Circular Orbits in Gravitational Fields (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9702
Circular orbits in gravitational fields
The orbits of most planets and satellites in the Solar System are nearly circular
The gravitational force between two bodies provides the centripetal force required to maintain a circular orbit
Consider a satellite with mass m orbiting Earth with mass M at a distance r from the centre, travelling with linear speed v
Equating the gravitational force to the centripetal force for a planet or satellite in orbit gives:
The mass of the satellite m will cancel out on both sides to give:
Where:
= orbital speed of the smaller mass (m s−1)
G = Newton's Gravitational Constant
M = mass of the larger mass being orbited (kg)
r = orbital radius (m)
This equation shows that all satellites moving in a circular orbit of fixed radius
will travel at a constant speed
The direction of a satellite orbiting in circular motion is constantly changing, which means that the satellite has
a velocity which is constantly changing
a centripetal acceleration that acts towards the satellite
a centripetal force, provided by the gravitational force, which causes the satellite to accelerate
Gravitational force and instantaneous velocity
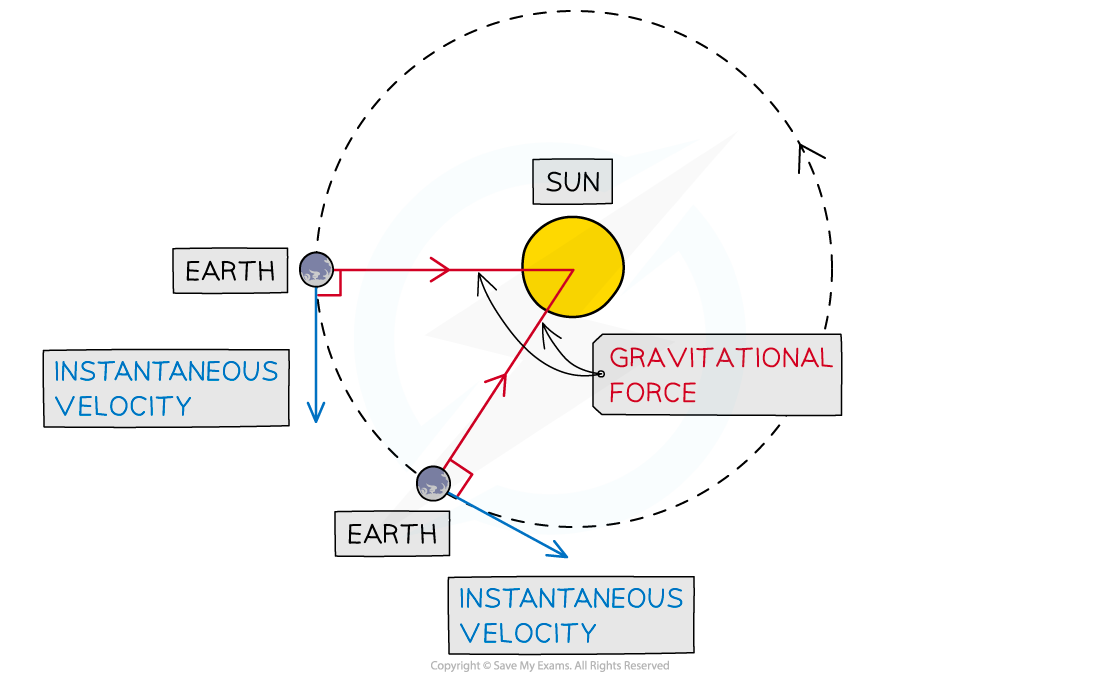
The direction of the instantaneous velocity and the gravitational force at different points of the Earth’s orbit around the sun
Worked Example
A binary star system consists of two stars orbiting about a fixed point B. The star of mass M1 has a circular orbit of radius R1 and mass M2 has a radius of R2. Both have an angular speed ⍵ about B.
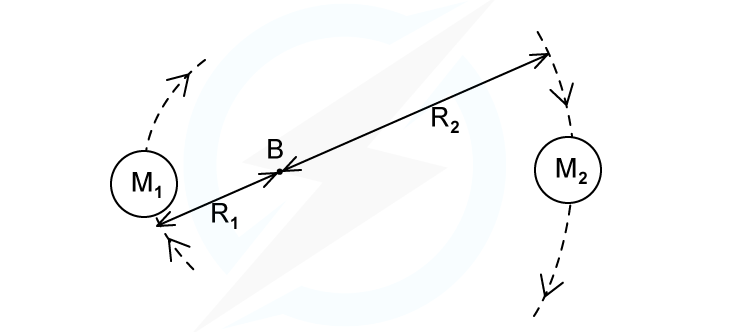
State the following formula, in terms of G, M2, R1 and R2
(a) The angular speed ⍵ of M1
(b) The time period T for each star in terms of angular speed ⍵
Answer:
(a)
Step 1: Equating the centripetal force of mass M1 to the gravitational force between M1 and M2
Step 2: M1 cancels on both sides
Step 3: Rearrange for angular velocity ⍵
Step 4: Square root both sides
(b)
Step 1: Angular speed equation with time period T
Step 2: Rearrange for T
Step 3: Substitute in ⍵
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Many of the calculations in the Gravitation questions depend on the equations for Circular motion. Be sure to revisit these and understand how to use them!

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
