Average Molecular Kinetic Energy (AQA A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 7408
Average Molecular Kinetic Energy
An important property of molecules in a gas is their average kinetic energy
This can be deduced from the ideal gas equations relating pressure, volume, temperature and speed
Recall the ideal gas equation:
pV = NkT
Also, recall the equation linking pressure and mean square speed of the molecules:
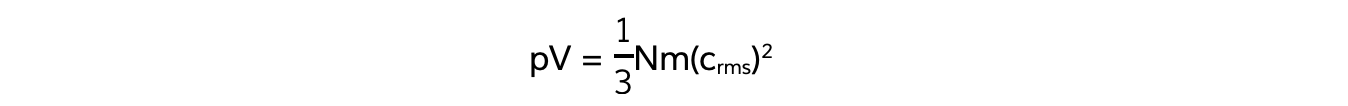
The left-hand side of both equations are equal (pV)
This means the right-hand sides are also equal:
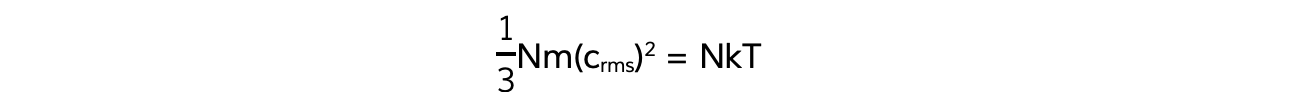
N will cancel out on both sides and multiplying by 3 on both sides too obtains the equation:
m(crms)2 = 3kT
Recall the familiar kinetic energy equation from mechanics:

Instead of v2 for the velocity of one particle, (crms)2 is the average speed of all molecules
Multiplying both sides of the equation by ½ obtains the average molecular kinetic energy of the molecules of an ideal gas:
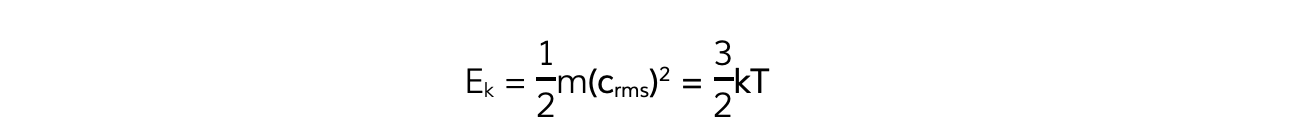
Where:
Ek = kinetic energy of a molecule (J)
m = mass of one molecule (kg)
(crms)2 = mean square speed of a molecule (m2 s-2)
k = Boltzmann constant
T = temperature of the gas (K)
Note: this is the average kinetic energy for only one molecule of the gas
A key feature of this equation is that the mean kinetic energy of an ideal gas molecule is proportional to its thermodynamic temperature
Ek ∝ T
The Boltzmann constant k can be replaced with
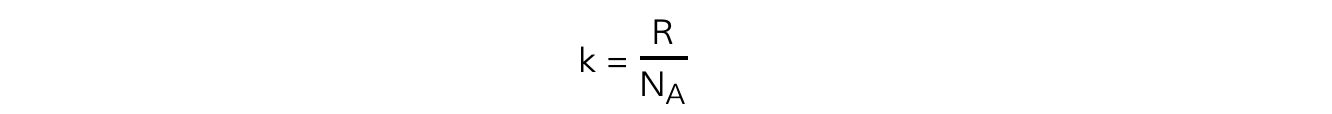
Substituting this into the average molecular kinetic energy equation means it can also be written as:

Internal Energy and Temperature
Recall from Ideal Gas Internal Energy that, for an ideal gas, internal energy is equal to the sum of all kinetic energies
This means that, for a system of N particles, the internal energy U is equal to:
This is just the kinetic energy of a single average particle, multiplied by N
This equation shows that internal energy and temperature are directly proportional
U ∝ T
Worked Example
Helium can be treated as an ideal gas. Helium molecules have a root-mean-square (r.m.s.) speed of 720 m s-1 at a temperature of 45 °C. Calculate the r.m.s. speed of the molecules at a temperature of 80 °C.
Answer:

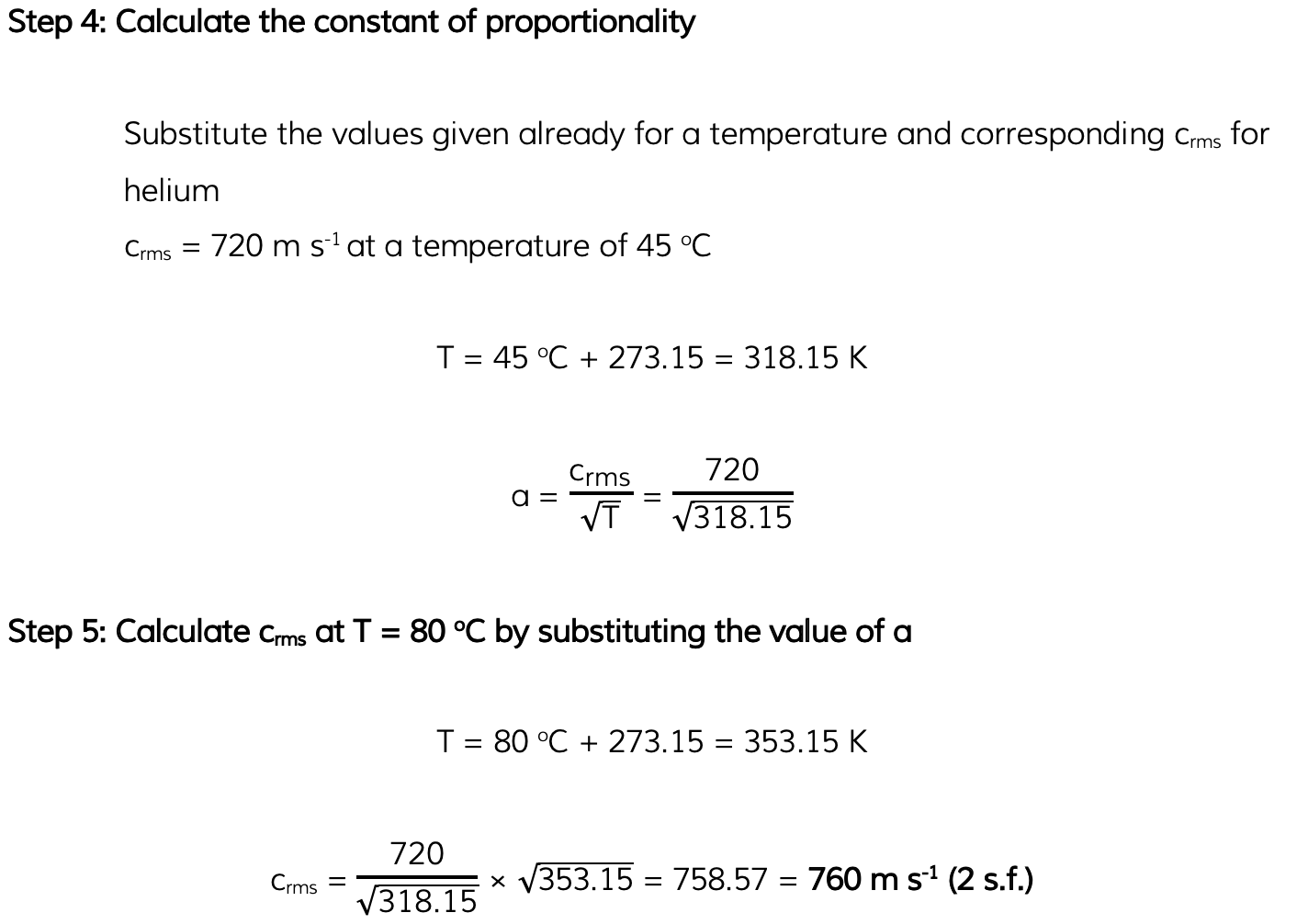
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Keep in mind this particular equation for kinetic energy is only for one molecule in the gas. If you want to find the kinetic energy for all the molecules, remember to multiply by N, the total number of molecules.You can remember the equation through the rhyme ‘Average K.E is three-halves kT’.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?