Nucleon & Proton Number (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9702
Nucleon & proton number
The nuclide notation of an element is used to describe the constituents of the nuclei
An example of this notation for Lithium is:
Where:
Li = lithium
7 = mass number or nucleon number
3 = atomic number or proton number
The mass number is the number of particles in the nucleus
The nucleus contains protons plus neutrons
The atomic number is the number of protons in the atom
Since atoms are neutral, this is also equal to the number of electrons in the atom
When given an atomic symbol, you can therefore figure out the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in the atom:
Protons: The atomic number
Electrons: Atoms are neutrals, so the number of negative electrons is equal to the number of positive protons. Therefore, this is also the atomic number
Neutrons: Subtract the proton number from the nucleon number
For the lithium atom, these numbers would be:
Protons: 3
Electrons: 3
Neutrons: 7 − 3 = 4
The term nucleon is the used to mean a particle in the nucleus – i.e. a proton or neutron
The term nuclide is used to refer to a nucleus with a specific combination of protons and neutrons
Worked Example
The atom is a neutral atom.
State the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in this atom.
| Protons | Neutrons | Electrons |
A | 77 | 192 | 77 |
B | 155 | 77 | 77 |
C | 192 | 77 | 192 |
D | 77 | 115 | 77 |
Answer: D
Step 1: Determine the nucleon and atomic numbers
Nucleon number = 192
Atomic number = 77
Step 2: Determine the number of protons
Number of protons = atomic number
Number of protons = 77
Step 3: Determine the number of neutrons
Number of neutrons = nucleon number − atomic number
Number of neutrons = 192 − 77
Number of neutrons = 115
Step 4: Determine the number of electrons
Number of electrons = number of protons
Number of electrons = 77
Isotopes
Although all atoms of the same element always have the same number of protons (and hence electrons), the number of neutrons can vary
An isotope is an atom (of the same element) that has an equal number of protons but different number of neutrons
The isotopes of hydrogen are deuterium and tritium:
Isotopes of hydrogen
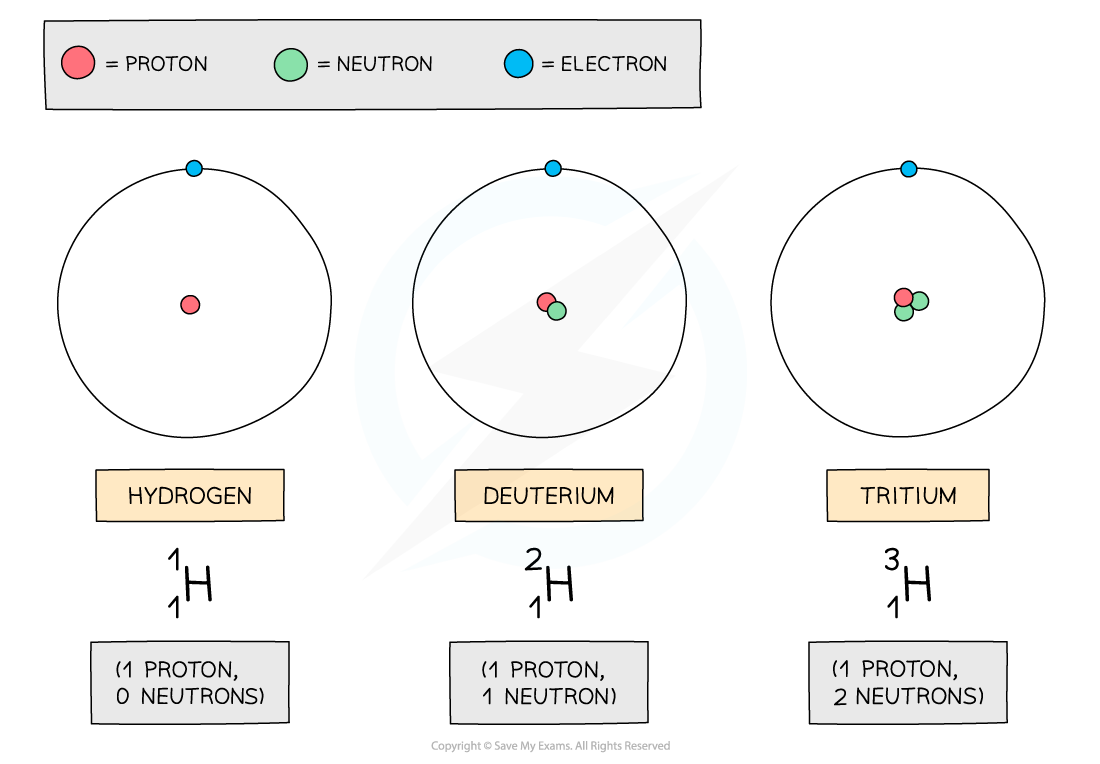
The three atoms shown above are all forms of hydrogen, but they each have different numbers of neutrons
Remember, the neutron number of an atom is found by subtracting the proton number from the nucleon number
Since nucleon number includes the number of neutrons, an isotope of an element will also have a different nucleon number
Since isotopes have an imbalance of neutrons and protons, they are unstable. This means they constantly decay and emit radiation to achieve a more stable form
This can happen from anywhere between a few nanoseconds to 100,000 years
Worked Example
One of the rows in the table shows a pair of nuclei that are isotopes of one another.
Which row shows the correct isotopes?
| Nucleon number | Number of neutrons |
A | 39 35 | 19 22 |
B | 37 35 | 20 18 |
C | 37 35 | 18 20 |
D | 35 35 | 20 18 |
Answer: B
Step 1: Recall the properties of isotopes
Isotopes are nuclei with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons
The nucleon number (mass number) is the total number of particles in the nucleus (protons + neutrons)
Therefore, isotopes have a different nucleon number too
Step 2: Calculate the number of protons in the first nucleus
Nucleon number = 37
Neutrons = 20
Protons = nucleon number − neutrons
Protons = 37 − 20 = 17
Step 3: Calculate the number of protons in the second nucleus
Nucleon number = 35
Neutrons = 18
Protons = 35 − 18 = 17
Step 4: Conclusion
The nuclei in answer B have the same number of protons and different numbers of neutrons, therefore these nuclei are isotopes of one another
AZX notation
Atomic symbols are written in a specific notation called AZX notation
Where:
X = chemical symbol of the element
A = nucleon (mass) number
Z = proton (atomic) number
The number A represents the nucleon number or the mass number
Nucleon number (A) = total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus
The lower number Z represents the proton or atomic number
Proton number (Z) = total number of protons in the nucleus

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?