Work Done on a Charge (AQA A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 7408
Work Done on a Charge
When a charge moves through an electric field, work is done
The work done in moving a charge q is given by:
Where:
ΔW = work done (J)
q = magnitude of charge moving in the field (C)
ΔV = potential difference between two points (J C−1)
Electrical Potential Difference
Two points at different distances from a charge will have different electric potentials
This is because the electric potential increases with distance from a negative charge and decreases with distance from a positive charge
Therefore, there will be an electric potential difference between the two points equal to:
Where:
Vf = final electric potential (J C−1)
Vi = initial electric potential (J C−1)
The potential difference due to a point charge can be written:
Where
Q = magnitude of point charge producing the potential
ε0 = permittivity of free space (F m−1)
rf = final distance from charge Q (m)
ri = initial distance from charge Q (m)
Electric Potential Energy
The electric potential energy of two point charges is given by:
Where:
Ep = electric potential energy (J)
Q1, Q2 = magnitudes of the charges (C)
r = distance between the centres of the two charges (m)
The work done on a point charge is therefore equal to the change in electric potential energy
When V = 0, then Ep = 0
The change in Ep, or work done on a point charge q at a distance r1 from the centre of a larger charge Q, to a distance of r2 further away can be written as:
Where:
Q = charge that is producing the electric field (C)
q = charge that is moving in the electric field (C)
r1 = initial distance of q from the centre of Q (m)
r2 = final distance of q from the centre of Q (m)
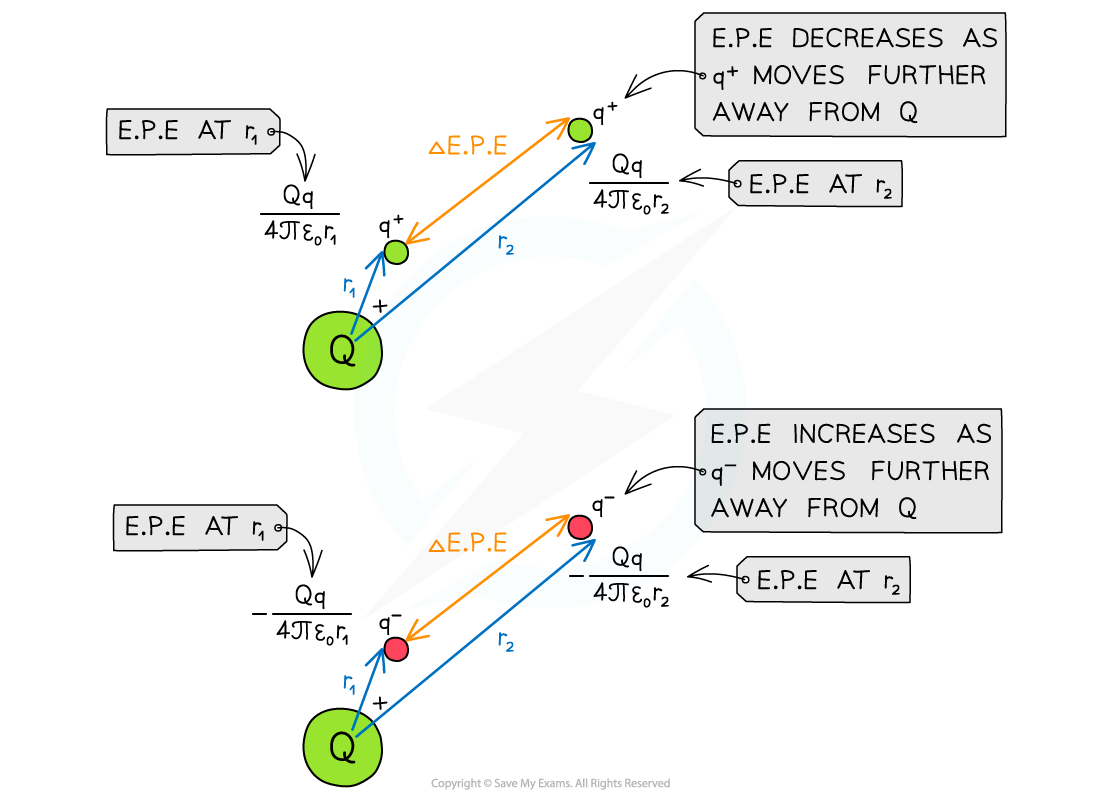
Work is done when moving a point charge away from another charge
Work is done when a positive charge in an electric field moves against the electric field lines or when a negative charge moves with the electric field lines
A graph of potential energy Ep against distance r can be drawn for two like charges and two opposite charges
The gradient of the graph at any particular point is equal to the electric force F at that point
Graph of electric potential energy against distance
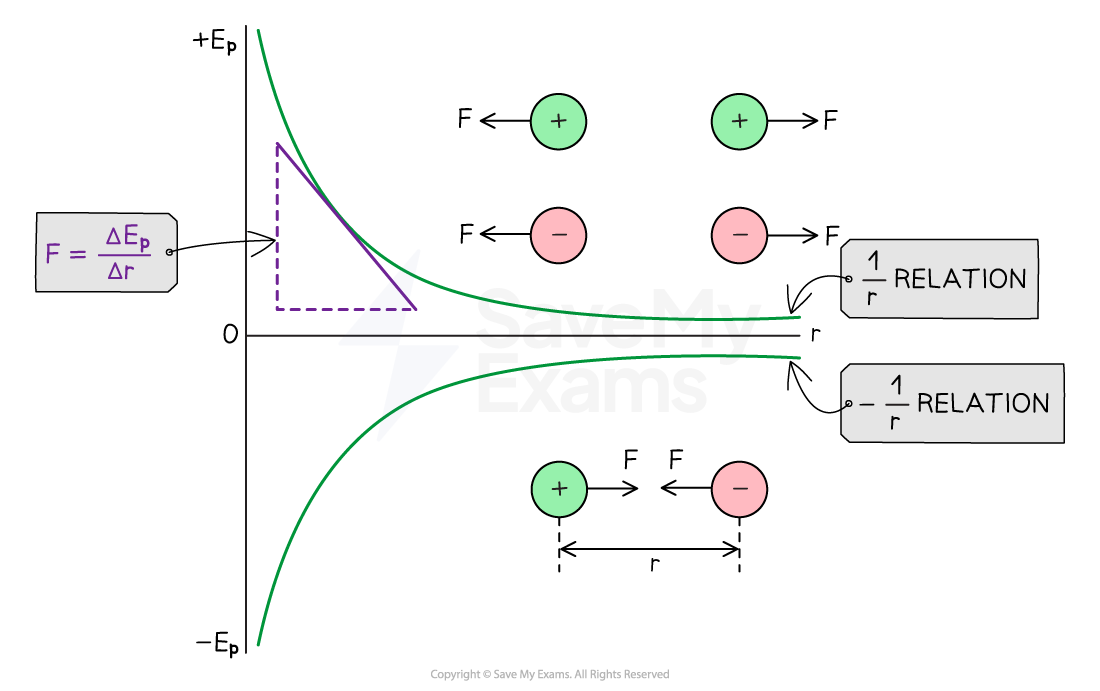
The electric potential energy of two similar charges decreases with distance and increases for two opposite charges
Worked Example
A point charge of +7.0 nC is located 150 mm and 220 mm from points S and R respectively.

Calculate the work done when a +3.0 nC charge moves from R to S.
Answer:
Step 1: Write down the known quantities
Final distance from charge, rS = 150 mm = 0.15 m
Initial distance from charge, rR = 220 mm = 0.22 m
Magnitude of charge producing the potential, Q = +7.0 nC = +7.0 × 10−9 C
Magnitude of charge moving in the potential, q = +3.0 nC = +3.0 × 10−9 C
Permittivity of free space, ε0 = 8.85 × 10−12 F m−1
Step 2: Calculate the electric potential difference between R and S
V
Step 3: Calculate the work done by the moving charge
J
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember that q in the work done equation is the charge that is being moved, whilst Q is the charge which is producing the potential. Make sure not to get these two mixed up, as both could be given in the question (like the worked example) and you will be expected to choose the correct one
Electrostatic Equipotential Surfaces
Equipotential lines (2D) and surfaces (3D) join together points that have the same electric potential
These are always:
perpendicular to the electric field lines in both radial and uniform fields
represented by dotted lines (unlike field lines, which are solid lines with arrows)
an equal distance from the source charge
Equipotential surfaces can be drawn to represent a fixed electric potential for a number of scenarios, such as
for a point charge
for two or more charges
between two oppositely charged parallel plates
Equipotential surface for a point charge
In a radial field, such as around a point charge, the equipotential lines:
are concentric circles around the charge
become progressively further apart with distance
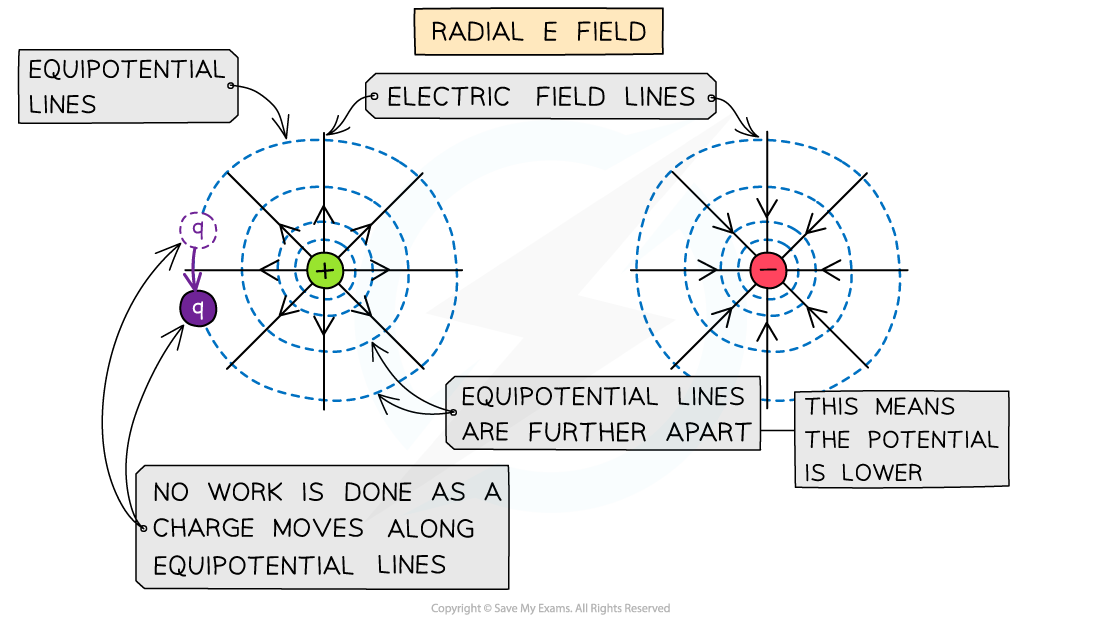
Equipotential lines for a radial electric field are concentric circles which increase in radius and are perpendicular to the field lines
If a charged conducting sphere replaced a point charge, the equipotential surface would be the same
Equipotential surface for multiple charges
The equipotential surfaces for a dipole (two opposite charges) and for two like charges are shown below:
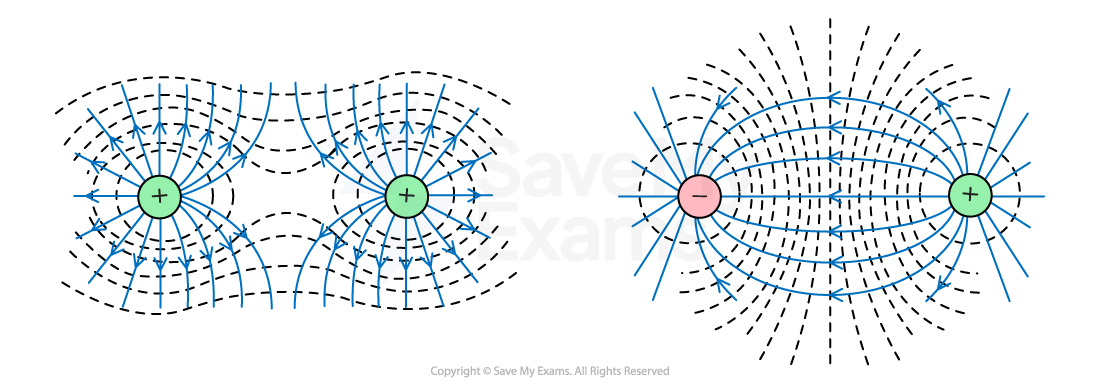
The equipotential surface for multiple charges can be obtained by drawing curves which are perpendicular to the field lines
An equipotential surface between two opposite charges can be identified by a central line at a potential of 0 V
This is the point where the opposing potentials cancel
An equipotential surface between two like charges can be identified by a region of empty space between them
This is the point where the resultant field is zero
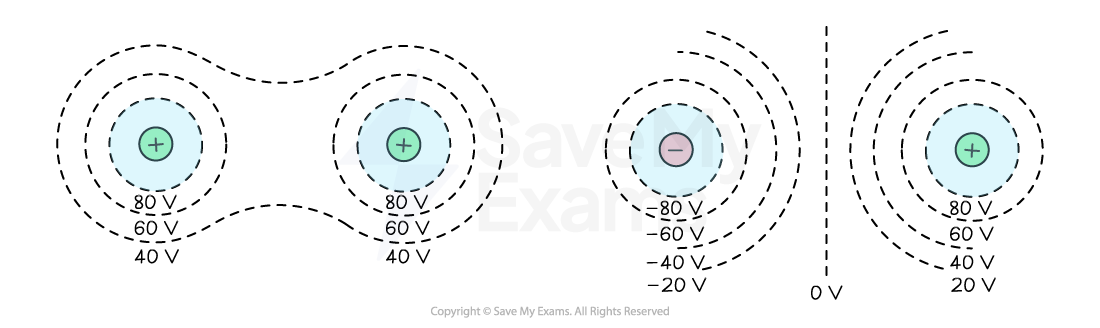
Equipotential lines show that the potential has the greatest value near the charge and decreases with distance
Equipotential surface between parallel plates
In a uniform field, such as between two parallel plates, the equipotential lines are:
horizontal straight lines
parallel
equally spaced
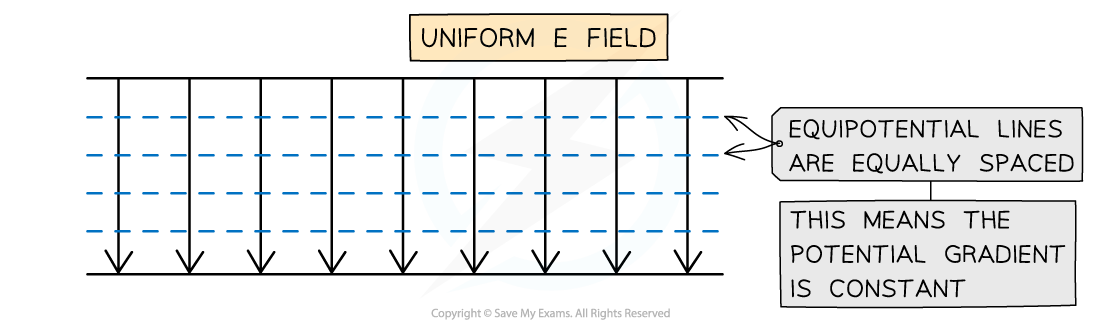
The equipotential lines for a uniform field are evenly spaced parallel lines which are perpendicular to the field lines
The spacing between equipotential lines indicates the strength of the electric field
This is because they represent potential gradient
Hence, equally spaced equipotential lines indicate a region of constant electric field strength
Worked Example
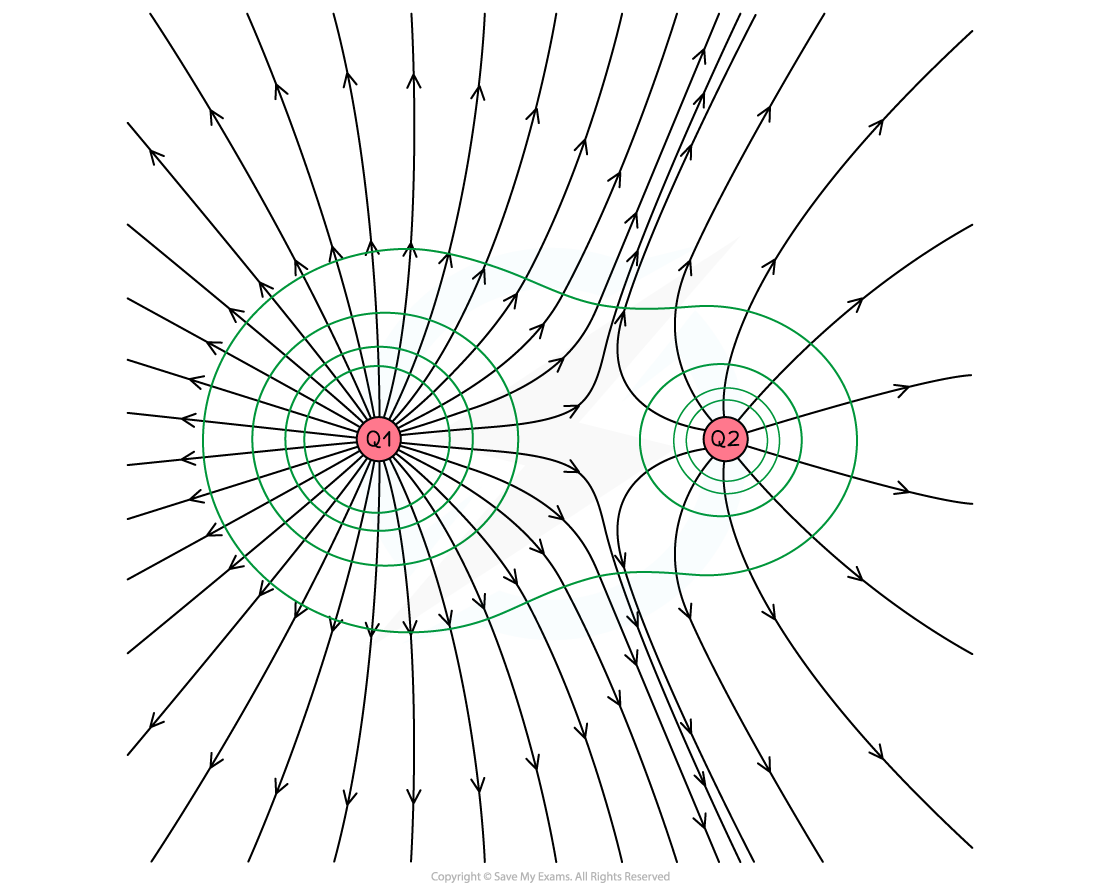
In the following diagram, two electric charges are shown which include the electric field lines

(a) Draw the lines of equipotential including at least four lines and at least one that encircles both charges
(b) By considering the field lines and equipotentials from part (a), state what can be assumed about the two charges
Answer:
Part (a)
The lines of equipotential need to be perpendicular to the field lines at all times
These lines are almost circular when they are near the charges
And when moving out further the lines of equipotential cover both charges.
The lines of equipotential can be seen below
Part (b)
It can be assumed that both charges are positive since the field lines point outwards.
It can also be assumed that the charge on the left has a larger charge than the charge on the right since:
It has a greater density of field lines
It has a larger sphere of influence shown by the lines of equipotential
The point of zero electric field strength between the two charges is closer to the right charge
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The distinction between radial and uniform fields is an important one, remember:
a radial field is made up of lines which follow the radius of a circle
a uniform field is made up of lines which are a uniform distance apart
When drawing equipotential lines, remember that they do not have arrows since they have no particular direction and are not vectors.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?