Radians (AQA A Level Physics) : Revision Note
Radians
In circular motion, it is more convenient to measure angular displacement in units of radians rather than units of degrees
The angular displacement θ of a body in circular motion is defined as:
The change in angle, in radians, of a body as it rotates around a circle
The angular displacement is the ratio of:
Note: both distances must be measured in the same units, e.g. metres
A radian (rad) is defined as:
The angle subtended at the centre of a circle by an arc equal in length to the radius of the circle
Angular displacement can be calculated using the equation:

When the angle is equal to one radian, the length of the arc (Δs) is equal to the radius (r) of the circle
Where:
Δθ = angular displacement, or angle of rotation (radians)
s = length of the arc, or the distance travelled around the circle (m)
r = radius of the circle (m)
Radians are commonly written in terms of π
The angle in radians for a complete circle (360o) is equal to:
Radian Conversions
If an angle of 360o = 2π radians, then 1 radian in degrees is equal to:
Therefore, use the following equation to convert from radians to degrees:
Use the following equation to convert from degrees to radians:
Table of common degrees to radians conversions

Worked Example
Convert the following angular displacement into degrees:

Answer:

Examiner Tips and Tricks
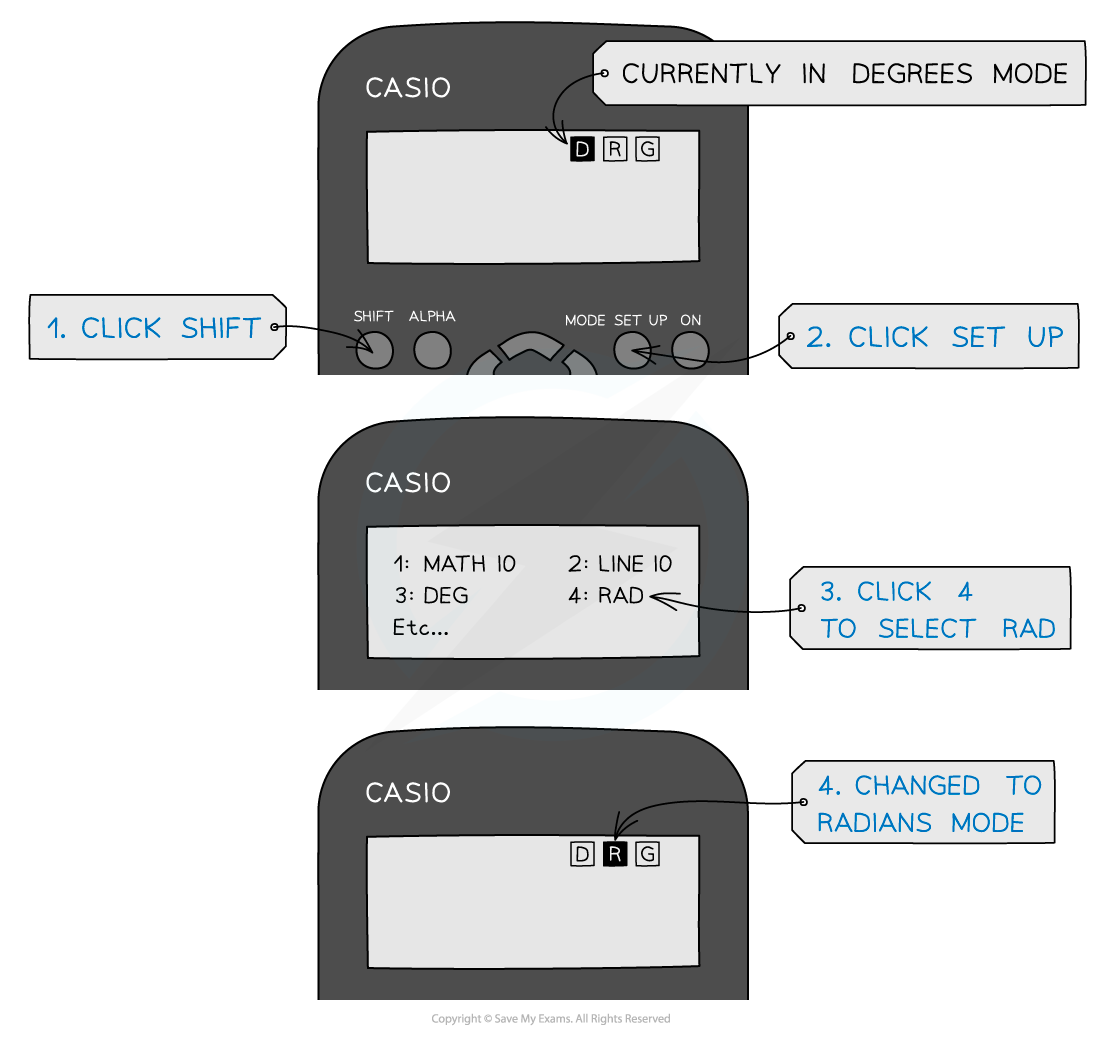
You will notice your calculator has a degree (Deg) and radians (Rad) mode
This is shown by the “D” or “R” highlighted at the top of the screen
Remember to make sure it’s in the right mode when using trigonometric functions (sin, cos, tan) depending on whether the answer is required in degrees or radians
It is extremely common for students to get the wrong answer (and lose marks) because their calculator is in the wrong mode - make sure this doesn’t happen to you!
This mode only matters if you're using sine, cos or tan

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
