Kinetic Theory of Gases (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9702
Assumptions of the kinetic theory of gases
The kinetic theory of gases is based on the following assumptions:
Molecules of a gas behave as identical (or all have the same mass)
Molecules of gas are hard, perfectly elastic spheres
The molecules are in continuous random motion
There are no forces of attraction or repulsion between the molecules
External forces (e.g. gravity) are ignored
Newton's laws apply
The volume of the molecules is negligible compared to the volume of the container
The molecules collide perfectly elastically with the walls of the container exerting a pressure upon them
The time of a collision is negligible compared to the time between collisions
There are a very large number of molecules
Gas molecules in a box
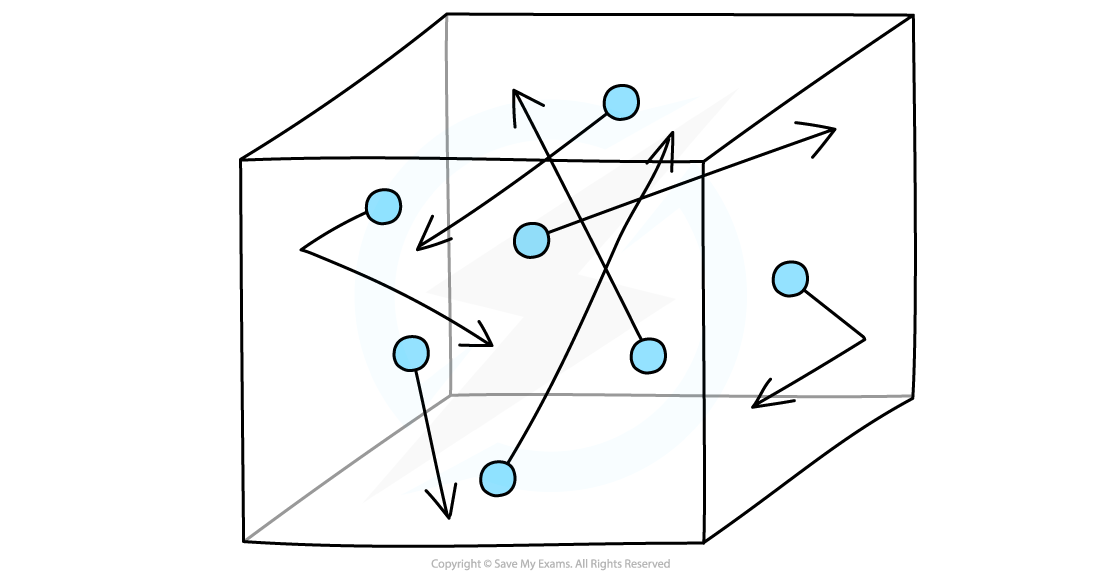
Gas molecules move about randomly at high speeds
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Make sure to memorise all the assumptions for your exams, as it is a common exam question to be asked to recall them.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?