Gravitational Fields (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Physics) : Revision Note
Defining gravitational field
There is a force of attraction between all masses
This force is known as the ‘force due to gravity’ or the weight
The Earth’s gravitational field is responsible for the weight of all objects on Earth
A gravitational field is an example of a field of force and is defined as:
Force per unit mass
The direction of the gravitational field is always towards the centre of the mass
Gravitational forces cannot be repulsive
Gravitational field strength
The strength of this gravitational field (g) at a point is the force (Fg) per unit mass (m) of an object at that point:
Where:
g = gravitational field strength (N kg-1)
Fg = force due to gravity, or weight (N)
m = mass (kg)
This equation tells us:
On planets with a large value of g, the gravitational force per unit mass is greater than on planets with a smaller value of g
This means objects will have a larger weight with a larger value of g
Weight of person on Earth and on Jupiter
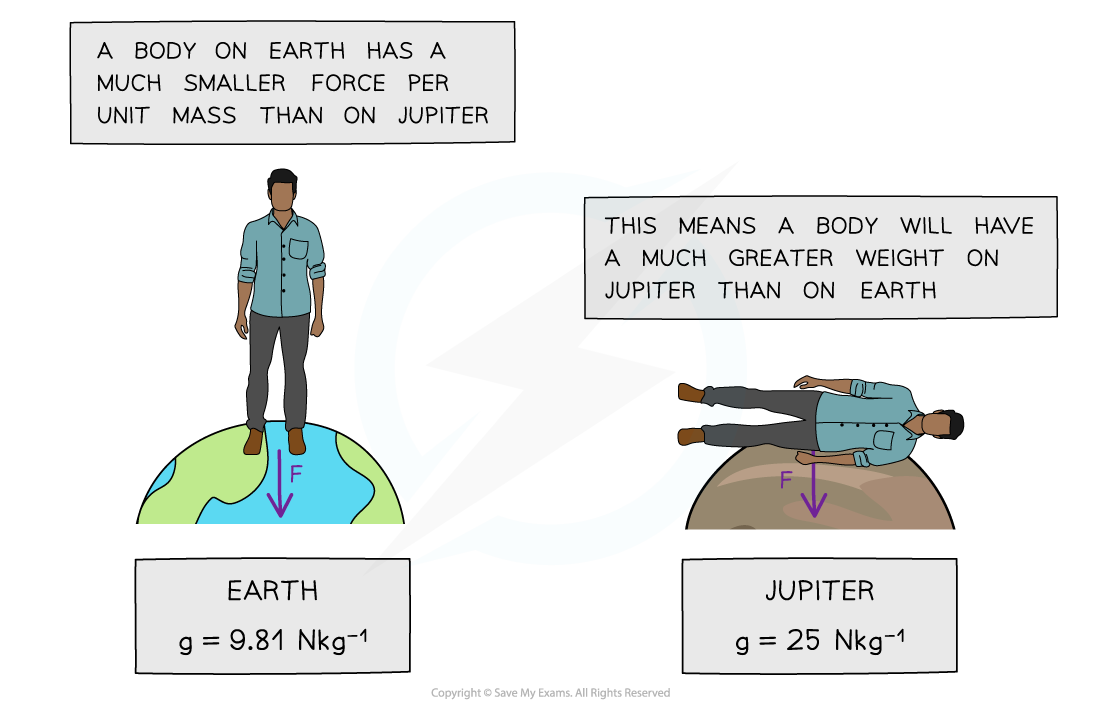
A person’s weight on Jupiter would be so large a human would be unable to fully stand up
Worked Example
Calculate the mass of an object with weight 10 N on Earth.
Answer:
Step 1: State the gravitational field strength equation
Step 2: Rearrange to make mass the subject
Step 3: Substitute in the known values to calculate
Examiner Tips and Tricks
There is a big difference between g and G (sometimes referred to as ‘little g’ and ‘big G’ respectively), g is the gravitational field strength and G is Newton’s gravitational constant. Make sure not to use these interchangeably!
Representing gravitational fields
The direction and magnitude of a gravitational field is represented by gravitational field lines
Gravitational fields can be uniform or non-uniform
Radial fields are non-uniform fields
The gravitational field strength g decreases with distance from the centre of the object
The gravitational field lines around a point mass are directed radially inwards
Parallel field lines represent a uniform field
The gravitational field strength g is the same throughout the field
The gravitational field lines of a uniform field, where the field strength is the same at all points, is represented by equally spaced parallel lines
The Earth's gravitational field near the surface is almost uniform; therefore, it can be approximated as uniform
Gravitational field lines for a point mass and for a uniform gravitational field
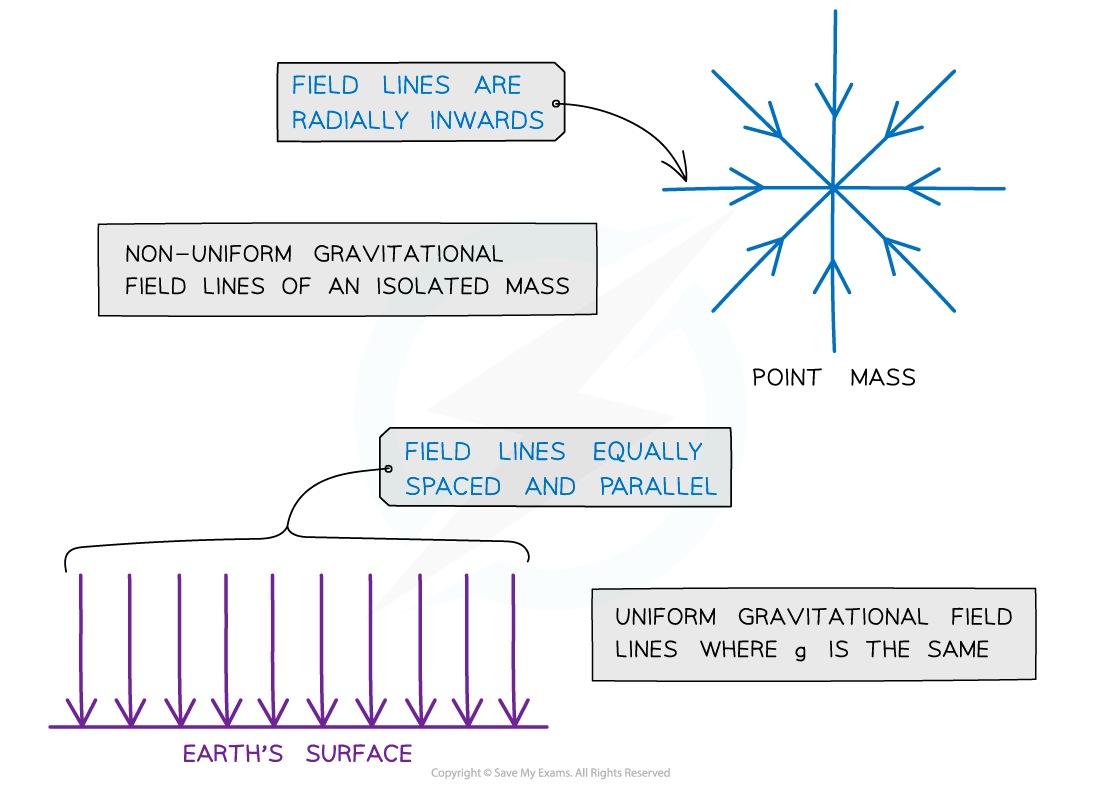
Gravitational field lines for a point mass are radial and, for a uniform gravitational field, are parallel
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Always add the arrows on the field lines! Gravitational forces are attractive only. Remember:
For a radial field: it is towards the centre of the sphere or point charge
For a uniform field: towards the surface of the object e.g. Earth

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?

