Angular Speed (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9702
Angular speed
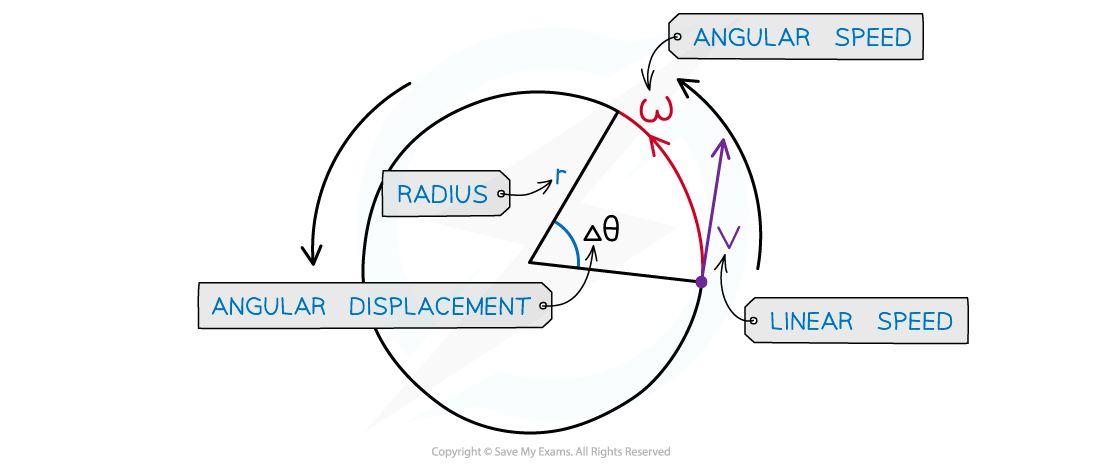
The angular speed (⍵) of a body in circular motion is defined as:
The rate of change in angular displacement with respect to time
Angular speed is a scalar quantity, and is measured in rad s-1
Any object travelling in a uniform circular motion at the same speed travels with a constantly changing velocity
This is because it is constantly changing direction, and is therefore accelerating
Angular speed in circular motion
When an object is in uniform circular motion, velocity constantly changes direction, but the speed stays the same
Calculating angular speed
Taking the angular displacement of a complete cycle as 2π, the angular speed ⍵ can be calculated using the equation:
Where:
Δθ = change in angular displacement (radians)
Δt = time interval (s)
T = the time period (s)
f = frequency (Hz)
Angular velocity is the same as angular speed, but it is a vector quantity
When an object travels at constant linear speed v in a circle of radius r, the angular velocity is equal to:
Where:
v is the linear speed (m s-1)
r is the radius of orbit (m)
This equation tells us:
The greater the rotation angle θ in a given amount of time, the greater the angular velocity ⍵
An object rotating further from the centre of the circle (larger r) moves with a smaller angular velocity (smaller ⍵)
Worked Example
A bird flies in a horizontal circle with an angular speed of 5.25 rad s-1 of radius 650 m.
Calculate:
a) The linear speed of the bird
b) The frequency of the bird flying in a complete circle
Answer:
Part (a)
Step 1: List the known quantities
Angular speed, ω = 5.25 rad s-1
Radius, r = 650 m
Step 2: State the linear speed equation
Step 3: Calculate linear speed
Part (b)
Step 1: Equate angular speed with the frequency equation
Step 2: Rearrange to make frequency the subject
Step 3: Substitute the known values to calculate

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?