Gravitational Potential (AQA A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 7408
Gravitational Potential
The gravitational potential energy (G.P.E) is the energy an object has when lifted off the ground given by the familiar equation:
G.P.E = mgΔh
The G.P.E on the surface of the Earth is taken to be zero
This means work is done to lift the object
This equation is only used for objects that are within the Earth's surface
However, outside the Earth’s surface, G.P.E can be defined as:
The energy an object possess due to its position in a gravitational field
The gravitational potential at a point is the gravitational potential energy per unit mass at that point
Therefore, it is defined as:
The work done per unit mass in bringing a test mass from infinity to a defined point
It is represented by the symbol, V and is measured in J kg-1
The gravitational potential is always a negative value. This is because:
It is defined as zero at infinity
Since the gravitational force is attractive, work must be done on a mass to reach infinity
This means that the gravitational potential is negative on the surface of a mass (such as a planet), and increases with distance from that mass (becomes less negative)
Work has to be done against the gravitational pull of the planet to take a unit mass away from the planet
The gravitational potential at a point depends on the mass of the object producing the gravitational field and the distance the point is from that mass
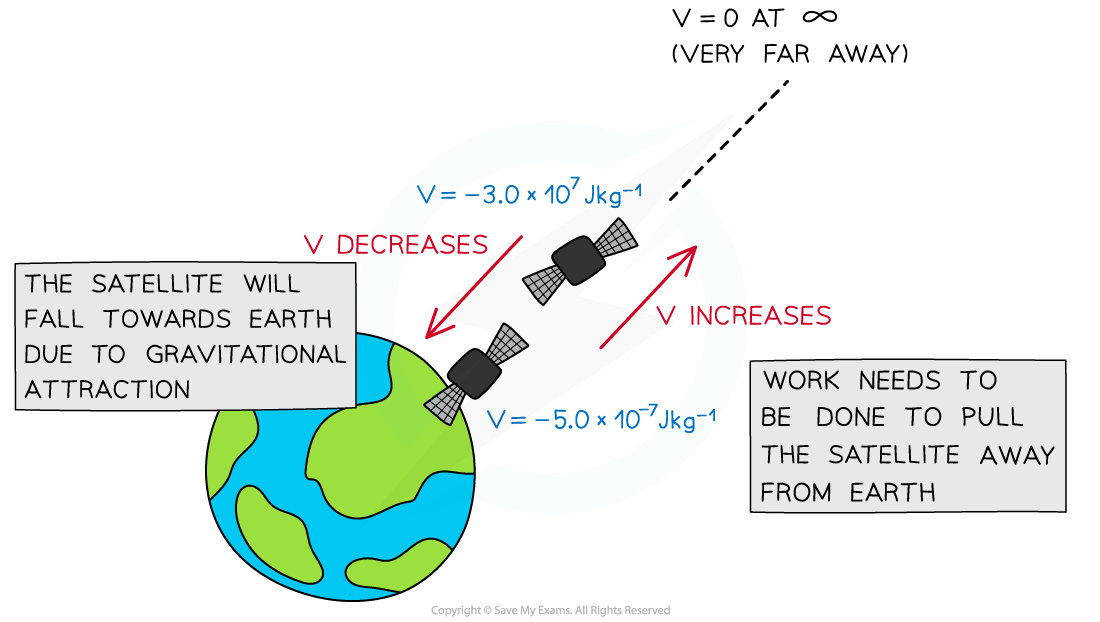
Gravitational potential decreases as the satellite moves closer to the Earth
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember to memorise the gravitational potential definition and the reason why it is negative, as these are very common exam questions
Gravitational Potential Difference
Two points at different distances from a mass will have different gravitational potentials
This is because the gravitational potential increases with distance from a mass
Therefore, there will be a gravitational potential difference between the two points
This is represented by the symbol ΔV
ΔV is normally given as the equation
ΔV = Vf – Vi
Where:
Vf = final gravitational potential (J kg-1)
Vi = initial gravitational potential (J kg-1)
A difference in gravitational potential will give a difference in gravitational potential energy, that can also be calculated
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When exam questions ask for the 'difference' or 'change in' a value (denoted by Δ), they are asking for the magnitude. Therefore, don't worry too much about negative or positive signs. As long as you consistently calculate the difference in two values as 'final value – initial value', a negative difference will mean that the value is decreasing and vice versa

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?