Internal energy (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9702
Defining internal energy
The internal energy U of a system is determined by the state of the system
Gases have the highest internal energy, and solids have the lowest
The molecules of all substances have both kinetic and potential energies
Kinetic energy is due to the speed of the molecules
Potential energy is due to the intermolecular forces between the molecules and varies with the separation of particles
The internal energy of a substance is defined as:
The sum of the random distribution of kinetic and potential energies within a system of molecules
Internal energy of water molecules

All molecules in a substance possess both kinetic and potential energies
The internal energy of a system can increase by:
doing work on it
adding thermal energy to it (heating it)
The internal energy of a system can decrease by:
losing thermal energy to its surroundings
it doing work on the surroundings (e.g. a gas pushing a piston)
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When an exam question asks you to define “internal energy”, you can lose a mark for not mentioning the “random motion” of the particles or the “random distribution” of the energies, so make sure you include one of these in your definition!
Internal energy & temperature
The rise in temperature of an object is related to an increase in its internal energy
Molecules in solids and liquids are close together and bound by intermolecular forces, so they have kinetic and potential energy
Molecules in solids and liquids are tightly packed, so they begin to vibrate more when heated
Molecules in a real gas also have intermolecular forces, so they have potential energy, as well as kinetic energy
When a gas is heated, the molecules begin to move around faster, increasing their kinetic energy
At a given temperature, the total potential energy of all of the molecules will remain constant
The change in internal energy of an ideal gas is proportional to the change in temperature, and can be written as:
ΔU ∝ ΔT
Where:
ΔU = change in internal energy (J)
ΔT = change in temperature (K)
Molecular movement at low and high temperatures
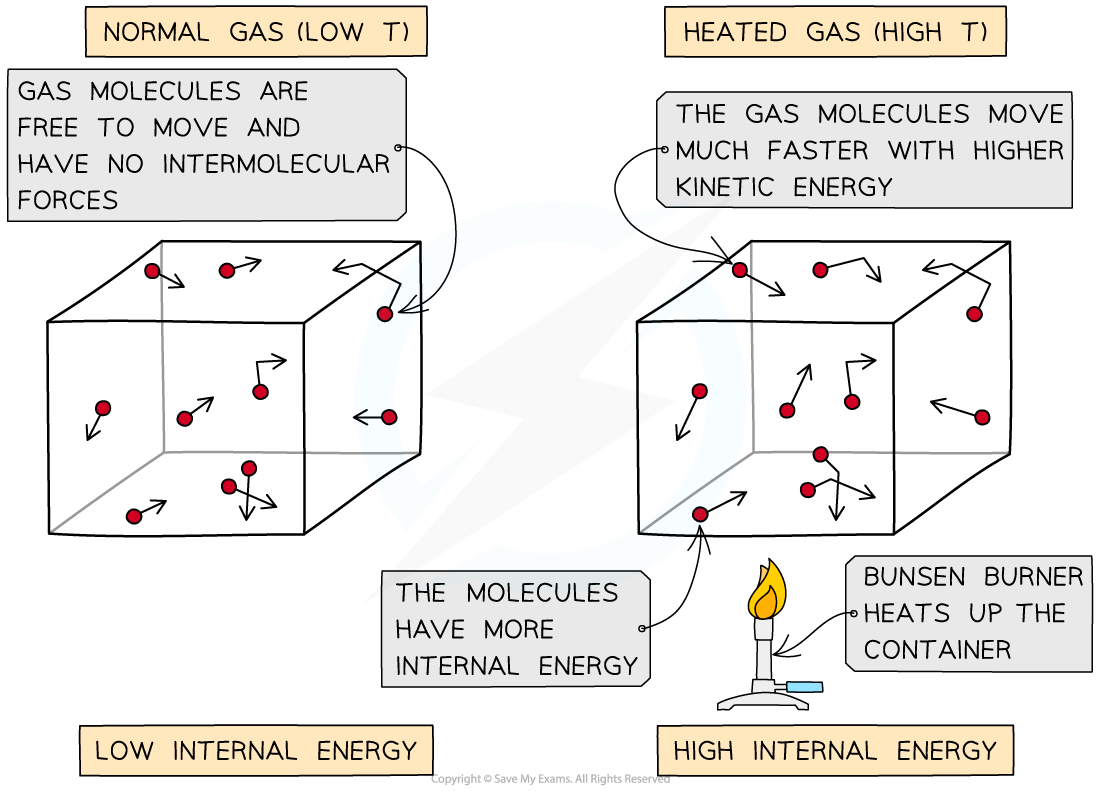
As the container is heated up, the gas molecules move faster with higher kinetic energy and therefore higher internal energy
Worked Example
A student suggests that, when an ideal gas is heated from 50 oC to 150 oC, the internal energy of the gas is tripled. State and explain whether the student’s suggestion is correct.
Answer:
Step 1: Write down the relationship between internal energy and temperature
The internal energy of an ideal gas is directly proportional to its temperature
ΔU ∝ ΔT
Step 2: Determine whether the change in temperature (in K) increases by three times
The temperature change is the thermodynamic temperature i.e. Kelvin
The temperature change in degrees from 50 oC to 150 oC increases by three times
The temperature change in Kelvin is:
50 oC + 273.15 = 323.15 K
150 oC + 273.15 = 423.15 K
Therefore, the temperature change, in Kelvin, does not increase by three times
Step 3: Write a concluding statement relating the temperature change to the internal energy
The internal energy is directly proportional to the temperature
The thermodynamic temperature has not tripled, therefore, neither has the internal energy
Therefore, the student is incorrect
Examiner Tips and Tricks
If an exam question about an ideal gas asks for the total internal energy, remember that this is equal to the total kinetic energy since an ideal gas has zero potential energy

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
