Mean Power (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9702
Mean power
In mains electricity, current and voltage are varying all the time
This also means the power varies constantly, recall the equations for power:
Where:
I = direct current (A)
V = direct voltage (V)
R = resistance (Ω)
The r.m.s values means equations used for direct current and voltage can now be applied to alternating current and voltage
These are also used to determine an average current or voltage for alternating supplies
Recall the equation for peak current:
The peak (maximum) power and the mean (average) power are given by:
Peak power can be written in terms of r.m.s current as
Therefore, peak power is related to mean power by:
Therefore, it can be concluded that:
The mean power in a resistive load is half the maximum power for a sinusoidal alternating current or voltage
Mean power on a graph
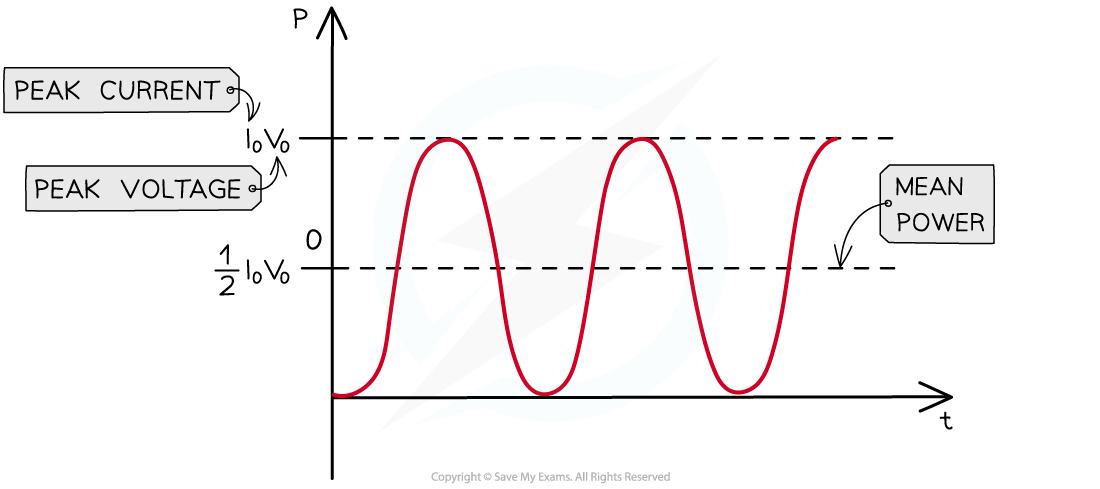
Mean power is exactly half the maximum power
Worked Example
An alternating voltage supplied across a resistor of 40 Ω has a peak voltage V0 of 240 V.
Calculate the mean power of this supply.
Answer:
Step 1: Write down the known quantities
Resistance, R = 40 Ω
Peak voltage, V0 = 240 V
Step 2: Write out the equation for the peak power and calculate
Step 3: Calculate the mean power
The mean power is half of the maximum (peak) power
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You do not need to remember the derivation for the mean power, but it is useful to know where it comes from. However, makes sure you remember its definition and know how to apply it in questions.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?