The Time Constant (AQA A Level Physics) : Revision Note
The Time Constant
The time constant of a capacitor discharging through a resistor is a measure of how long it takes for the capacitor to discharge
The definition of the time constant is:
The time taken for the charge, current or voltage of a discharging capacitor to decrease to 37% of its original value
Alternatively, for a charging capacitor:
The time taken for the charge or voltage of a charging capacitor to rise to 63% of its maximum value
37% is 0.37 or 1 / e (where e is the exponential function) multiplied by the original value (I0, Q0 or V0)
This is represented by the Greek letter tau,
, and measured in units of seconds (s)
The time constant provides an easy way to compare the rate of change of similar quantities eg. charge, current and p.d.
It is defined by the equation:
= RC
Where:
= time constant (s)
R = resistance of the resistor (Ω)
C = capacitance of the capacitor (F)
For example, to find the time constant from a voltage-time graph, calculate 0.37V0 and determine the corresponding time for that value

The time constant shown on a charging and discharging capacitor
The time to half, t1/2 (half-life) for a discharging capacitor is:
The time taken for the charge, current or voltage of a discharging capacitor to reach half of its initial value
This can also be written in terms of the time constant:
t1/2 = 0.69 = 0.69RC
Worked Example
A capacitor of 7 nF is discharged through a resistor of resistance R. The time constant of the discharge is 5.6 × 10-3 s. Calculate the value of R.
Answer:
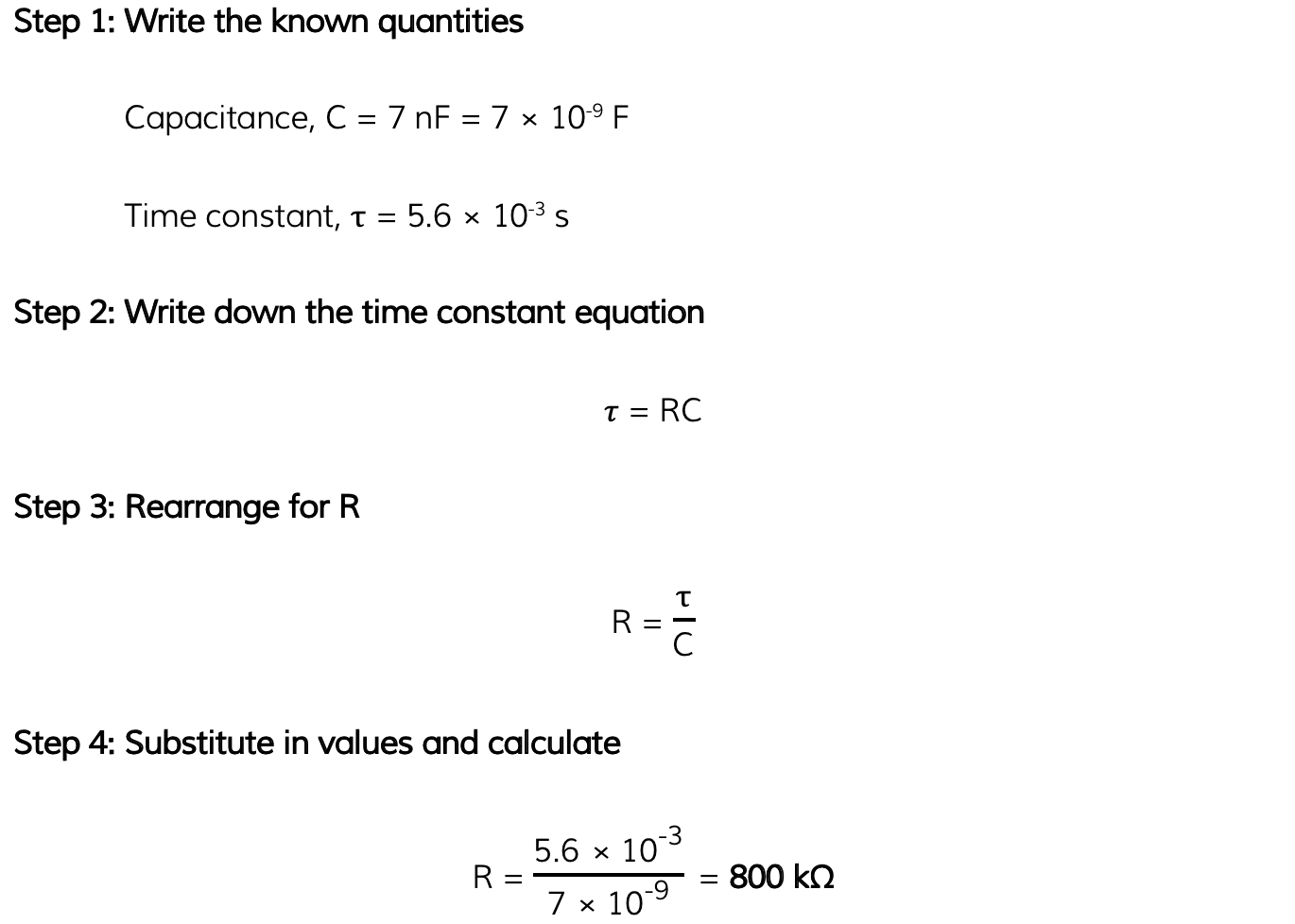
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember to check the context of an exam question, i.e., whether the capacitor is charging or discharging. The definition of the time constant depends on it!
For a charging capacitor, the time constant refers to the time taken to reach 63% of its maximum potential difference or charge stored
For a discharging capacitor, the time constant refers to the time take to discharge to 37% of its initial potential difference or charge stored

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
