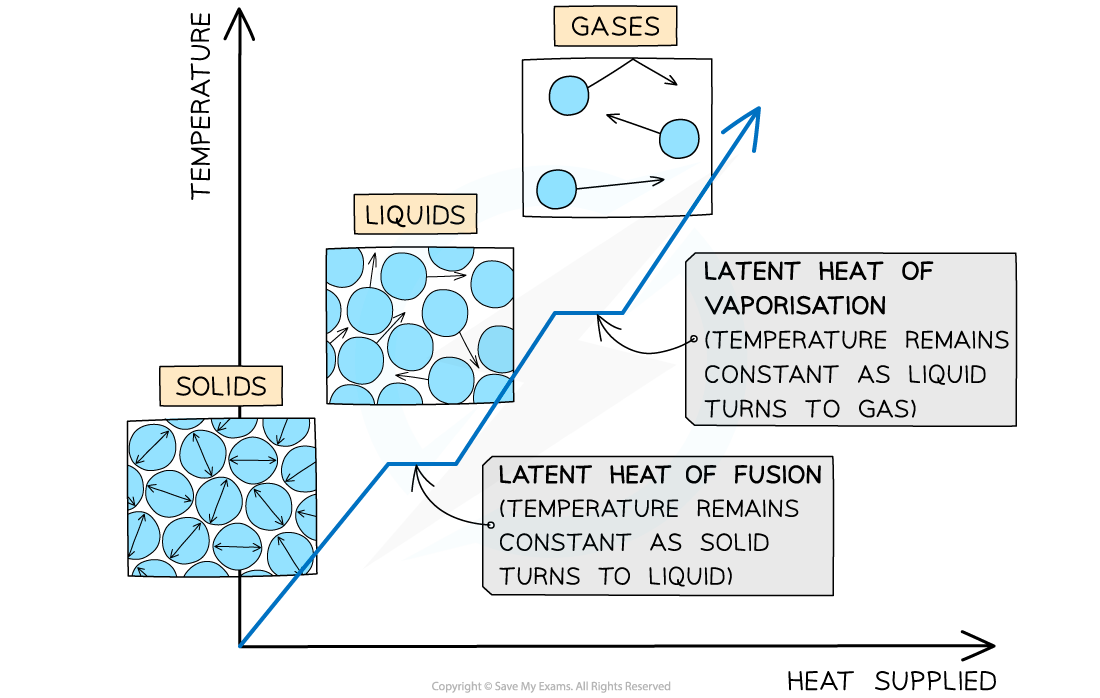
The changes of state with heat supplied against temperature. There is no change in temperature during changes of state.
The specific latent heat of fusion is defined as:
The thermal energy required to convert 1 kg of solid to liquid with no change in temperature
This is used when melting a solid or freezing a liquid
The specific latent heat of vaporisation is defined as:
The thermal energy required to convert 1 kg of liquid to gas with no change in temperature
This is used when vaporising a liquid or condensing a gas
Calculating specific latent heat
The amount of energy Q required to melt or vaporise a mass of m with latent heat L is:
Where:
Q = amount of thermal energy to change the state (J)
L = latent heat of fusion or vaporisation (J kg-1)
m = mass of the substance changing state (kg)
The values of latent heat for water are:
Specific latent heat of fusion = 330 kJ kg-1
Specific latent heat of vaporisation = 2.26 MJ kg-1
Therefore, evaporating 1 kg of water requires roughly seven times more energy than melting the same amount of ice to form water
The reason for this is to do with intermolecular forces:
When ice melts: energy is required to just increase the molecular separation until they can flow freely over each other
When water boils: energy is required to completely separate the molecules until there are no longer forces of attraction between the molecules, hence this requires much more energy
Worked Example
The energy needed to boil a mass of 530 g of a liquid is 0.6 MJ.
Calculate the specific latent heat of the liquid and state whether it is the latent heat of vaporisation or fusion.
Step 1: Write the thermal energy required to change state equation
Step 2: Rearrange for latent heat
Step 3: Substitute in the values
m = 530 g = 530 × 10-3 kg
Q = 0.6 MJ = 0.6 × 106 J
L is the latent heat of vaporisation because the change in state is from liquid to gas (boiling)
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Use these reminders to help you remember which type of latent heat is being referred to:
Latent heat of fusion = imagine ‘fusing’ the liquid molecules together to become a solid
Latent heat of vaporisation = “water vapour” is steam, so imagine vaporising the liquid molecules into a gas

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
