Avogadro, Molar Gas & Boltzmann Constant (AQA A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 7408
Written by: Katie M
Updated on
Avogadro, Molar Gas & Boltzmann Constant
Avogadro's Constant
The atomic mass unit (u) is approximately the mass of a proton or neutron = 1.66 × 10-27 kg
This means that an atom or molecule has a mass approximately equal to the number of protons and neutrons it contains
A carbon-12 atom has a mass of:
12 u = 12 × 1.66 × 10-27 = 1.99 × 10-26 kg
The exact number for a mole is defined as the number of molecules in exactly 12 g of carbon:
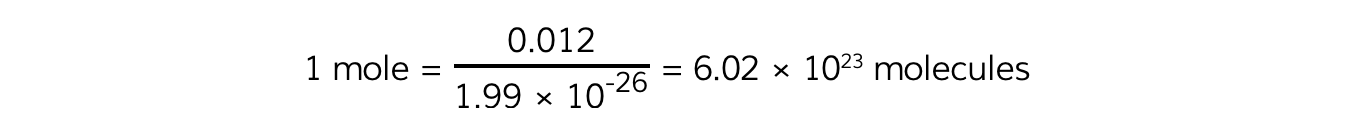
Avogadro’s constant (NA) is defined as:
The number of atoms of carbon-12 in 12 g of carbon-12; equal to 6.02 × 1023 mol-1
For example, 1 mole of sodium (Na) contains 6.02 × 1023 atoms of sodium
The number of atoms (or molecules) can be determined if the number of moles is known by multiplying by NA, for example:
2.0 mol of helium contains: 2.0 × NA = 2.0 × 6.02 × 1023 = 1.20 × 1024 atoms
Moles and Atomic Mass
One mole of any element is equal to the relative atomic mass of that element in grams
For example, helium has an atomic mass of 4, meaning 1 mole of helium has a mass of 4 g
If the substance is a compound, add up the relative atomic masses, for example, water (H2O) is made up of
2 hydrogen atoms (each with an atomic mass of 1) and 1 oxygen atom (atomic mass of 16)
So, 1 mole of water would have a mass of (2 × 1) + 16 = 18 g
Molar Mass
The molar mass of a substance is the mass, in grams, in one mole
Its unit is g mol-1
The number of moles from this can be calculated using the equation:
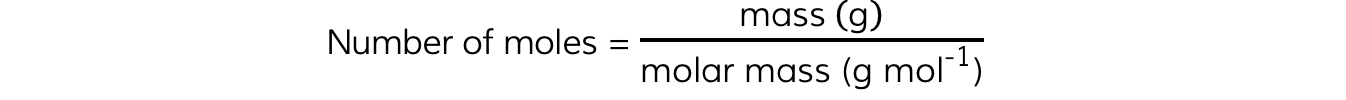
Boltzmann & The Molar Gas Constant
The Boltzmann constant k is used in the ideal gas equation and is defined by the equation:
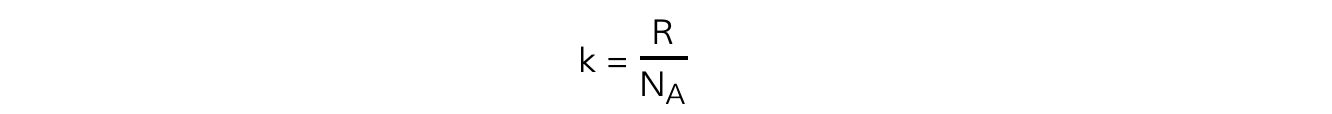
Where:
R = molar gas constant
NA = Avogadro’s constant
Boltzmann’s constant, therefore, has a value of:
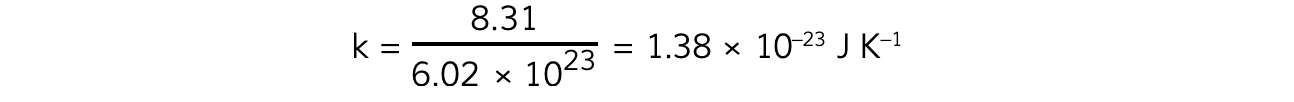
The Boltzmann constant relates the properties of microscopic particles (e.g. kinetic energy of gas molecules) to their macroscopic properties (e.g. temperature)
This is why the units are J K-1
Its value is very small because the increase in kinetic energy of a molecule is very small for every incremental increase in temperature
Worked Example
How many atoms are there in 6 g of magnesium-24?
Answer:
Step 1: Calculate the mass of 1 mole of magnesium
One mole of any element is equal to the relative atomic mass of that
element in grams
1 mole = 24 g of magnesium
Step 2: Calculate the amount of moles in 6 g
Step 3: Convert the moles to number of atoms
1 mole = 6.02 × 1023 atoms
0.25 moles = 0.25 × 6.02 × 1023 = 1.51 × 1023 atoms
Examiner Tips and Tricks
If you want to find out more about the mole, check out the AQA A Level Chemistry revision notes.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
