Calculating Centripetal Force (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9702
Calculating centripetal force
Centripetal force can be calculated using the equation:
Where:
= magnitude of the centripetal force, measured in newtons (N)
= mass of object, measured in kilograms (kg)
= velocity, measured in meters per second (m s-1)
= radius of circular path, measured in metres (m)
Another form of the equation can be written using the equation linking linear and angular velocity:
Where
= angular velocity measured in radians per second (rad s-1)
Substituting into the first centripetal force equation
Simplify the equation
Centripetal force in circular motion
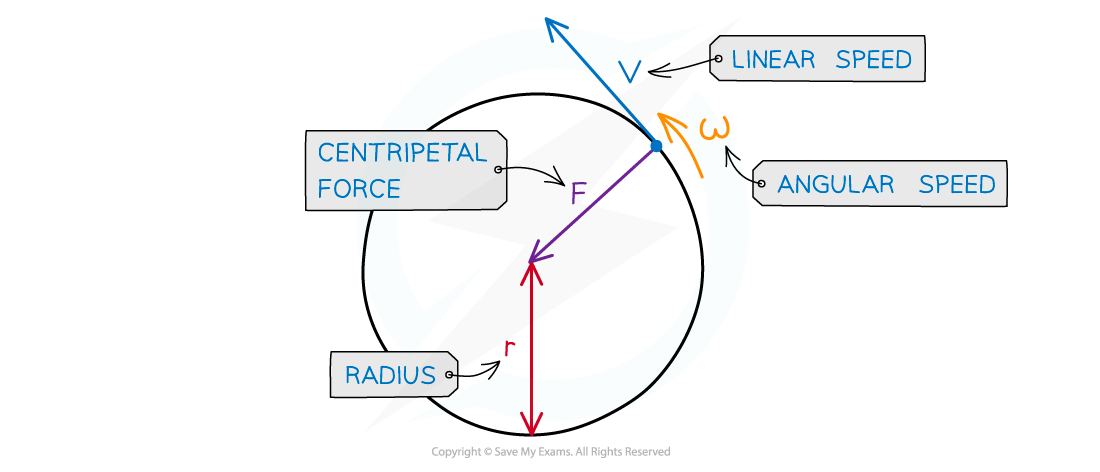
Centripetal force is always perpendicular to the direction of travel
Worked Example
A bucket of mass 8.0 kg is filled with water is attached to a string of length 0.5 m.
What is the minimum speed the bucket must have at the top of the circle so no water spills out?
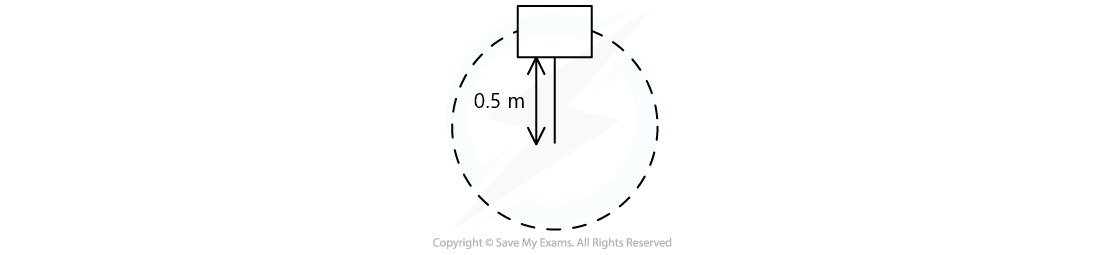
Answer:
Step 1: Draw the forces on the bucket at the top
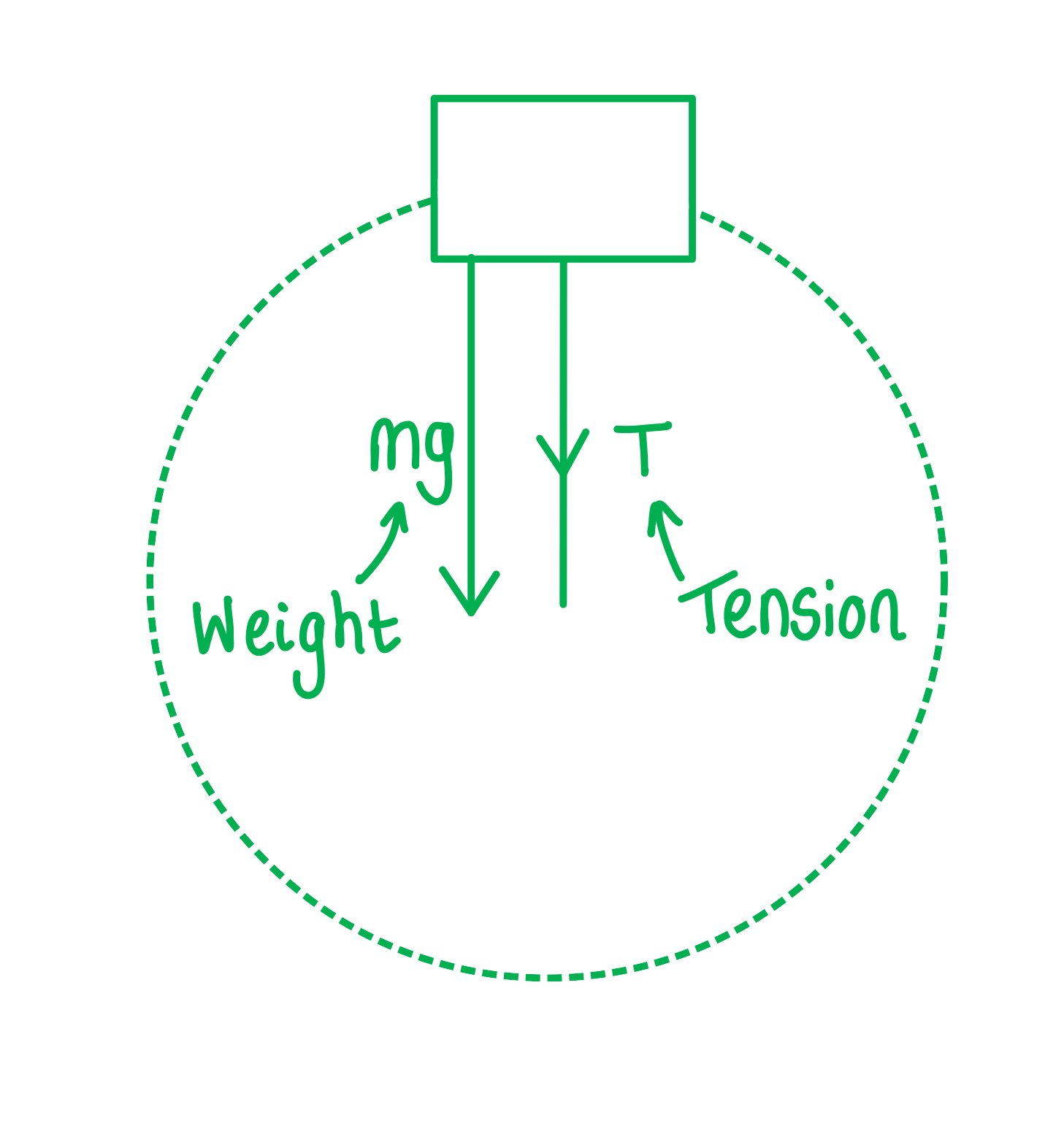
Step 2: Calculate the centripetal force
The weight of the bucket = mg
This is equal to the centripetal force since it is directed towards the centre of the circle
Step 3: Rearrange for velocity v
m cancels from both sides
Step 4: Substitute in values

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?