Resolving Power of Telescopes (AQA A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 7408
Minimum Angular Resolution
A circular aperture, such as a lens in a telescope, is designed so that a cone of light can enter into a region behind it
This allows light to act like a point source once it passes through
When two point sources are placed near each other, or viewed from a large distance, they will appear to be a single unresolved source of light
For example, two distant car headlights may initially appear as a single point source until the car moves close enough for your eyes to resolve them into two individual headlights
Light from any object passing through a circular aperture, including the human eye, will diffract and create interference fringes upon the detector inside
The pattern is circular and is an approximate pattern for a circular aperture
The large central maximum is called an Airy disc and is twice as wide as the further maxima in the pattern

Diffraction of Light using a Circular Aperture
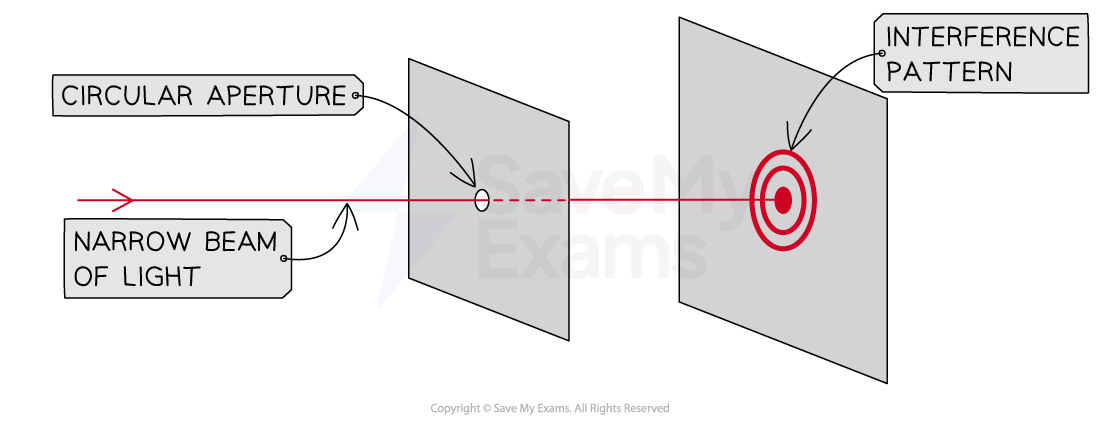
A circular interference pattern can be seen when light is diffracted through a circular aperture instead of a rectangular slit
Diffraction also affects how well a telescope can resolve fine detail
The resolving power or minimum angular resolution of a telescope can be determined using the Rayleigh criterion
The Rayleigh criterion states that:
Two sources will be resolved if the central maximum of one diffraction pattern coincides with the first minimum of the other
The resolution, or resolving power, of a telescope can be increased by reducing the amount the light diffracts, for example, by:
increasing the diameter of the aperture
operating at a shorter wavelength of light
Visual diffraction pattern | Variation of intensity with separation |
|---|---|
 |  |
A. Two sources that cannot be resolved | Two sources (red & blue curves) that are too close together appear as one single source (purple curve) |
 |  |
B. Two sources that can only just be resolved, as defined by the Rayleigh criterion | Two sources (red & blue curves) which do not overlap significantly, but just about appear as two sources (purple curve) |
 |  |
C. Two sources that are clearly resolved | Two sources (red & blue curves) which are far apart enough to appear as two distinct sources (purple curve) |
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The terms 'resolution' and 'resolving power' are often both used interchangeably to describe the quality of a telescope in terms of the minimum angular separation it can achieve
For example, saying
A telescope has a resolution (or resolving power) of 0.005 degrees
Is the same as saying
A telescope can resolve two stars which have an angular separation of at least 0.005 degrees
Remember that the 'Airy disc' is just the central maximum of the interference pattern, not the name of the whole pattern itself.
The Rayleigh Criterion
The Rayleigh Criterion can be mathematically described by considering angular separation and single-slit diffraction through a circular aperture
Angular separation can be calculated using the equation:
Where:
θ = angular separation (rad)
s = distance between the two sources (m)
d = distance between the sources and the observer (m)

Angular separation, θ, is equal to the separation, s, of two sources divided by the distance, d, between the sources and the observer
In single-slit diffraction, minima in the pattern appear at angles given by:
Where:
θ = the angle of diffraction (rad)
n = the order of the minimum (1,2,3 etc)
λ = the wavelength of the light (m)
D = the slit width (m)
Intensity Pattern from a Circular Aperture
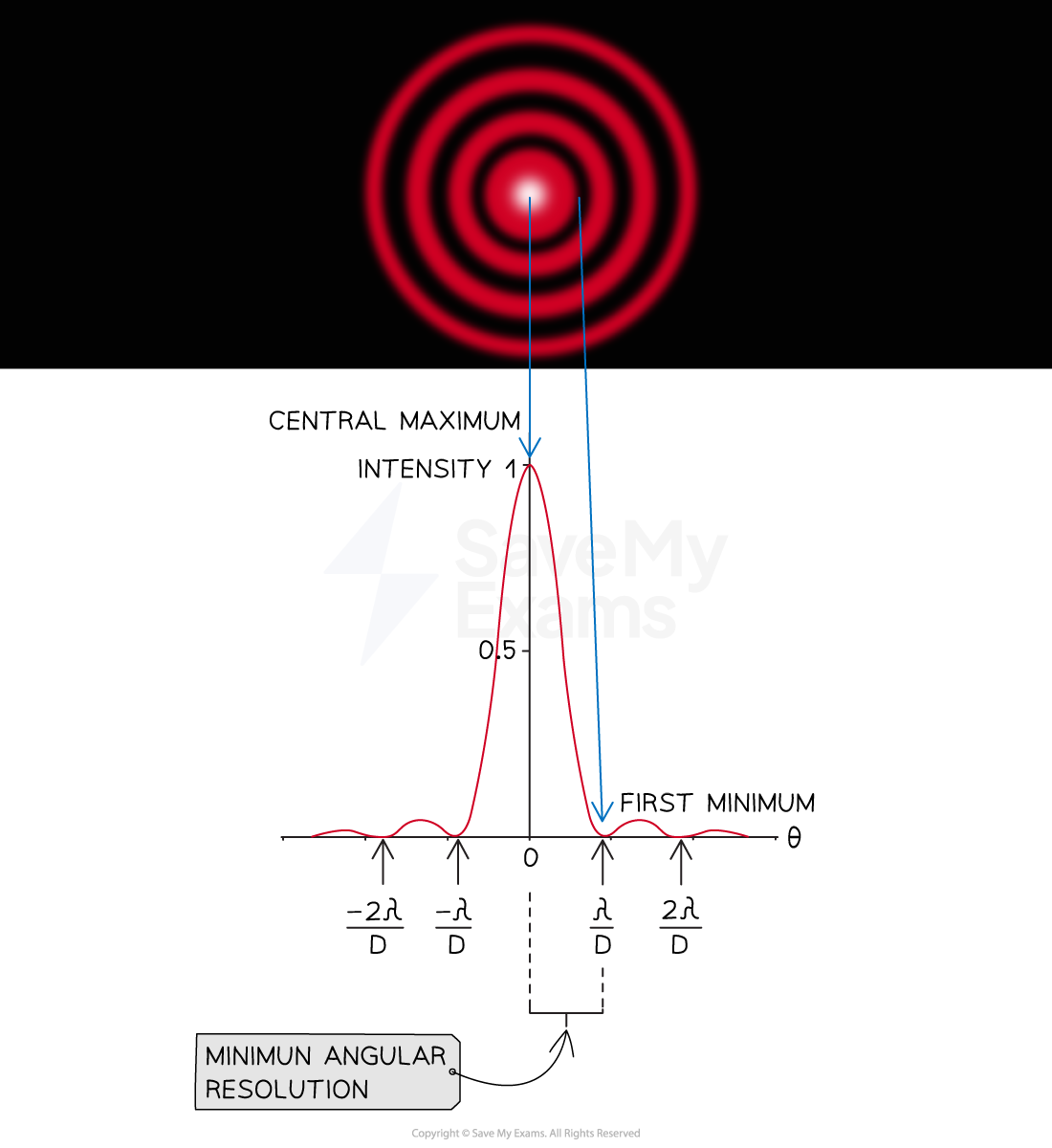
The minimum angular resolution of a telescope can be determined using the angular separation between a source's central maximum and the first minimum
For a telescope, the first minimum (when n = 1) occurs when the angle of diffraction is:
Using the small-angle approximation
, we obtain an expression for the minimum angular resolution of the telescope (The Rayleigh Criterion)
Where:
θ = minimum angular resolution of the telescope (rad)
λ = operating wavelength of the telescope (m)
D = diameter of the telescope's aperture (m)
The Rayleigh criterion can therefore be written mathematically as follows:
1. Sources are resolvable when
2. Sources are just resolvable when
3. Sources are not resolvable when
For a circular aperture, the value is multiplied by a factor of 1.22
This is the same as the expression for two sources that are 'just resolvable' but removes the need for the "approximately equals" (
) sign
Worked Example
The supermassive black hole at the centre of the Milky Way galaxy is 25,000 light years from Earth. It has a Schwarzchild radius of 1.2 × 1010 m and emits radio waves at a frequency of 230 GHz.
The Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) is an array of radio telescopes which has the same resolution as a single radio telescope with a diameter of 8000 km.
(a) Calculate the minimum angular separation which could be resolved by the EHT.
(b) Deduce whether the resolution of the EHT is suitable to obtain a detailed view of the supermassive black hole. Support your answer with a calculation.
Answer:
Part (a)
Step 1: List the relevant quantities
Frequency of the radio waves,
= 230 GHz = 230 × 109 Hz
Speed of light,
= 3 × 108 m s−1
Diameter of EHT,
= 8000 km = 8000 × 103 m
Step 2: Write down the equation for the minimum angular separation and substitute in the wave equation
Wave equation:
Minimum angular separation:
Step 3: Calculate the minimum angular separation the EHT can resolve
= 1.63 × 10−10 rad
This means the EHT can obtain a detailed view of objects down to an angular size of 1.63 × 10−10 rad
Part (b)
Step 1: List the relevant quantities
Diameter of the black hole, s = 2 × (1.2 × 1010) m = 2.4 × 1010 m
Light year, 1 ly = 9.46 × 1015 m (included in the data booklet)
Distance to black hole, d = 25 000 ly
Step 2: Write down the equation for angular size
Angular size = angle subtended by the black hole (i.e. 2 × Schwarzchild radius):
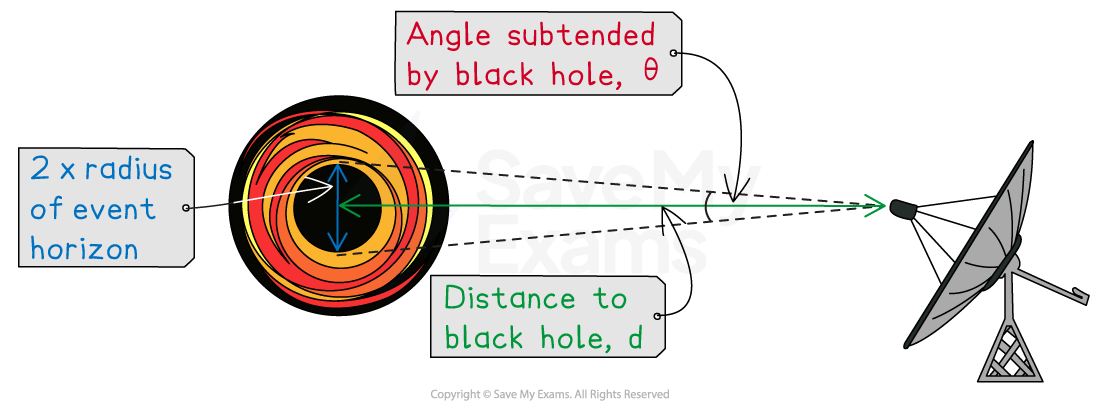
Step 3: Carry out a supporting calculation and write a conclusion
You could use...
Method 1: Calculate the angle subtended by the black hole
At a distance of 25 000 ly, the black hole subtends an angular size of:
= 1.01 × 10−10 rad
Compare with the resolution of the EHT:
So, 1.63 × 10−10 rad > 1.01 × 10−10 rad
Conclusion:
The angle subtended by the black hole, 1.01 × 10−10 rad, is approximately 1.6 times greater than the limit of the resolution of the EHT, 1.63 × 10−10 rad.
Therefore, it will not be able to suitably resolve detail in an image of the black hole.
The angle of the black hole as viewed from Earth is wider than the angle that the telescope can view.
Or, you could use...
Method 2: Calculate the size of an object that could just be resolved at this distance
At a distance of 25 000 ly, the smallest object the EHT could resolve in detail is:
= 3.85 × 1010 m
Compare with the diameter of the black hole:
So, 3.85 × 1010 m > 2.40 × 1010 m
Conclusion:
The smallest object the EHT could just resolve at this distance, 3.85 × 1010 m, is approximately 1.6 times greater than the diameter of the black hole, 2.40 × 1010 m.
Therefore, it will not be able to suitably resolve detail in an image of the black hole.
The distance between two objects that can be identified as two when viewed from Earth is much greater than the diameter of the black hole.
Examiner Tips and Tricks
It is better to say that θ is the 'minimum angular resolution' of the telescope instead of 'resolving power', as this implies that θ is a power (in watts) instead of an angle. However, if you are asked for the resolving power in the exam, it means to calculate θ.
Remember that the wavelength and diameter must be in the same units.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?