Resistors in Series (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9702
Deriving the equation for resistors in series
In a series circuit, the combined resistance of two or more resistors is the sum of the individual resistances
In a series circuit:
The current is the same through all resistors
The potential difference is shared between all the resistors
The equation for combined resistors in series is derived using Kirchhoff’s laws:

Resistors in series
When two or more components are connected in series:
The combined resistance of the components is equal to the sum of the individual resistances
Resistors in series
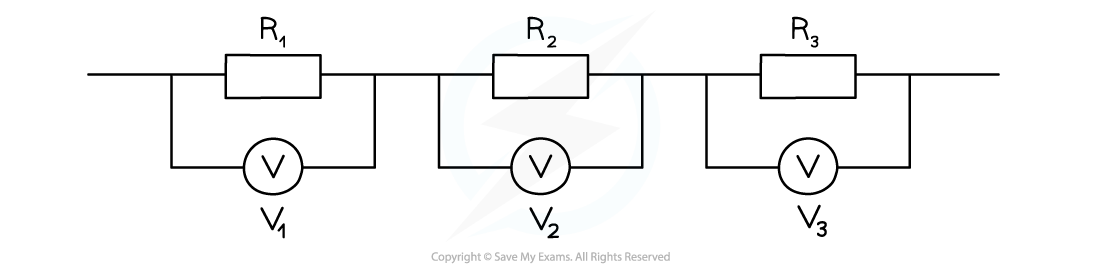
Resistors connected in series each have their own separate potential difference
The equation for the combined resistance, R of resistors in series is:
Worked Example
The combined resistance R in the following series circuit is 60 Ω.
What is the resistance value of R2?
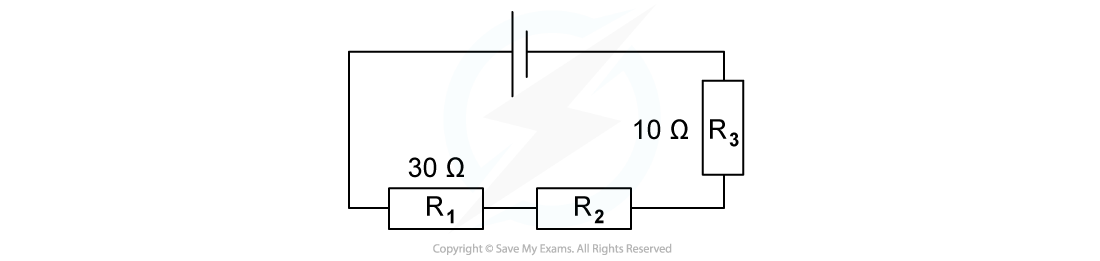
A. 100 Ω
B. 30 Ω
C. 20 Ω
D. 40 Ω
Answer: C
Step 1: State the equation for the combined resistance for resistors in series
Step 2: Rearrange for resistance R2
Step 3: Substitute the values

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?