Work Done by a Gas (AQA A Level Physics) : Revision Note
Work Done by a Gas
When a gas expands, it does work on its surroundings by exerting pressure on the walls of its container
This is important, for example, in a steam engine where expanding steam pushes a piston to turn the engine
The work done when a volume of gas changes at constant pressure is defined as:
W = pΔV
Where:
W = work done (J)
p = pressure of gas in piston (Pa)
ΔV = change in volume of gas (m3)
This is assuming that the pressure of the gas in the piston p does not change as the gas expands
When the gas expands (V increases), work is done by the gas
When the gas is compressed (V decreases), work is done on the gas
For a gas inside a cylinder enclosed by a moveable piston, the force exerted by the gas pushes the piston outwards
Therefore, the gas does work on the piston
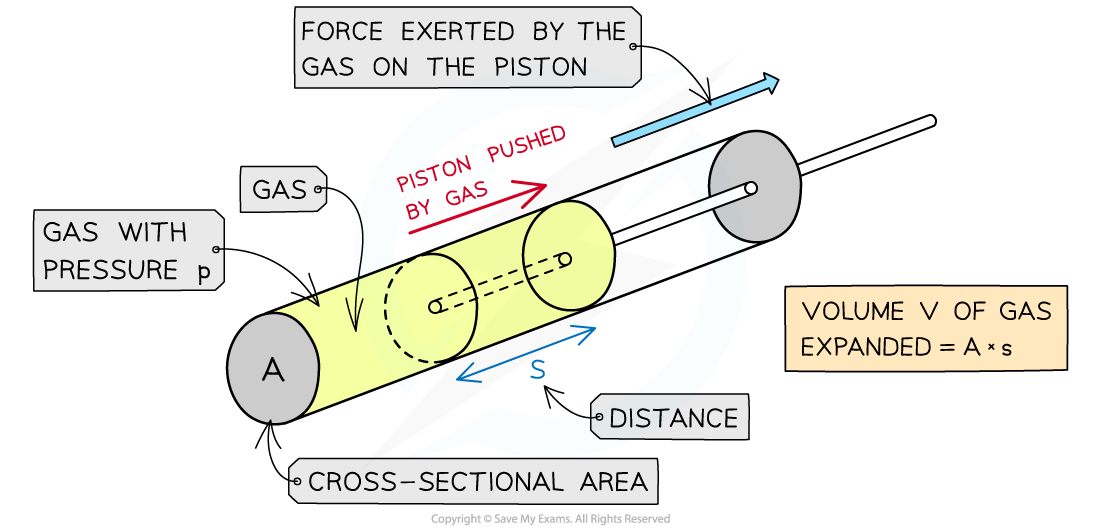
The gas expansion pushes the piston a distance s
Worked Example
When a balloon is inflated, its rubber walls push against the air around it. Calculate the work done when the balloon is blown up from 0.015 m3 to 0.030 m3. Pressure inside the balloon remains constant at = 1.0 × 105 Pa.
Answer:
Step 1: Write down the equation for the work done by a gas
W = pΔV
Step 2: Substitute in values
ΔV = final volume − initial volume = 0.030 − 0.015 = 0.015 m3
W = (1.0 × 105) × 0.015 = 1500 J

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
